Our first encounter with E.T. technology could be as baffling to us as a smartphone would have been to a Neandertal.


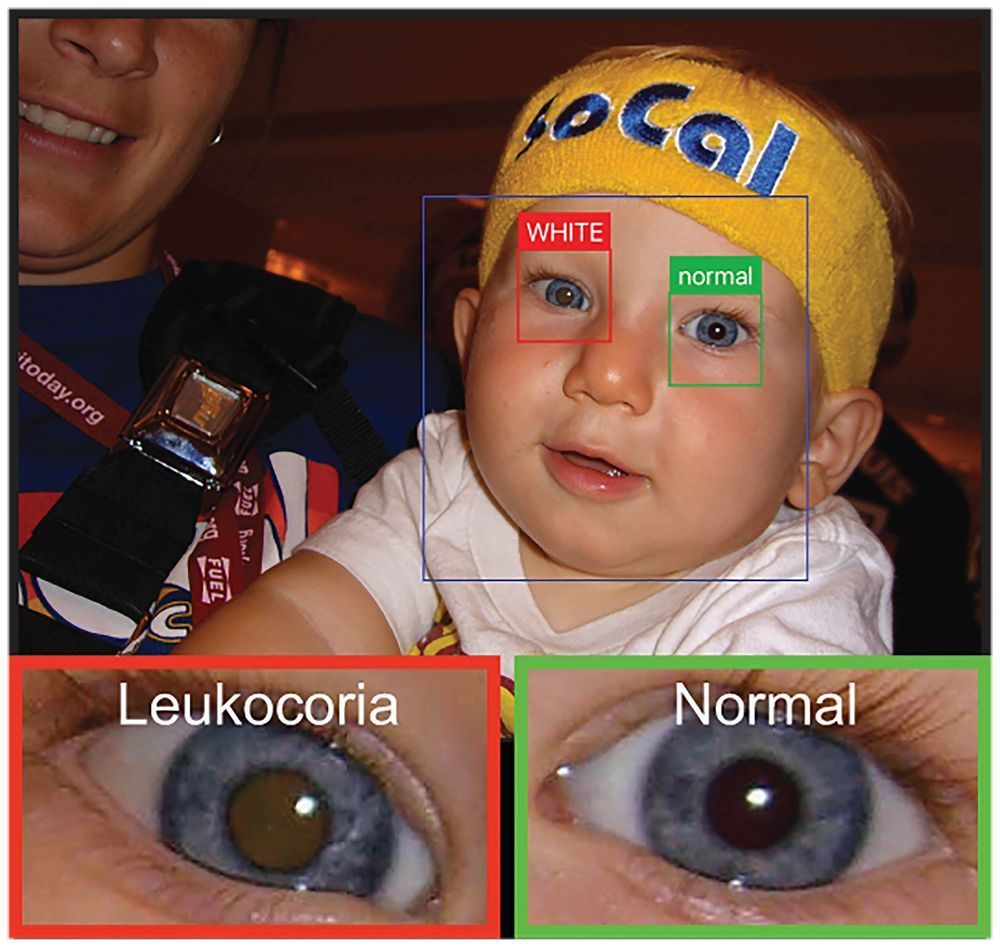
A team of researchers from Baylor University, with assistance from staff at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute has developed and tested a smartphone app that is able to detect “white eye” in children by analyzing stored photographs. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes how the app was developed and tested, and how well it works.
Most everyone has seen pictures of people seemingly possessed by the devil because their pupils glow red—this is caused by light bouncing off their retinas. However, such pictures sometimes produce white instead of red retinas. Sometimes it can happen due to ambient lighting conditions, but other times, it can indicate an eye ailment. Such problems can include retinoblastoma, a type of eye cancer, retinopathy, or even cataracts.
The idea for an app that could detect white eye came from the experience of one of the researchers, Brian Shaw, and his son, who developed retinoblastoma and subsequently lost an eye. The team developed the app and made it available to the public back in 2014, but it was not until more recently that the team decided to test the app to see how well it works.
