Lipids are abundant in the brain, where they are found not just in the cell membranes of neurons, whose properties they modulate, but also in the so-called myelin sheaths insulating axons — the brain’s ‘wiring.’ The brain is therefore a surprisingly ‘fat’ organ — in fact, it is nearly 60% fat, the study’s first author, Anna Tkachev from Skoltech, said.
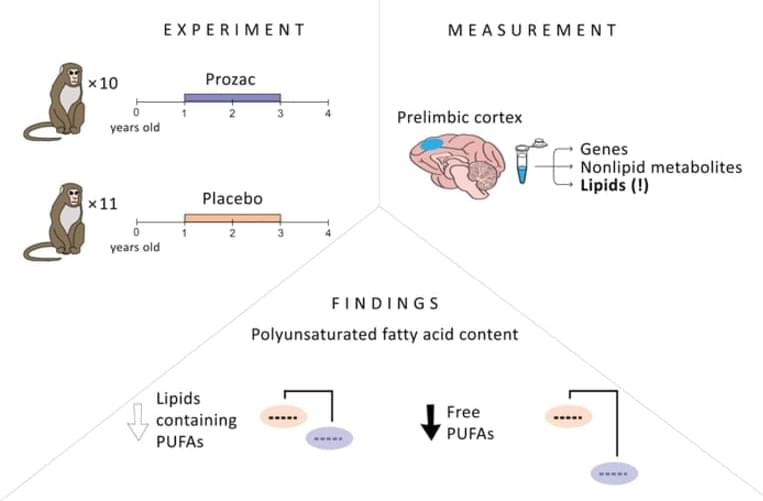
Summary: Prozac reduced polyunsaturated fatty acid lipid concentrations in the brains of juvenile macaque monkeys.
Source: Skoltech
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia, Germany, and the U.S. have found Prozac to reduce lipid concentrations in juvenile macaques who received the antidepressant for two years, compared to a control group of untreated animals.
While none of the monkeys in the study were depressed, the findings still offer a plausible biochemical explanation for the drug’s side effects, particularly in young patients. The paper was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.