SEALSQ partners with Quantix Edge Security on €19.6M government-backed quantum chip facility in Murcia, Spain. Project starts H1 2026, includes QS7001 chip launch in November 2025.



Researchers at UBC have found a way to mimic the elusive Schwinger effect using superfluid helium, where vortex pairs appear out of thin films instead of electron-positron pairs in a vacuum. Their work not only offers a cosmic laboratory for otherwise unreachable phenomena, but also changes the way scientists understand vortices, superfluids, and even quantum tunneling.
In 1951, physicist Julian Schwinger theorized that by applying a uniform electrical field to a vacuum, electron-positron pairs would be spontaneously created out of nothing, through a phenomenon called quantum tunneling.
The problem with turning the matter-out-of-nowhere theory into Star Trek replicators or transporters? Enormously high electric fields would be required — far beyond the limits of any direct physical experiments.
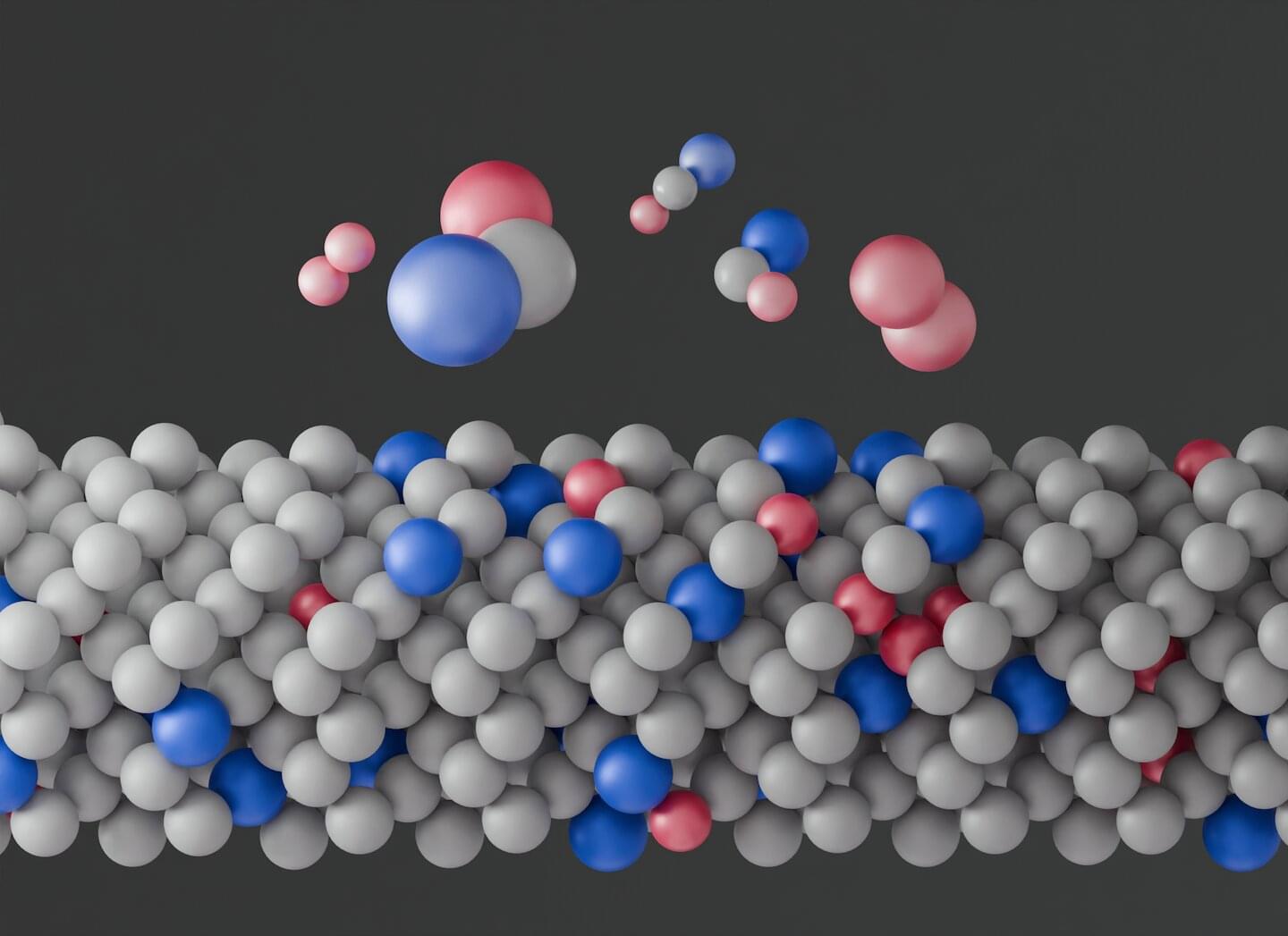
Inside the microchips powering the device you’re reading this on, the atoms have a hidden order all their own. A team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and George Washington University has confirmed that atoms in semiconductors will arrange themselves in distinctive localized patterns that change the material’s electronic behavior.
