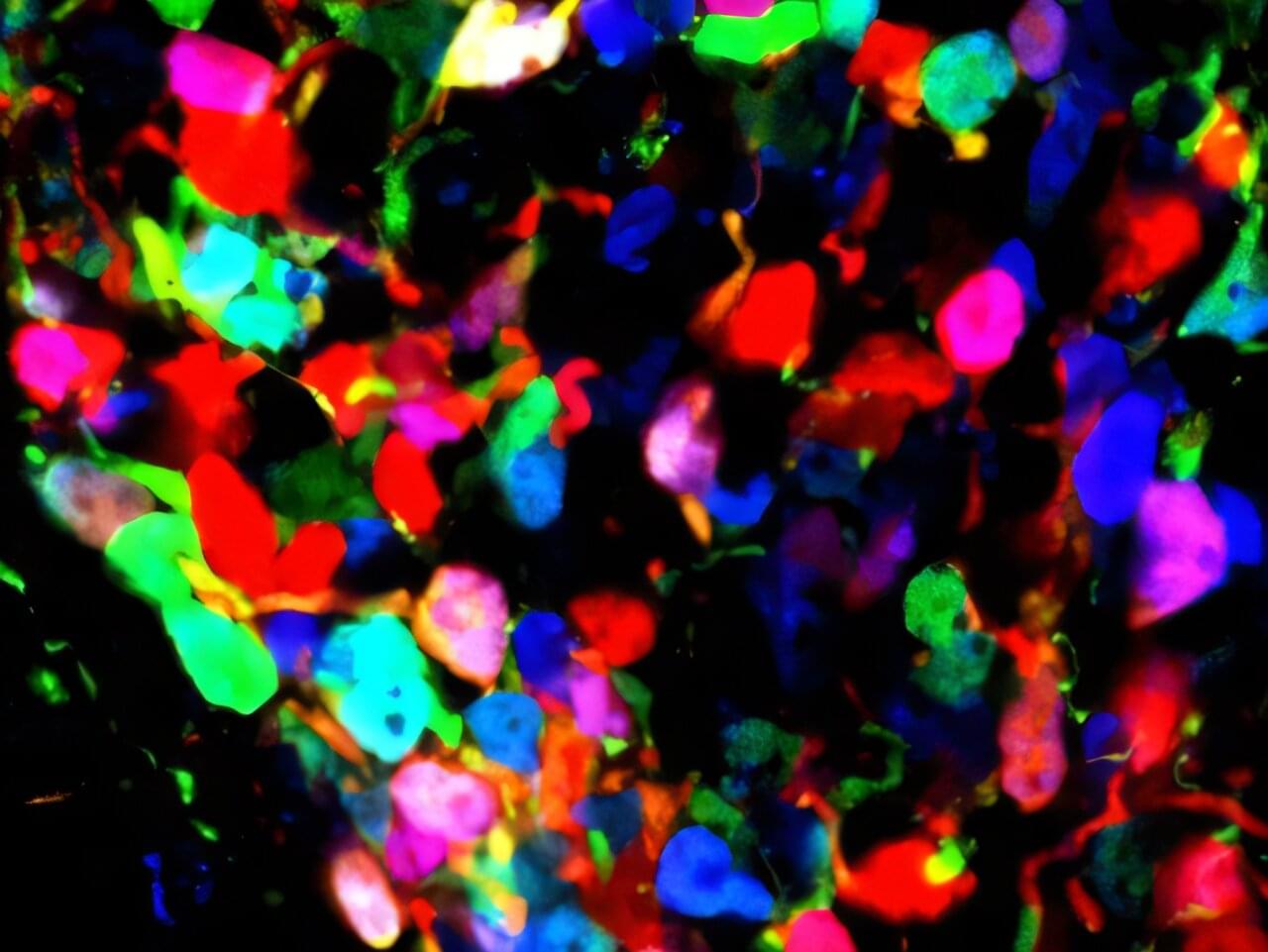
Tumor-immune-neural circuit in cancer cachexia.
The mechanisms involved in cancer-mediated cachexia and anorexia are not well understood.
