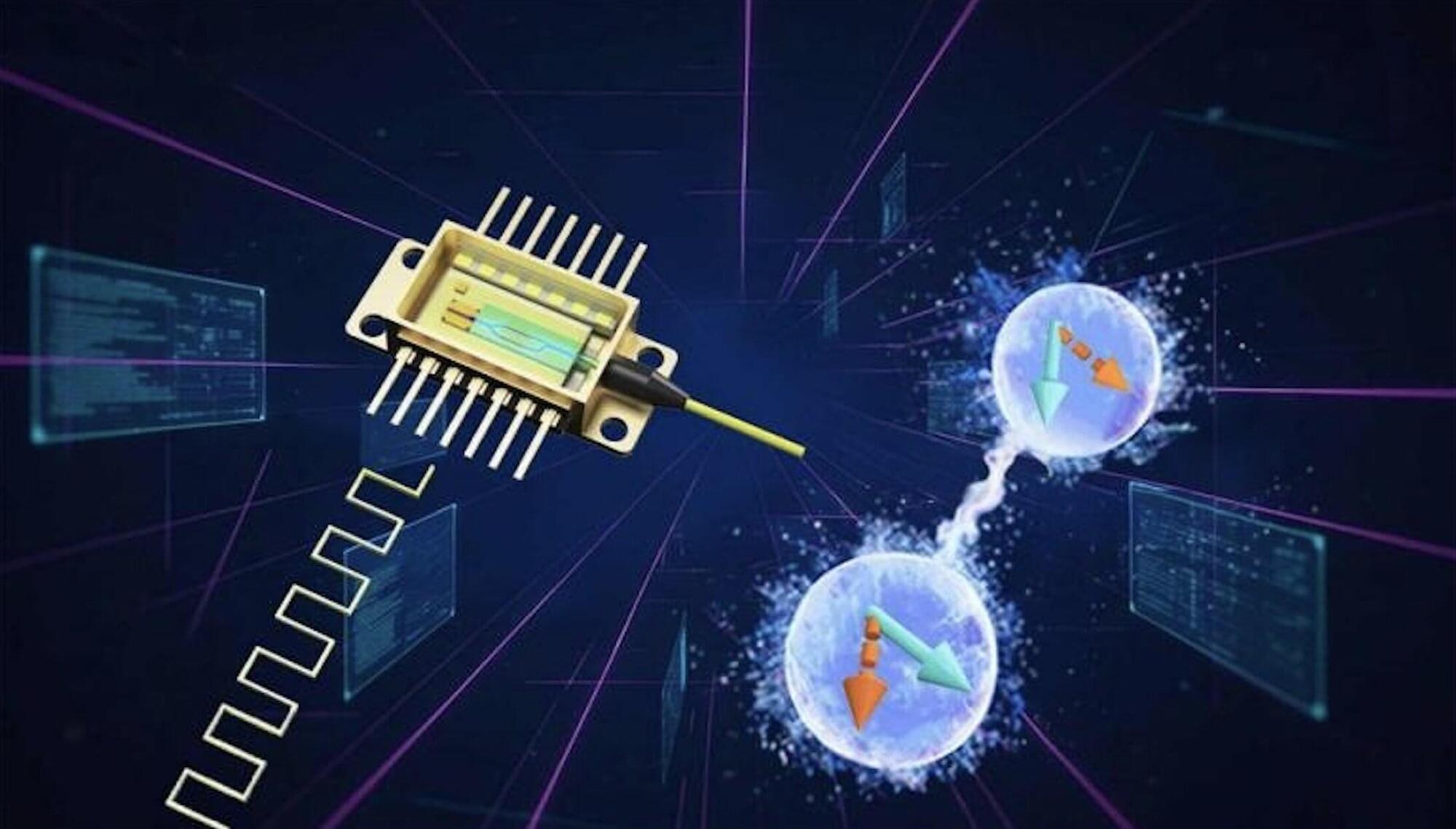
Quantum technologies are cutting-edge systems that can process, transfer, or store information leveraging quantum mechanical effects, particularly a phenomenon known as quantum entanglement. Entanglement entails a correlation between two or more distant particles, whereby measuring the state of one also defines the state of the others.
In recent years, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to realize devices that operate leveraging the entanglement between individual particles of light (i.e., photons). The reliable operation of these devices relies on so-called entangled photon sources (EPSs), components that can generate entangled pairs of photons.
Researchers at University of Science and Technology of China, Jinan Institute of Quantum Technology, CAS Institute of Semiconductors and other institutes recently realized a new EPS integrated onto a single photonic chip, which can generate entangled photons via an electrically powered laser. Their study is published in Physical Review Letters.