The research, published in Science, may provide a foundation for designing specialized semiconductors for quantum-computing and optoelectronic devices for defense technologies.
On the atomic scale, semiconductors are crystals made of different elements arranged in repeating lattice structures. Many semiconductors are made primarily of one element with a few others added to the mix in small quantities. There aren’t enough of these trace additives to cause a repeating pattern throughout the material, but how these atoms are arranged next to their immediate neighbors has long been a mystery.
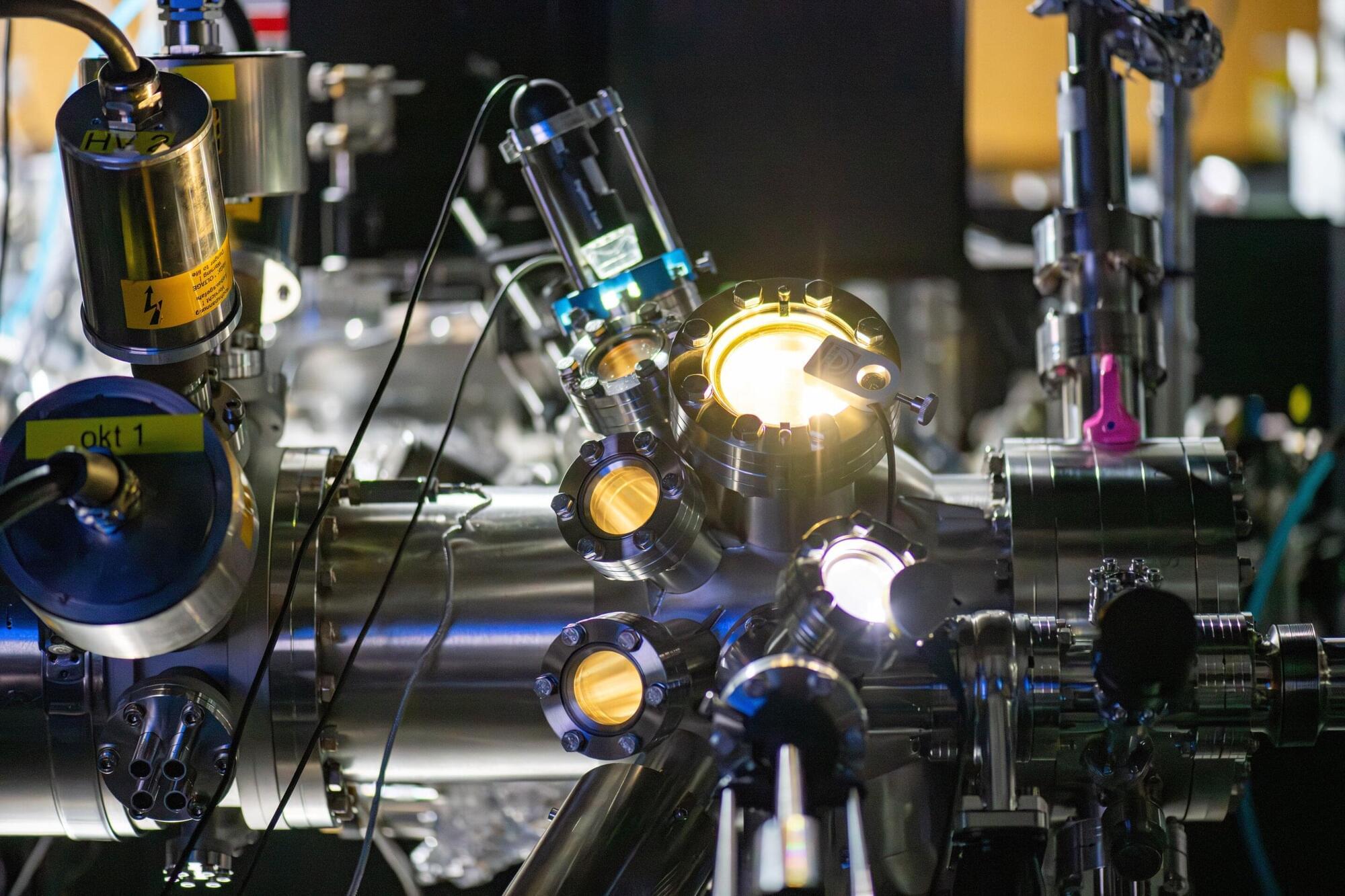
The precise imaging of many-body systems, which are comprised of many interacting particles, can help to validate theoretical models and better understand how individual particles in these systems influence each other. Ultracold quantum gases, collections of atoms cooled to temperatures close to absolute zero, are among the most promising experimental platforms for studying many-body interactions.
