The development of innovative magnetic nanodevices is one step closer to reality thanks to the observation by RIKEN physicists of a type of rotation that can be realized in materials consisting of light elements.
The ability to use electric currents to turn revolving mechanical parts led to the development of electric motors and caused an explosion in electrical devices. Now, physicists are trying to do the same thing but on a nanoscale. However, the development of innovative magnetic nanodevices requires the efficient electrical generation of rotation, or torque.
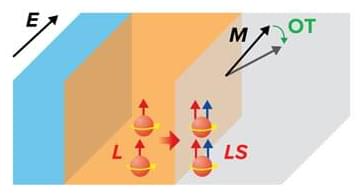
Usually, torque is generated in magnetic systems by converting electric charge to spin by using the strong spin–orbit interaction of a heavy-metal layer. The resulting spin current is then injected into adjacent ferromagnetic layers. But heavy-element materials are often incompatible with scalable production processes, and their high resistance makes them unsuitable for some applications.