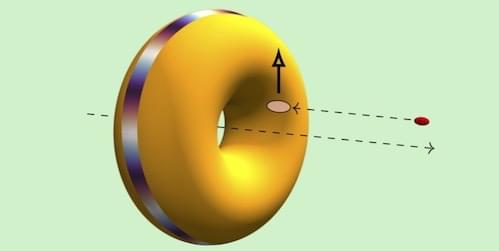
Photons, electrons, and other particles can propagate as wave packets with helical wave fronts that carry an orbital angular momentum. These vortex states can be used to probe the dynamics of atomic, nuclear, and hadronic systems. Recently, researchers demonstrated vortex states of x-ray photons and proposed ways to realize such states for particles at higher energies (MeV to GeV). But verifying high-energy vortex states will be challenging, because characterization techniques used at lower energies would perform poorly. Zhengjiang Li of Sun Yat-sen University in China and his colleagues at Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics propose a new diagnostic method for high-energy vortex states. Their approach would reveal such states through an exotic scattering phenomenon called a superkick.
A superkick is a theorized effect occurring when an atom placed near the axis of a vortex light beam absorbs a photon. Under such conditions, the atom may get kicked to the side with a transverse momentum greater than that carried by the photon. Li and his colleagues considered a similar superkick involving electrons. They analyzed the elastic head-on collision of two electron wave packets at 10 MeV, one in a vortex state and the other in a nonvortex one. According to their calculations, two electrons in the beam, upon scattering, would acquire a nonzero total transverse momentum that could be detectable. The researchers predict an unmistakable signature of the vortex state: The momentum imbalance increases as the collision point gets closer to the vortex axis.
The researchers expect the superkick effect—which has never been observed—to be detectable with realistic experimental settings. They say the idea could be extended to high-energy vortices of photons, ions, and even hadrons.