The findings affirm a 90-year-old theory about how electrons can assemble without atoms.

A future quantum network of optical fibers will likely maintain communication between distant quantum computers. Sending quantum information rapidly across long distances has proved difficult, in part because most photons don’t survive the trip. Now Viktor Krutyanskiy of the University of Innsbruck, Austria, and his colleagues have more than doubled the success rate for sending photons that are quantum mechanically entangled with atoms to a distant site [1]. Instead of the previous approach of sending photons one at a time and waiting to see if each one arrives successfully, the researchers sent photons in groups of three. They believe that sending photons in larger numbers should be feasible in the future, allowing much faster transmission of quantum information.
Quantum networks require entanglement distribution, which involves sending a photon entangled with a local qubit to a distant location. The distribution system must check for the arrival and for the entanglement of each photon at the remote site before another attempt can be made, which can be time consuming. For a 100-km-long fiber, the light travel time combined with losses in the fiber and other inefficiencies limit the rate for this process to about one successful photon transfer per second using state-of-the-art equipment.
For faster distribution, Krutyanskiy and his colleagues trapped three calcium ions (qubits) in an optical cavity and performed repeated rounds of their protocol: in rapid sequence, each ion was triggered to emit an entangled photon that was sent down a 101-km-long, spooled optical fiber. In one experiment, the team performed nearly 900,000 of these “attempts,” detecting entangled photons at the far end 1906 times. The effective success rate came out to 2.9 per second. The team’s single-ion success rate was 1.2 per second.
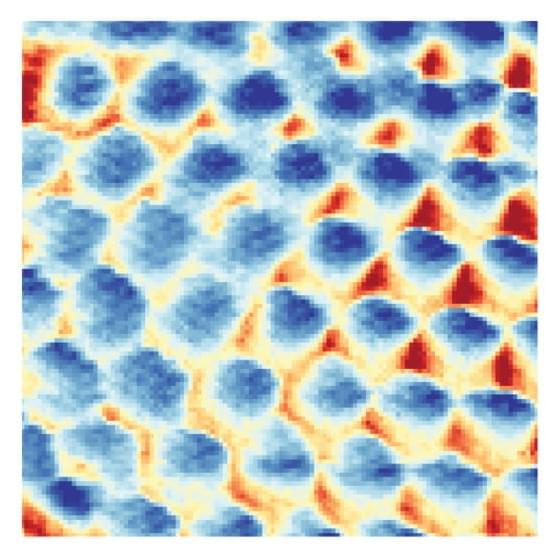
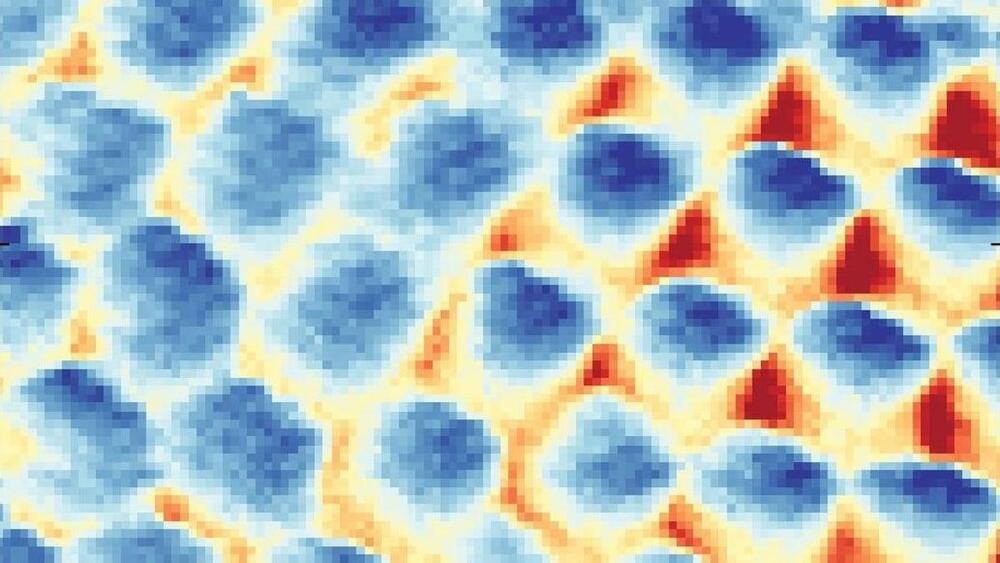
Electrons—the infinitesimally small particles that are known to zip around atoms—continue to amaze scientists despite the more than a century that scientists have studied them. Now, physicists at Princeton University have pushed the boundaries of our understanding of these minute particles by visualizing, for the first time, direct evidence for what is known as the Wigner crystal—a strange kind of matter that is made entirely of electrons.
