
Category: neuroscience – Page 836

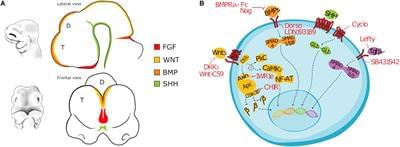
Pluripotent Stem Cells for Brain Repair: Protocols and Preclinical Applications in Cortical and Hippocampal Pathologies
Circa 2019 immortality in the human brain 🧠
Brain injuries causing chronic sensory or motor deficit, such as stroke, are among the leading causes of disability worldwide, according to the World Health Organization; furthermore, they carry heavy social and economic burdens due to decreased quality of life and need of assistance. Given the limited effectiveness of rehabilitation, novel therapeutic strategies are required to enhance functional recovery. Since cell-based approaches have emerged as an intriguing and promising strategy to promote brain repair, many efforts have been made to study the functional integration of neurons derived from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), or fetal neurons, after grafting into the damaged host tissue. PSCs hold great promises for their clinical applications, such as cellular replacement of damaged neural tissues with autologous neurons. They also offer the possibility to create in vitro models to assess the efficacy of drugs and therapies. Notwithstanding these potential applications, PSC-derived transplanted neurons have to match the precise sub-type, positional and functional identity of the lesioned neural tissue. Thus, the requirement of highly specific and efficient differentiation protocols of PSCs in neurons with appropriate neural identity constitutes the main challenge limiting the clinical use of stem cells in the near future. In this Review, we discuss the recent advances in the derivation of telencephalic (cortical and hippocampal) neurons from PSCs, assessing specificity and efficiency of the differentiation protocols, with particular emphasis on the genetic and molecular characterization of PSC-derived neurons. Second, we address the remaining challenges for cellular replacement therapies in cortical brain injuries, focusing on electrophysiological properties, functional integration and therapeutic effects of the transplanted neurons.
Brain injuries represent a large variety of disabling pathologies. They may originate from different causes and affect distinct brain locations, leading to an enormous multiplicity of various symptoms ranging from cognitive deficits to sensorimotor disabilities. They can also result in secondary disturbances, such as epileptic foci, which occur within the lesioned and perilesional tissues (Herman, 2002). Indeed, frequently a secondary functional damage can take place in a region distant from the first insult (e.g., the hippocampus after traumatic brain injury), providing an explanation for cognitive and memory deficits arising after a brain lesion (Girgis et al., 2016). Brain injuries can have traumatic or non-traumatic etiologies, including focal brain lesions, anoxia, tumors, aneurysms, vascular malformations, encephalitis, meningitis and stroke (Teasell et al., 2007). In particular, stroke covers a vast majority of acquired brain lesions.

Why Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Neurons To Die?
A study reveals one of the reasons why neurons die in Parkinson’s patients
According to World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, around 7 million individuals worldwide suffer from Parkinson’s disease. Although the origins of this neurodegenerative disorder are not entirely understood, it is known that many of its symptoms are caused by the death of neurons that create dopamine.
A study conducted in mice by a research team at the University of Cordoba has uncovered one of the causes of this neuronal loss: the key resides in the protein called DJ1, whose association with Parkinson’s disease has previously been established, but its specific role was unknown until now.

