Deep generative models are a popular data generation strategy used to generate high-quality samples in pictures, text, and audio and improve semi-supervised learning, domain generalization, and imitation learning. Current deep generative models, however, have shortcomings such as unstable training objectives (GANs) and low sample quality (VAEs, normalizing flows). Although recent developments in diffusion and scored-based models attain equivalent sample quality to GANs without adversarial training, the stochastic sampling procedure in these models is sluggish. New strategies for securing the training of CNN-based or ViT-based GAN models are presented.
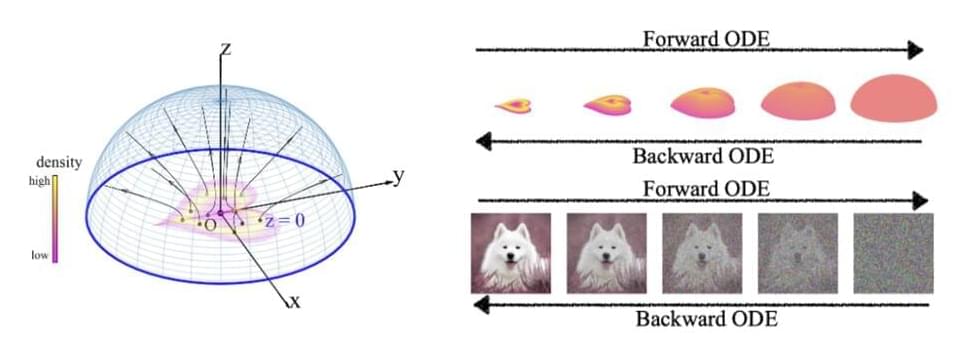
They suggest backward ODEsamplers (normalizing flow) accelerate the sampling process. However, these approaches have yet to outperform their SDE equivalents. We introduce a novel “Poisson flow” generative model (PFGM) that takes advantage of a surprising physics fact that extends to N dimensions. They interpret N-dimensional data items x (say, pictures) as positive electric charges in the z = 0 plane of an N+1-dimensional environment filled with a viscous liquid like honey. As shown in the figure below, motion in a viscous fluid converts any planar charge distribution into a uniform angular distribution.
A positive charge with z 0 will be repelled by the other charges and will proceed in the opposite direction, ultimately reaching an imaginary globe of radius r. They demonstrate that, in the r limit, if the initial charge distribution is released slightly above z = 0, this rule of motion will provide a uniform distribution for their hemisphere crossings. They reverse the forward process by generating a uniform distribution of negative charges on the hemisphere, then tracking their path back to the z = 0 planes, where they will be dispersed as the data distribution.