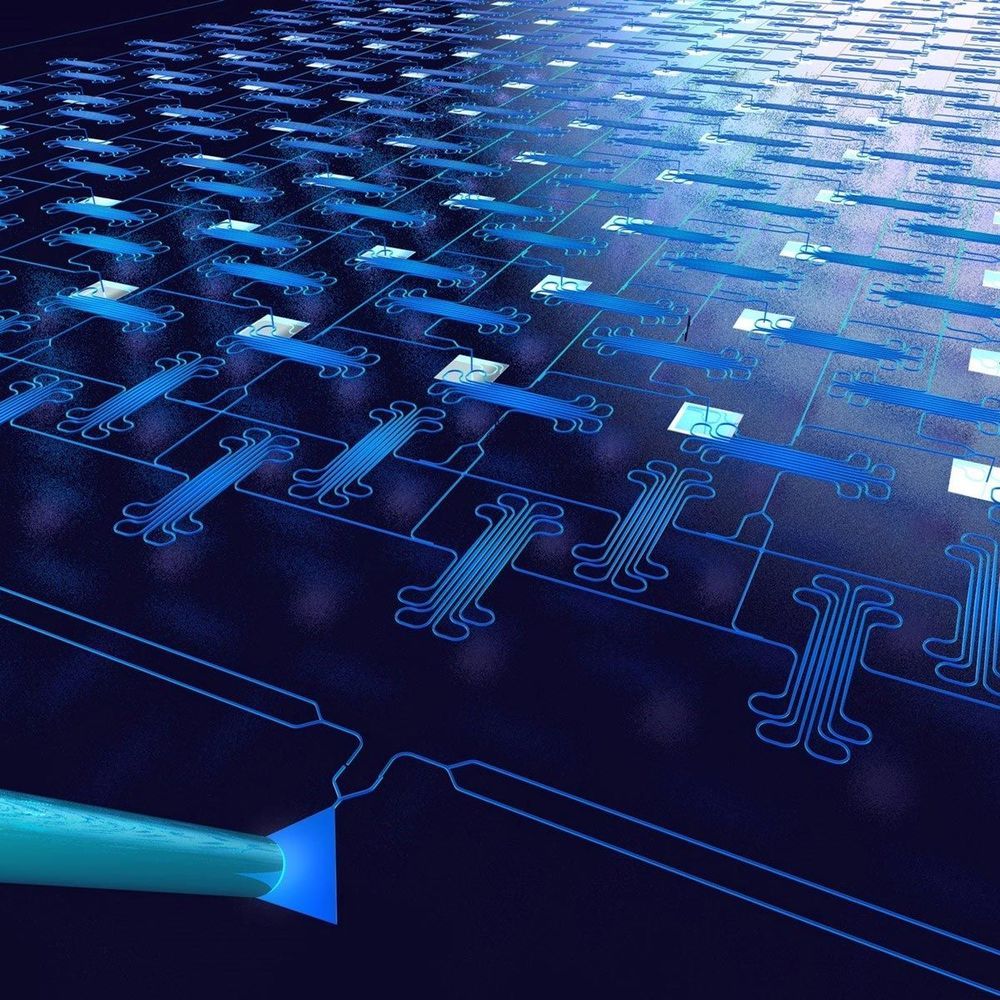
Washington — Researchers have developed a new microwave imager chip that could one day enable low-cost handheld microwave imagers, or cameras. Because microwaves can travel through certain opaque objects, the new imagers could be useful for imaging through walls or detecting tumors through tissue in the body.
In Optica, The Optical Society’s (OSA) journal for high-impact research, the researchers describe how they used a standard semiconductor fabrication process to make a microwave imager chip containing more than 1,000 photonic components. The square chip measures just over 2 millimeters on each side, making it about half the width of a pencil eraser.