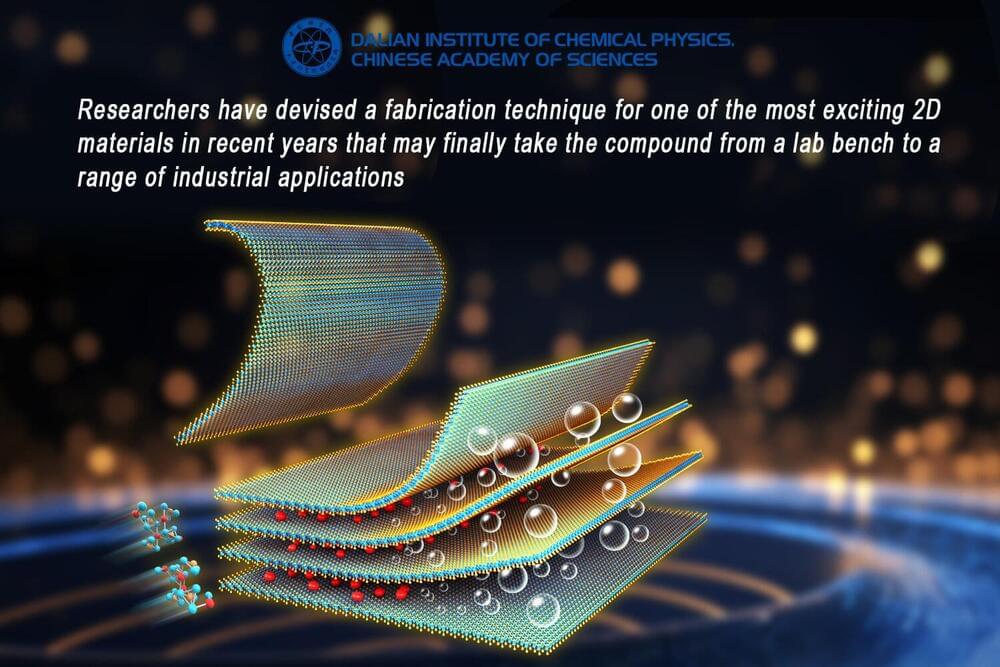
But a team of researchers has recently developed a novel fabrication technique —the use of chemical solutions to peel off thin layers from their parent compounds, creating atomically thin sheets—that looks set to deliver on the ultra-thin substance’s promise finally.
The researchers describe their fabrication technique in a study published in Nature.
In the world of ultra-thin or ‘two-dimensional’ materials—those containing just a single layer of atoms—transition metal telluride (TMT) nanosheets have, in recent years, caused great excitement among chemists and materials scientists for their particularly unusual properties.
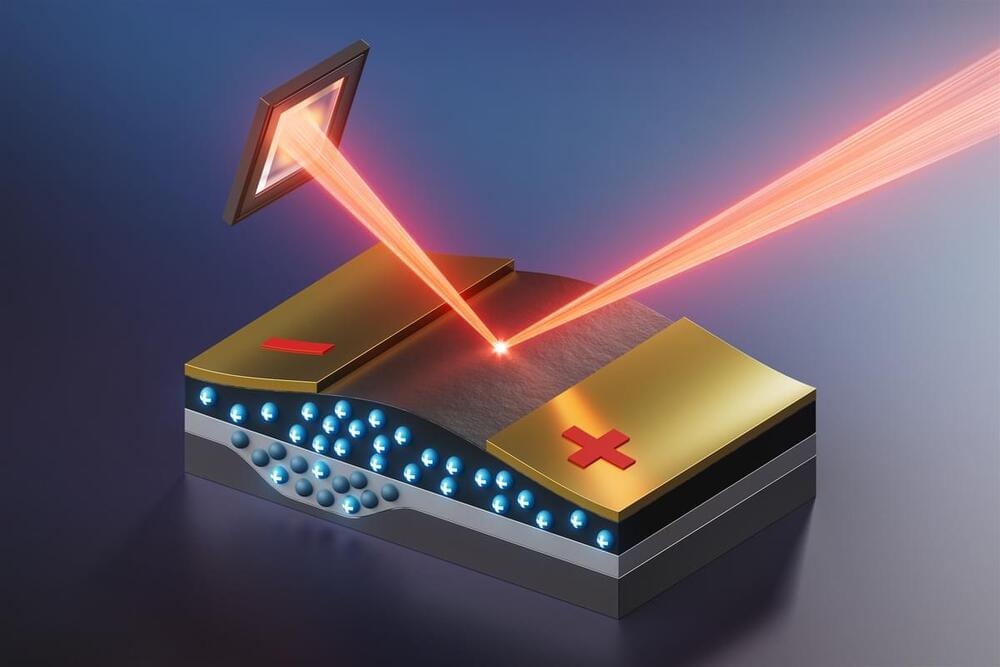
“We found to our great surprise that this substrate is very much active, jiving and responding in completely surprising ways as the film switches from an insulator to a metal and back when the electrical pulses arrive,” Gopalan said. “This is like watching the tail wagging the dog, which stumped us for a long while. This surprising and previously overlooked observation completely changes how we need to view this technology.”
