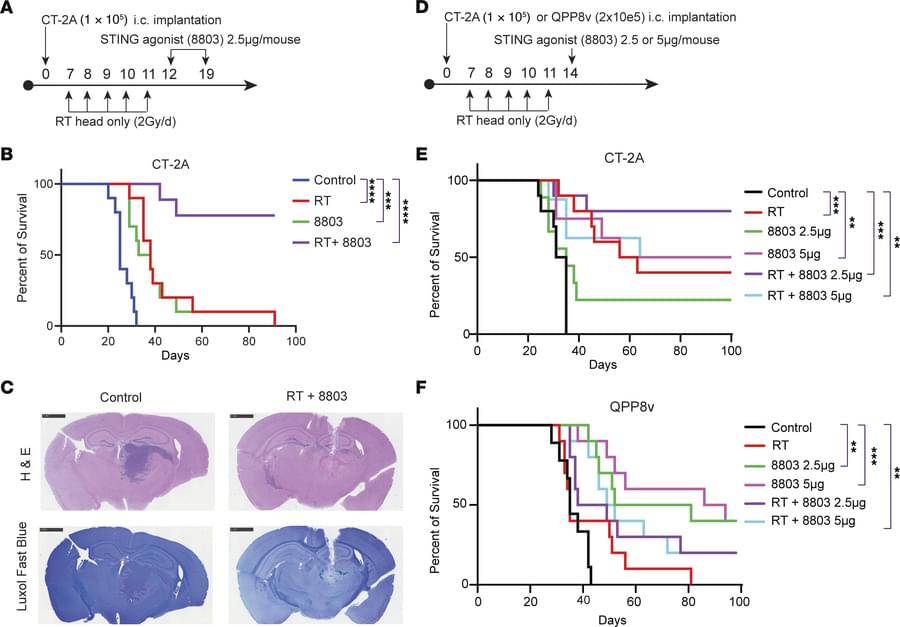
What was I thinking? This is not as easy or straightforward a question as I would have thought. As soon as you try to record and categorise the contents of your consciousness – the sense impressions, feelings, words, images, daydreams, mind-wanderings, ruminations, deliberations, observations, opinions, intuitions and occasional insights – you encounter far more questions than answers, and more than a few surprises. I’d always assumed that my stream of consciousness consisted mainly of an interior monologue, maybe sometimes a dialogue, but was surely composed of words; I’m a writer, after all. But it turns out that a lot of my so-called thoughts – a flattering term for these gossamer traces of mental activity – are preverbal, often showing up as images, sensations, or concepts, with words trailing behind as a kind of afterthought, belated attempts to translate these elusive wisps of meaning into something more substantial and shareable.
I discovered this because I’ve been going around with a beeper wired to an earpiece that sends a sudden sharp note into my left ear at random times of the day. This is my cue to recall and jot down whatever was going on in my head immediately before I registered the beep. The idea is to capture a snapshot of the contents of consciousness at a specific moment in time by dipping a ladle into the onrushing stream.
Sounds simple, but what the ladle scoops up is harder to describe than you might expect. Yes, these are my own thoughts, and who should know more about them than me, their thinker? Yet I’m finding that what we know about our own thinking is considerably less than we think.
The beeper exercise is part of a psychology experiment I volunteered to take part in. Descriptive experience sampling is a research method developed by Russell T Hurlburt, a social psychologist at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas; he has been using it for 50 years – which is to say, his entire career. To give you some perspective, beepers didn’t exist 50 years ago. Hurlburt, trained as an engineer, had to design and build his own unit, on which he holds a patent. It looks like an old-timey pocket radio: grey plastic, with one of those corrugated dials you rotate with your thumb to turn the thing on and boost the volume; the earpiece is flesh-toned, as that term was understood in 1973. For half a century now, Hurlburt has been scrupulously collecting reports of people’s inner experiences at random moments – and just as scrupulously resisting the urge to draw premature conclusions. A die-hard empiricist, he is as devoted to data as he is allergic to theories.
Scientists and philosophers studying the mind have discovered how little we know about our inner experiences.
By Michael Pollan