To study these gases, most physicists use a technique known as single atom –resolved imaging, which allows them to detect individual atoms and probe correlations in their behavior. Despite its advantages, this imaging method has a relatively low resolution, thus it fails to pick up a system’s subtler features.
Researchers at Heidelberg University recently devised a new strategy to magnify atomic wave functions, offering a mathematical description of the system’s quantum state, which could help to overcome the limitations of conventional single-atom imaging techniques.
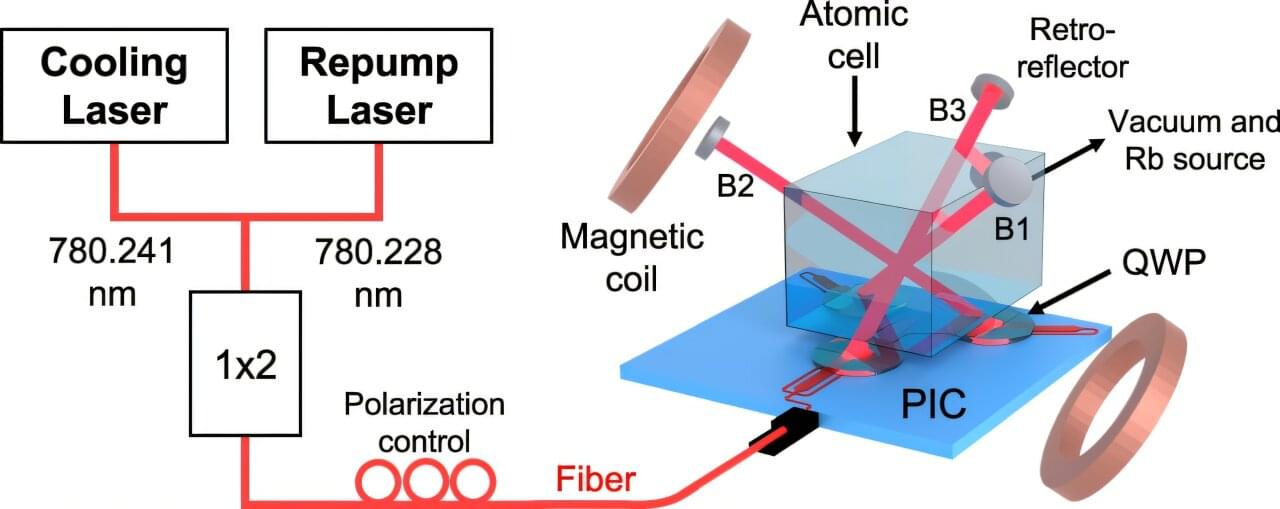
Cold atom experiments are among the most powerful and precise ways of investigating and measuring the universe and exploring the quantum world. By trapping atoms and exploiting their quantum properties, scientists can discover new states of matter, sense even the faintest of signals, take ultra-precise measurements of time and gravity, and conduct quantum sensing and computing experiments.
