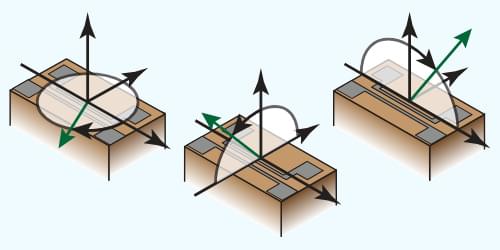
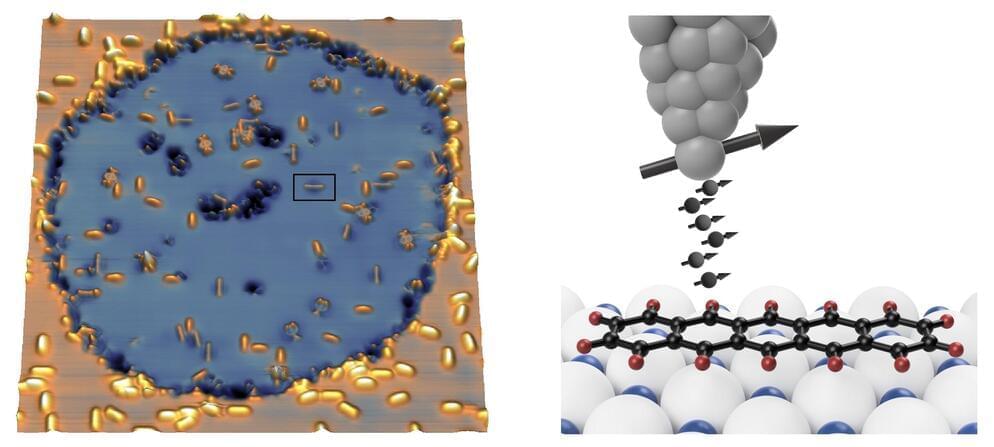
Spin-orbit torque effects involve the transfer of angular momentum between a spin current and a magnetic layer mediated by the exchange interaction between conduction and localized electron.
Measuring these effects in magnetic materials continues to be a very active area of interest in spintronics…
Electrons have an intrinsic angular momentum, the so-called spin, which means that they can align themselves along a magnetic field, much like a compass needle. In addition to the electric charge of electrons, which determines their behavior in electronic circuits, their spin is increasingly used for storing and processing data.
Already, one can buy MRAM memory elements (magnetic random access memories), in which information is stored in very small but still classical magnets—that is, containing very many electron spins. The MRAMs are based on currents of electrons with spins aligned in parallel that can change the magnetization at a particular point in a material.
Pietro Gambardella and his collaborators at ETH Zurich now show that such spin-polarized currents can also be used to control the quantum states of single electron spins. Their results, which have just been published in the journal Science, could be used in different technologies in the future, for instance in the control of quantum states of quantum bits (qubits).