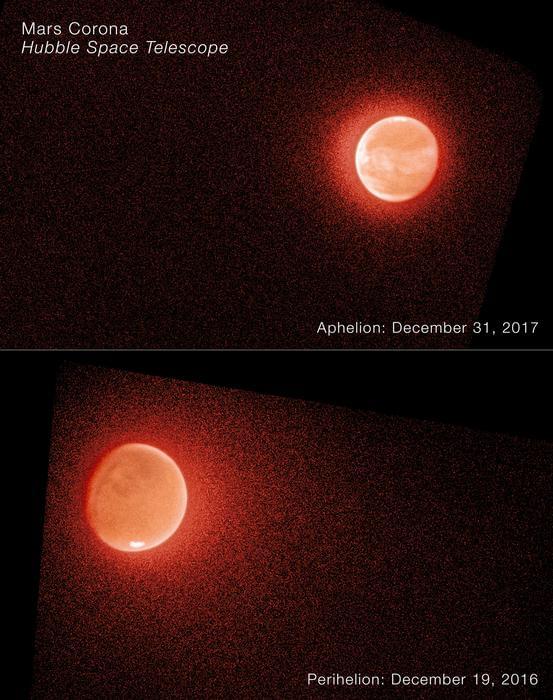
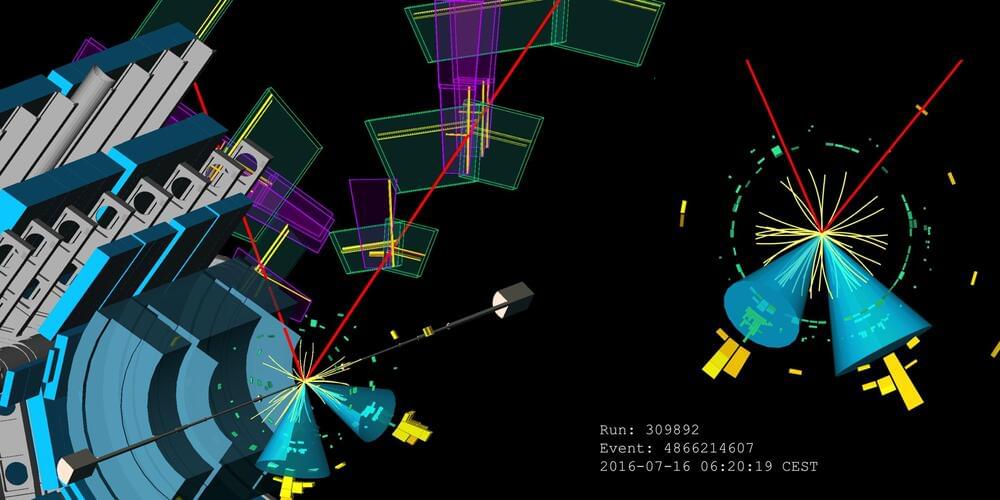
“In recent years scientists have found that Mars has an annual cycle that is much more dynamic than people expected 10 or 15 years ago,” said Dr. John Clarke.
What happened to all the liquid water on Mars and what can this teach us about Earth-like exoplanets? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the atmospheric and atomic processes responsible for Mars losing its water over time. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the evolution of Mars, specifically regarding the loss of water, and what implications this holds for Earth-like exoplanets.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of data from NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) and Hubble Space Telescope (HST) spacecraft to measure the ratio of hydrogen and deuterium that escapes from Mars over three Martian years, with each Martian year comprising 687 Earth days. Deuterium is also called “heavy hydrogen” since it is a hydrogen atom with a neutron in its nucleus, making its mass greater than hydrogen.
Since deuterium is heavier, this means hydrogen is lost to space faster, and measuring this present-day loss can help scientists determine how much was lost in Mars’s ancient past. Additionally, Mars’ orbit is more elliptical than Earth, meaning it orbits farther away from the Sun at certain times of the year, and this could also contribute to hydrogen loss, as well. In the end, the team found that this ratio changes as Mars is closer to the Sun and farther away, which challenges longstanding hypotheses regarding Mars’s atmospheric evolution.