It’s unbelievable all that’s going on at the moment in astronomy” — DER SPIEGEL — international.
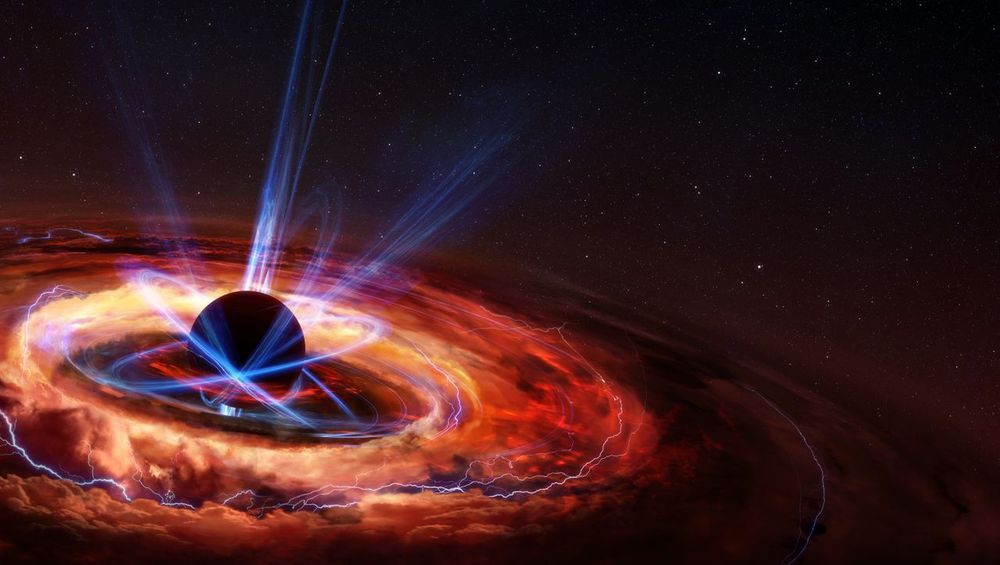
DER SPIEGEL: Wherever black holes are discussed, that picture is shown. And you are now telling us that we don’t really even know what it is?
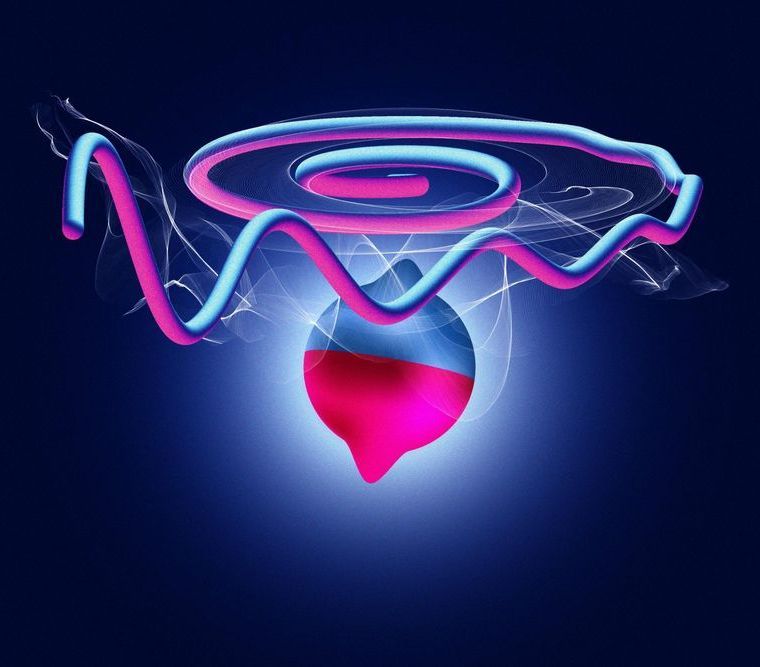
Genzel: Exactly. It could be that we are looking at the shadow of a black hole, as it is commonly portrayed. But it could also be the outer wall of a jet that is coming directly at us at the speed of light. To know for sure, we need additional measurements. But we have a problem at the moment: the corona pandemic. Most Earth-based telescopes have been switched off.
DER SPIEGEL: Tell us a little bit about your research. What is the importance of a black hole at the center of the Milky Way?