Scientists recently broke their own laser-fusion record! But they must replicate their success soon to preserve research in thermonuclear weapons.
Category: physics – Page 260


Fundamental mechanics help increase battery storage capacity and lifespan
Batteries are widely used in everyday applications like powering electric vehicles, electronic gadgets and are promising candidates for sustainable energy storage. However, as you’ve likely noticed with daily charging of batteries, their functionality drops off over time. Eventually, we need to replace these batteries, which is not only expensive but also depletes the rare earth elements used in making them.
A key factor in battery life reduction is the degradation of a battery’s structural integrity. To discourage structural degradation, a team of researchers from USC Viterbi School of Engineering are hoping to introduce “stretch” into battery materials so they can be cycled repeatedly without structural fatigue. This research was led by Ananya Renuka-Balakrishna, WiSE Gabilan Assistant Professor of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, and USC Viterbi Ph.D candidate, Delin Zhang, as well as Brown University researchers from Professor Brian Sheldon’s group. Their work was published in the Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids.
A typical battery works through a repetitive cycle of inserting and extracting Li-ions from electrodes, Zhang said. This insertion and extraction expands and compresses the electrode lattices. These volume shifts create microcracks, fractures and defects over time.
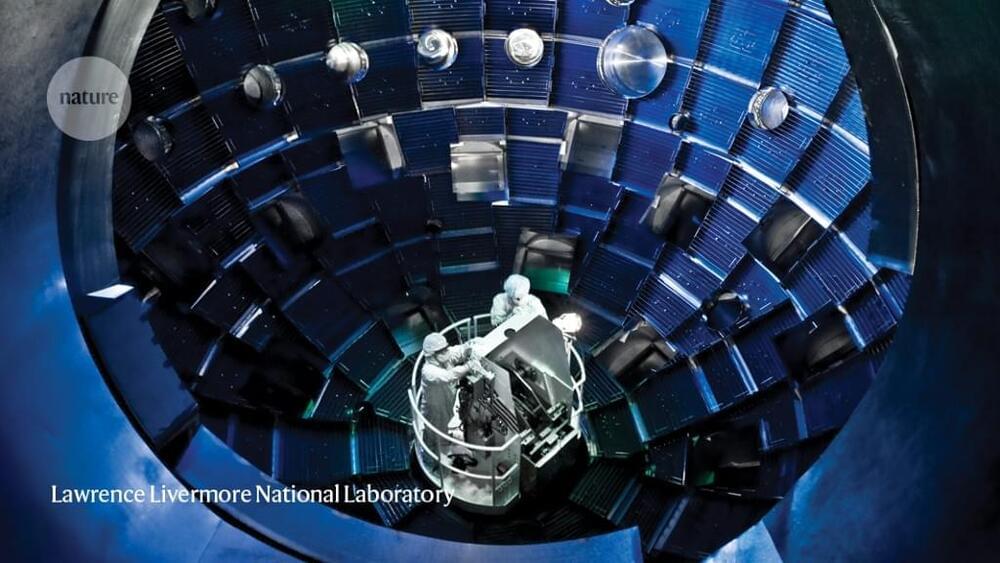