To understand these findings, the theory and simulation effort — led by Long-Qing Chen, Hamer Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, professor of engineering science and mechanics and of mathematics at Penn State — developed a theoretical framework to explain the entire process of the film and the substrate bulging instead of shrinking. When their model incorporated naturally occurring missing oxygen atoms in this material of two types, charged and uncharged, the experimental results could be satisfactorily explained.
“These neutral oxygen vacancies hold a charge of two electrons, which they can release when the material switches from an insulator to a metal,” Gopalan said. “The oxygen vacancy left behind is now charged and the crystal swells up, leading to the observed surprising bulging in the device. This response can also happen in the substrate. All of these physical processes are beautifully captured in the phase-field theory and modeling performed in this work for the first time by the postdoc Yin Shi in Prof. Chen’s group.”

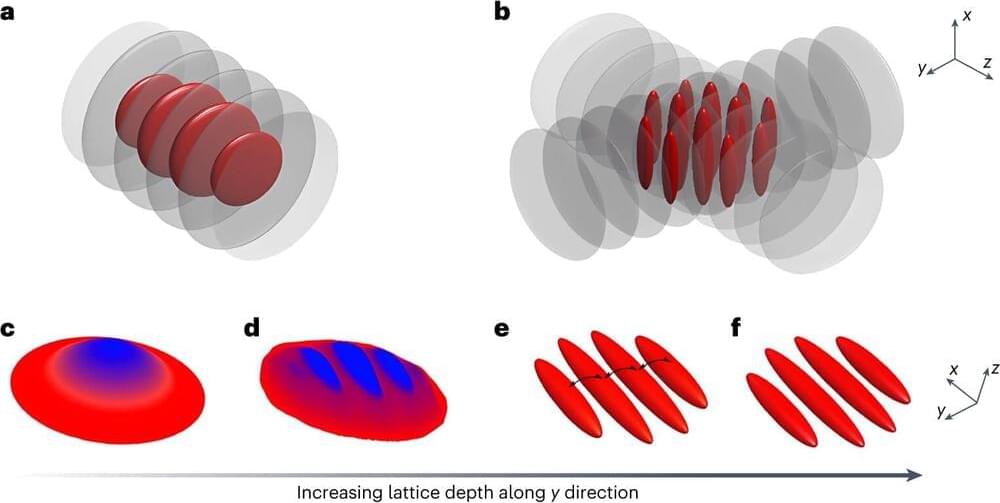
An international research team from Innsbruck and Geneva has, for the first time, probed the dimensional crossover for ultracold quantum matter. In the regime between one and two dimensions, the quantum particles perceive their world as being 1D or 2D depending on the length scale on which they are probed: For short distances, their world is 1D, but it is 2D for long distances.
The discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012 slotted in the final missing piece of the Standard Model puzzle. Yet, it left lingering questions. What lies beyond this framework? Where are the new phenomena that would solve the universe’s remaining mysteries, such as the nature of dark matter and the origin of matter-antimatter asymmetry?

Researchers have successfully transformed CO2 into methanol by shining sunlight on single atoms of copper deposited on a light-activated material, a discovery that paves the way for creating new green fuels.
An international team of researchers from the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry, University of Birmingham, University of Queensland, and University of Ulm have designed a material made up of copper anchored on nanocrystalline carbon nitride.
The copper atoms are nested within the nanocrystalline structure, which allows electrons to move from carbon nitride to CO2, an essential step in the production of methanol from CO2 under the influence of solar irradiation. The research has been published in the Sustainable Energy & Fuels journal.