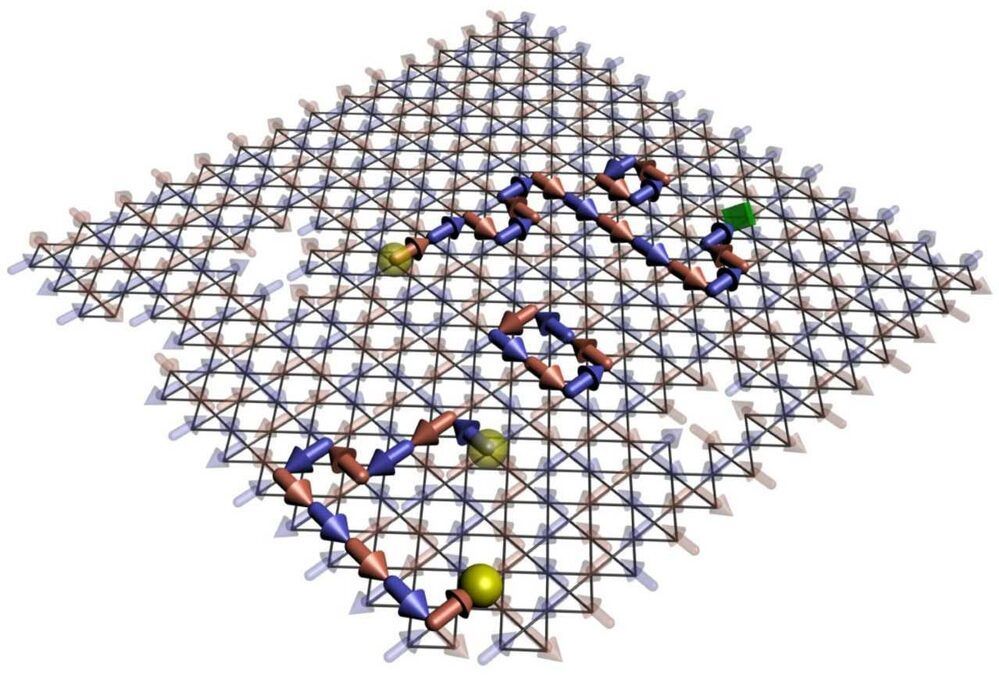
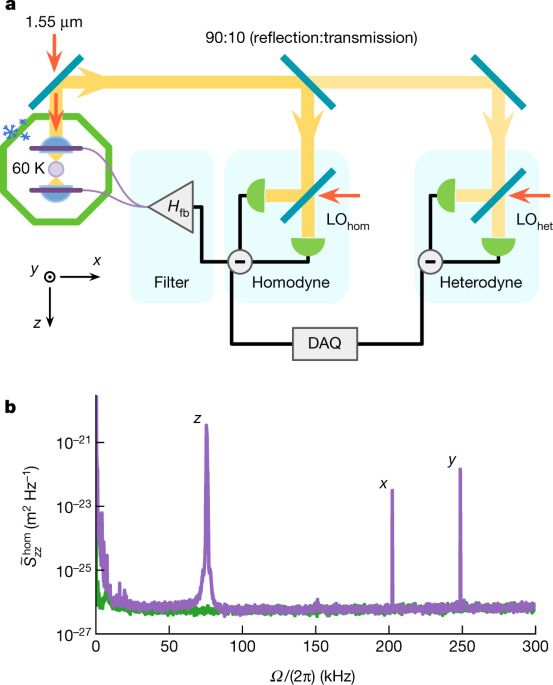
Forget Google Search and Fuchsia. Researchers from Google, Stanford, Princeton, and other universities might have made a computer discovery so big we can’t fully comprehend it yet. Even Google researchers aren’t entirely sure that their time crystal discovery is valid. But if it turns out to be accurate, then Google might be one of the first companies to give the world a crucial technological advancement for the future. Time crystals will be an essential building block in quantum computers, the kind of computers that can solve complex problems with incredible speed and power technologies that aren’t even invented.
What is a quantum computer?
Google isn’t the only company building quantum computers, and these types of machines keep popping up in the news with regularity. Quantum computers won’t reach your phone, and they’re not going to play games. Even if they did, Nintendo will totally ignore the latest computer technology when designing future consoles.