Using a camera with 2-picosecond time resolution, researchers show that the atoms in a laser-induced plasma are more highly ionized than theory predicts.
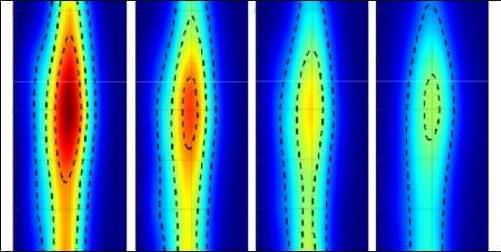
With an astonishing 500 billion frames per second, a new movie captures the evolution of a laser-induced plasma, revealing that its atoms have lost more electrons—and thus have stronger interactions within the plasma—than models predict [1]. The movie relies on a ten-year-old technology, called compressed ultrafast photography (CUP), that packs all the information for hundreds of movie frames into a single image. The results suggest that models of plasma formation may need revising, which could have implications for inertial-confinement-fusion experiments, such as those at the National Ignition Facility in California.
Dense plasmas occur in many astrophysical settings and laboratory experiments. Their behavior is difficult to predict, as they often change on picosecond (10−12 s) timescales. A traditional method for probing this behavior is to use a streak camera, which collects a movie on a single image by capturing a small slice of each movie frame. “It’s one picture, but every line occurs at a different time,” explains John Koulakis from UCLA. He and his colleagues have used streak cameras to study anomalous behavior in plasmas [2], but the small region of plasma visible with this technique left doubts about what they were seeing, he says.