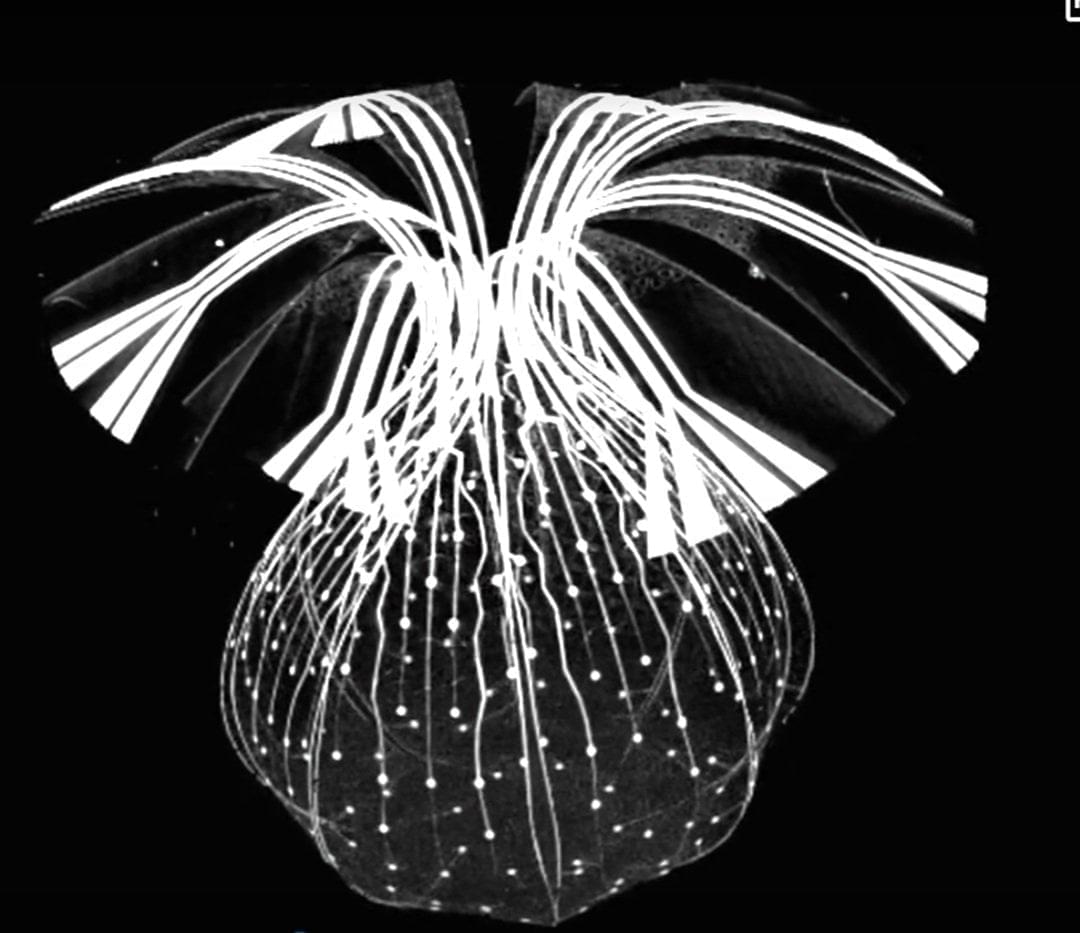
The researchers in this study delineate an interplay among tumor cells, immune cells, and the nervous system that drives cancer cachexia and anorexia.
The authors show thay loss of GDF15 protects against appetite loss, muscle wasting, and fat loss in pancreatic, lung, and skin cancers.
Disrupting this feedforward loop with GDF15-neutralizing antibody, anti-CSF1R antibody, or Rearranged during Transfection (RET) inhibitor alleviates cachexia and anorexia across cancer models. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/Tumor-immune-neural-circuit
Shi et al. delineate an interplay among tumor cells, immune cells, and the nervous system that drives cancer cachexia and anorexia. Specifically, tumor-derived CSF1 induces macrophage GDF15, which signals through the GFRAL-RET neural axis to enhance β-adrenergic activity and systemic wasting. Disrupting this feedforward loop alleviates cachexia across cancer models.