Key to spreading inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis found
Remote inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis spreads by neuron crosstalk, and the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) plays a key role in this.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder that mainly causes painful joints. It’s estimated to affect over 450,000 Australians.
Remote inflammation is a key feature – where inflammation spreads from one joint to another. Research has shown that factors involved include cells migrating from the joints and neural circuits, but until now the mechanism behind this spread had not been explained.
Now, a new study in mice has found that remote inflammation spreads by neuron crosstalk, and that the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) plays a key role in this by acting as a neurotransmitter and inflammation enhancer.
Exemption from Controlled Drugs and Substances Act: Personal possession of small amounts of certain illegal drugs in British Columbia (January 31, 2023 to January 31, 2026)
In response to a request from the province of British Columbia (BC), from January 31, 2023 to January 31, 2026, adults (18 and over) in BC will not be subject to criminal charges for the possession of up to 2.5 grams of certain illegal drugs for personal use.
The federal Minister of Mental Health and Addictions and Associate Minister of Health granted the province of British Columbia (BC)’s request for a subsection 56 exemption under the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act for adults (18 years of age and older) in the province to possess small amounts of certain illegal drugs for personal use. BC has referred to this as “decriminalization of personal possession of illegal drugs”.
What this means is that from January 31, 2023 to January 31, 2026, adults (18 and over) in BC will not be subject to criminal charges for the possession of a cumulative total of up to 2.5 grams of certain illegal drugs for personal use. Instead, all individuals found in possession of substances listed in the exemption of up to 2.5 grams for personal use will, at minimum, be provided with information on available local health and social services. They can also be provided with assistance to connect with those services if requested. The exemption only covers possession for personal use by adults (18 and over) in BC with no intent to traffic, produce or export.
British Columbia has been greatly impacted by overdose deaths and related harms, and declared the overdose crisis a public health emergency in 2016. As part of the province’s comprehensive public health response, BC requested a subsection 56 exemption under the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (CDSA) so that adults in the province will not be subject to criminal charges for personal possession of small amounts of certain illegal drugs.

Gene-edited tomatoes could be a new source of vitamin D
Tomatoes gene-edited to produce vitamin D, the sunshine vitamin, could be a simple and sustainable innovation to address a global health problem.
Researchers used gene editing to turn off a specific molecule in the plant’s genome which increased provitamin D3 in both the fruit and leaves of tomato plants. It was then converted to vitamin D3 through exposure to UVB light.
Vitamin D is created in our bodies after skin’s exposure to UVB light, but the major source is food. This new biofortified crop could help millions of people with vitamin D insufficiency, a growing issue linked to higher risk of cancer, dementia, and many leading causes of mortality. Studies have also shown that vitamin D insufficiency is linked to increased severity of infection by Covid-19.


Elon Musk versus the Woke Cartel
Many criticisms have been leveled against Elon Musk—that he’s part of the elite, that Tesla has been the beneficiary of government handouts and exemptions, that his transhumanist Neuralink is a brain-data-mining operation. Yet his planned purchase of Twitter, his supposed free-speech absolutism, and his subsequent renunciation of the Democratic Party as “the party of hate” have put Musk squarely in the crosshairs of the woke cartel.
Vitriolic Twitter storms, a New York Times-Financial Times biographical exposé, a slew of hit pieces and scaremongering segments in the legacy media, and allegations of sexual harassment have dogged the automobile magnate ever since his Twitter bid. In response, Musk announced on Twitter that he’s assembling a legal crew to sue defamers and defend Tesla (and likely himself) against lawsuits.
But the best indication that the woke cartel has really gone berserk is its removal of Tesla from the S&P 500’s ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Index. This last rebuff proves that “ESG is a scam.”
More life — Decoding the secret of aging | DW Documentary
This just came out, a day or so ago.
Can the aging process be reversed — or even halted, altogether? If we manage to decode this final mystery of our human biology, we might soon be able to eradicate age-related illnesses like cancer, dementia and heart problems.
The race to invent the miracle pill is well underway. Today, international researchers are getting astonishingly close to realizing humanity’s dream of immortality.
The hunt for immortality gained traction with the discovery of Costa Rica’s so-called “Blue Zone, by Luis Rosero-Bixby. In the “Blue Zone, on the Nicoya Peninsular, he found a remarkable number of centenarians. Here, male life expectancy is the highest in the world. Their healthy lifestyle is one factor, but the promise of longevity is probably also because their telomeres — sections of DNA found at the end of chromosomes — are longer than those of the average person.
It’s a field of research currently being explored by Maria Blasco in Madrid. But this is just one of many possible factors influencing the process of aging. Senescent cells may also play a key role. Also known as “zombie cells, these attack our body in old age and flood it with alarm signals until, at some point, we collapse under their weight. That’s a theory proposed by another researcher in Spain, Manuel Serrano.