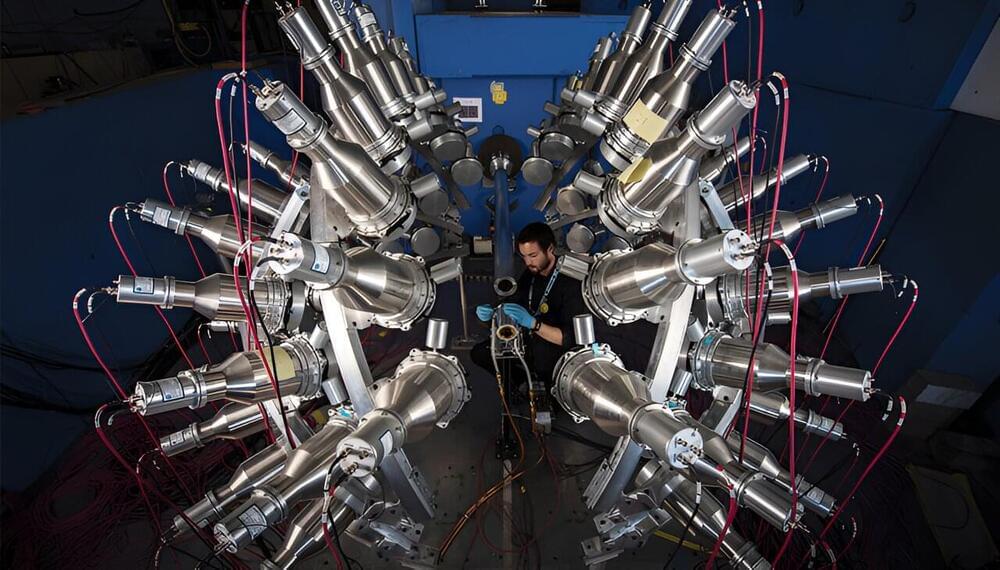
The results of the Chi-Nu physics experiment at Los Alamos National Laboratory have contributed essential, never-before-observed data for enhancing nuclear security applications, understanding criticality safety and designing fast-neutron energy reactors. The Chi-Nu project, a years-long experiment measuring the energy spectrum of neutrons emitted from neutron-induced fission, recently concluded the most detailed and extensive uncertainty analysis of the three major actinide elements—uranium-238, uranium-235 and plutonium-239.
“Nuclear fission and related nuclear chain reactions were only discovered a little more than 80 years ago, and experimenters are still working to provide the full picture of fission processes for the major actinides,” said Keegan Kelly, a physicist at Los Alamos National Laboratory. “Throughout the course of this project, we have observed clear signatures of fission processes that in many cases were never observed in any previous experiment.”
The Los Alamos team’s final Chi-Nu study, on the isotope uranium-238, was recently published in Physical Review C. The experiment measured uranium-238’s prompt fission neutron spectrum: the energy of the neutron inducing the fission—the neutron that crashes into a nucleus and splits it—and the potentially wide-ranging energy distribution (the spectrum) of the neutrons released as a result. Chi-Nu focuses on “fast-neutron-induced” fission, with incident neutron energies in millions of electron volts, where there have typically been very few measurements.