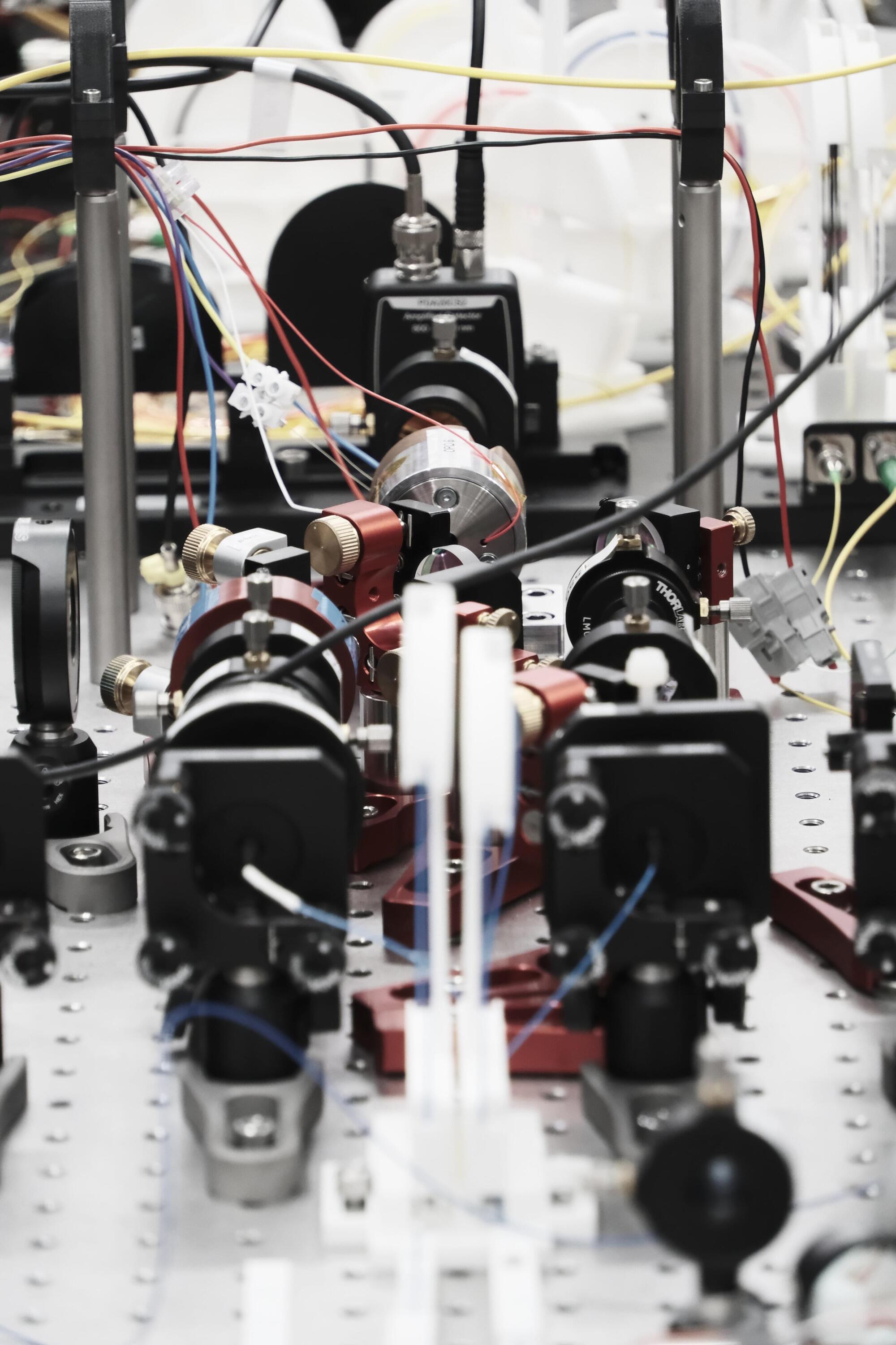
Amid high expectations for quantum technology, a new paper in Science reports a proven quantum advantage. In an experiment, entangled light has allowed researchers to learn a system’s noise with very few measurements.
Researchers at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) and international partners have demonstrated that entangled light can cut the number of measurements needed to learn the behavior of a complex, noisy quantum system by an enormous factor.
“This is the first proven quantum advantage for a photonic system,” says corresponding author Ulrik Lund Andersen, a professor at DTU Physics. “Knowing that such an advantage is possible with a straightforward optical setup should help others look for areas where this approach would pay off, such as sensing and machine learning.”