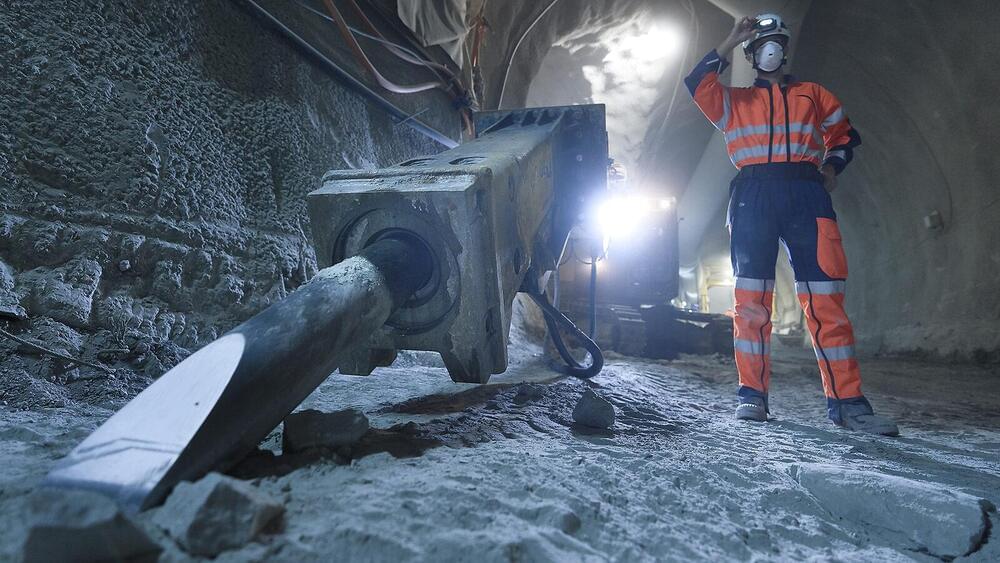
US achieves laser-fusion record: what it means for nuclear-weapons research
Housed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, the US$3.5-billion facility wasn’t designed to serve as a power-plant prototype, however, but rather to probe fusion reactions at the heart of thermonuclear weapons. After the United States banned underground nuclear testing at the end of the cold war in 1,992 the energy department proposed the NIF as part of a larger science-based Stockpile Stewardship Program, designed to verify the reliability of the country’s nuclear weapons without detonating any of them.
With this month’s laser-fusion breakthrough, scientists are cautiously optimistic that the NIF might live up to its promise, helping physicists to better understand the initiation of nuclear fusion — and thus the detonation of nuclear weapons. “That’s really the scientific question for us at the moment,” says Mark Herrmann, Livermore’s deputy director for fundamental weapons physics. “Where can we go? How much further can we go?”
Here Nature looks at the NIF’s long journey, what the advance means for the energy department’s stewardship programme and what lies ahead.

Volume 596 Issue 7873, 26 August 2021
Proteins are essential to life, and understanding their 3D structure is key to unpicking their function. To date, only 17% of the human proteome is covered by an experimentally determined structure. Two papers in this week’s issue dramatically expand our structural understanding of proteins. Researchers at DeepMind, Google’s London-based sister company, present the latest version of their AlphaFold neural network. Using an entirely new architecture informed by intuitions about protein physics and geometry, it makes highly accurate structure predictions, and was recognized at the 14th Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction last December as a solution to the long-standing problem of protein-structure prediction. The team applied AlphaFold to 20,296 proteins, representing 98.5% of the human proteome.
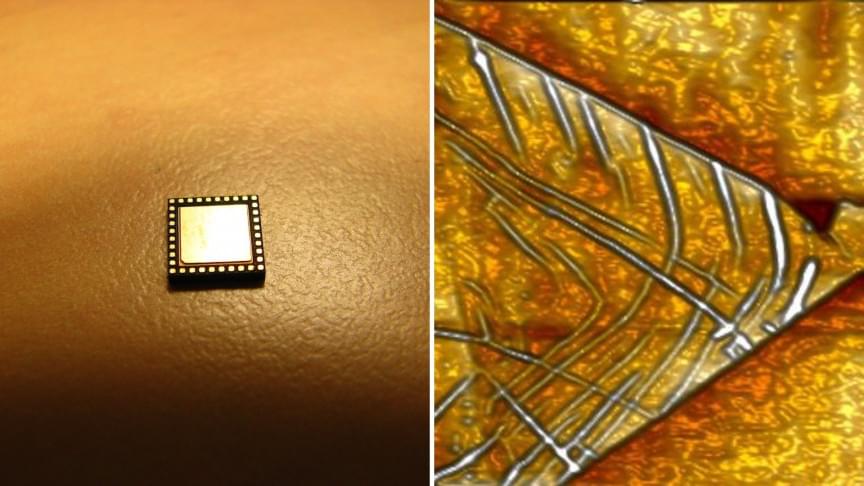

Physicists Discover New Electronic Phenomenon
Physics researchers at the University of North Florida’s Atomic LEGO Lab discovered a new electronic phenomenon they call “asymmetric ferroelectricity”. The research led by Dr. Maitri Warusawithana, UNF physics assistant professor, in collaboration with researchers at the University of Illinois and the Arizona State University, demonstrated this phenomenon for the first time in engineered two-dimensional crystals.
Einstein’s E=mc2 equation creates matter from light for first time
Albert Einstein’s most famous equation, E = mc2, used in the theory of general relativity, has been used to create matter from light, scientists have said in a new study.
Researchers from New York’s Brookhaven National Laboratory used the Department of Energy’s Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC), ordinarily used for nuclear physics research, to speed up two gold ions that are positively charged, in a loop.