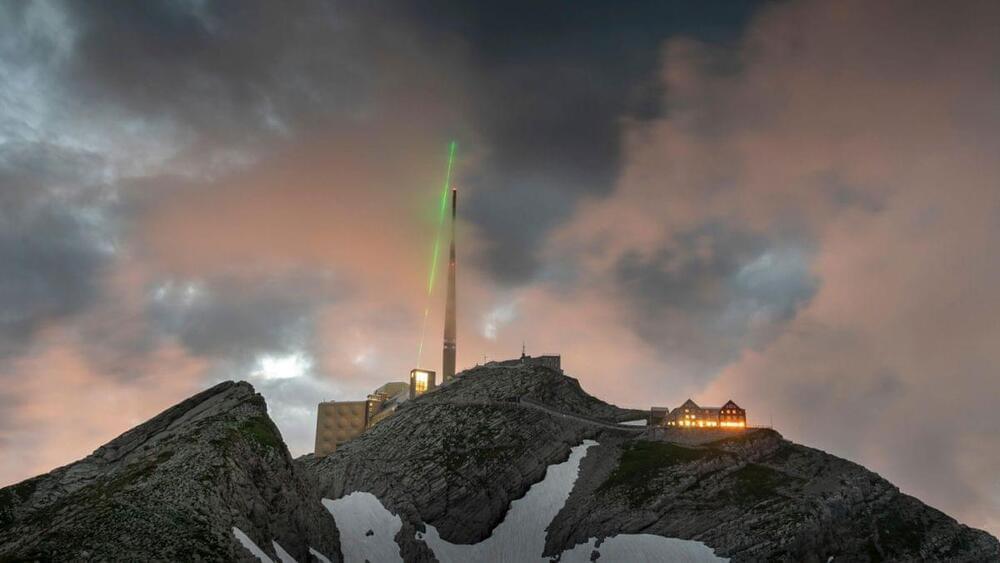
“Although this research field has been very active for more than 20 years, this is the first field-result that experimentally demonstrates lightning guided by lasers,” the researchers wrote in the study. “This work paves the way for new atmospheric applications of ultrashort lasers and represents an important step forward in the development of a laser based lightning protection for airports, launchpads or large infrastructures.”
Lightning emerges when atmospheric static electricity, generated by the friction of ice clumps and rain in stormclouds, separates electrons from atoms. The negatively charged electrons then pool at the stormcloud’s base and attract positive charges from the ground. As electrons steadily accumulate, they begin to overcome the resistance of the air to their flow, ionizing the atmosphere below them as they approach the ground in multiple forking (and invisible) “leader” paths. When the first leader path makes contact with the ground, electrons hop to the earth from the point of contact, discharging from the bottom up in a flash of lightning (called the return stroke) that travels to the top of the cloud.