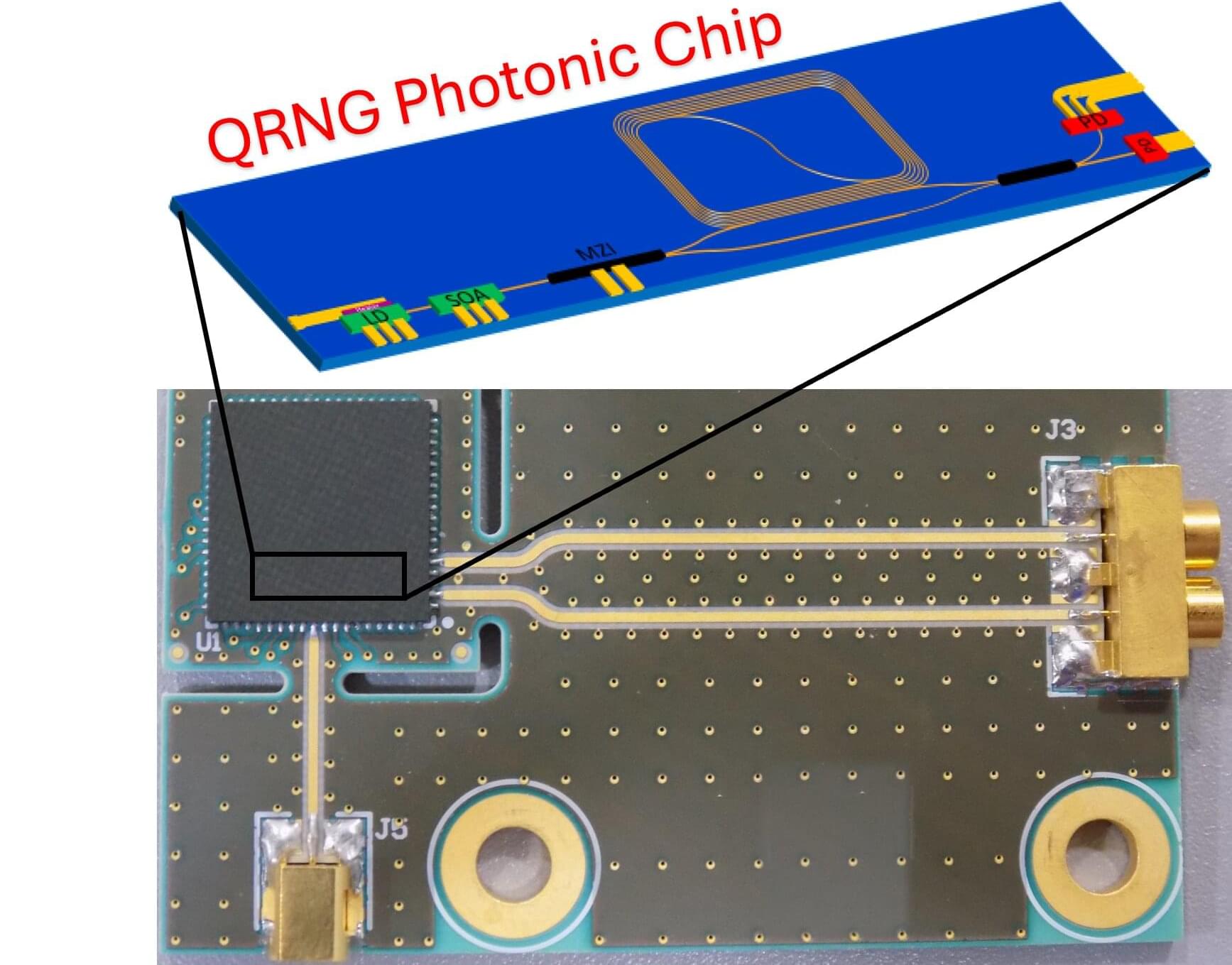
Researchers have developed a chip-based quantum random number generator that provides high-speed, high-quality operation on a miniaturized platform. This advance could help move quantum random number generators closer to being built directly into everyday devices, where they could strengthen security without sacrificing speed.
In a world-first, researchers from the Femtosecond Spectroscopy Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have directly observed the evolution of the elusive dark excitons in atomically thin materials, laying the foundation for new breakthroughs in both classical and quantum information technologies.
Their findings have been published in Nature Communications.
Professor Keshav Dani, head of the unit, says, Dark excitons have great potential as information carriers, because they are inherently less likely to interact with light, and hence less prone to degradation of their quantum properties. However, this invisibility also makes them very challenging to study and manipulate.

For almost a century, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle has stood as one of the defining ideas of quantum physics: a particle’s position and momentum cannot be known at the same time with absolute precision. The more you know about one, the less you know about the other.
In a new study published in Science Advances, our team demonstrates how to work around this restriction, not by breaking physics but by reshaping uncertainty itself.
The result is a breakthrough in the science of measurement that could power a new generation of ultra-precise quantum sensors operating at the scale of atoms.