“Today’s practical microwave imagers are bench-top systems that are bulky and expensive,” said research team leader Firooz Aflatouni from the University of Pennsylvania, USA. “Our new near-field imager uses optical, rather than electronic, devices to process the microwave signal. This enabled us to make a chip-based imager similar to the optical camera chips in many smartphones.”

Security researcher Axi0mX published the exploit, called “checkm8,” Friday on Github. It affects every Apple device with an A5 through A11 chipset, meaning every iPhone model from 4S to X. Though it isn’t an all-in-one jailbreak on its own, the exploit provides an extensive foundation for researchers to build off of in customizing jailbreaks for every vulnerable model of device that would allow them to totally take over the unit, run software far beyond what Apple normally allows, and program apps to interact and share data in ways that Apple’s protections usually preclude.
Any iPhone device from 2011 to 2017 could soon be jailbroken, thanks to an underlying flaw that there’s no way to patch.

A quasi-particle that travels along the interface of a metal and dielectric material may be the solution to problems caused by shrinking electronic components, according to an international team of engineers.
“Microelectronic chips are ubiquitous today,” said Akhlesh Lakhtakia, Evan Pugh University Professor and Charles Godfrey Binder Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics, Penn State. “Delay time for signal propagation in metal-wire interconnects, electrical loss in metals leading to temperature rise, and cross-talk between neighboring interconnects arising from miniaturization and densification limits the speed of these chips.”
These electronic components are in our smartphones, tablets, computers and security systems and they are used in hospital equipment, defense installations and our transportation infrastructure.

The effects of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies have already been experienced by the people globally and the increasing utilization of technology has proven a revolutionary advancement in the current scenario of digitization. Knowledge reasoning, planning, machine learning, robotics, computer vision, and graphics are few of the most commonly used areas where the AI has exposed the potential to ease the result oriented operations. In addition to the above, the most common machinery i.e. smartphones are even now available with high-end AI rich features and functionalities. AI enabled smartphones can now be noticed in terms of learning the continued user behavior and applying the same itself, improved security of rich features and enhanced voice assistants exhibiting AI rich functionalities. However, the exposure of Artificial Intelligence like broadest technologies must not be limited up to improved machinery rich features along with process optimization and automation. There are the other best set of fields predicted to get benefit under the global hug of AI worldwide which are hereby mentioned below.
The need to make some hardware systems tinier and tinier and others bigger and bigger has been driving innovations in electronics for a long time. The former can be seen in the progression from laptops to smartphones to smart watches to hearables and other “invisible” electronics. The latter defines today’s commercial data centers—megawatt-devouring monsters that fill purpose-built warehouses around the world. Interestingly, the same technology is limiting progress in both arenas, though for different reasons.
The culprit, we contend, is the printed circuit board. And the solution is to get rid of it.
Our research shows that the printed circuit board could be replaced with the same material that makes up the chips that are attached to it, namely silicon. Such a move would lead to smaller, lighter-weight systems for wearables and other size-constrained gadgets, and also to incredibly powerful high-performance computers that would pack dozens of servers’ worth of computing capability onto a dinner-plate-size wafer of silicon.
If you have more than one pet, then you know how chaotic feeding time can be. Italian company Volta is hoping to make the process just a little bit easier with its AI-driven pet feeder, Mookkie, which visually recognizes each individual cat or dog and places their prepared food at each pet’s disposal.
The Mookkie, winner of the Innovation Award in the Smart Home category at CES 2019, features a wide-angle camera that deploys logic similar to the “face-unlock” feature of smartphones.
Mookkie records images of the animal for which the food is intended, then deploys operations necessary for visual recognition, allowing the product to visually identify the presence of the pet and activate a door opening to allow access to food.
Apple says the iPhone 11 and iPhone 11 Pro feature the “toughest glass in a smartphone” and yesterday we saw the first drop test videos emerge. Now, PhoneBuff has shared a new video pitting the durability of the iPhone 11 Pro Max vs the Galaxy Note 10+.
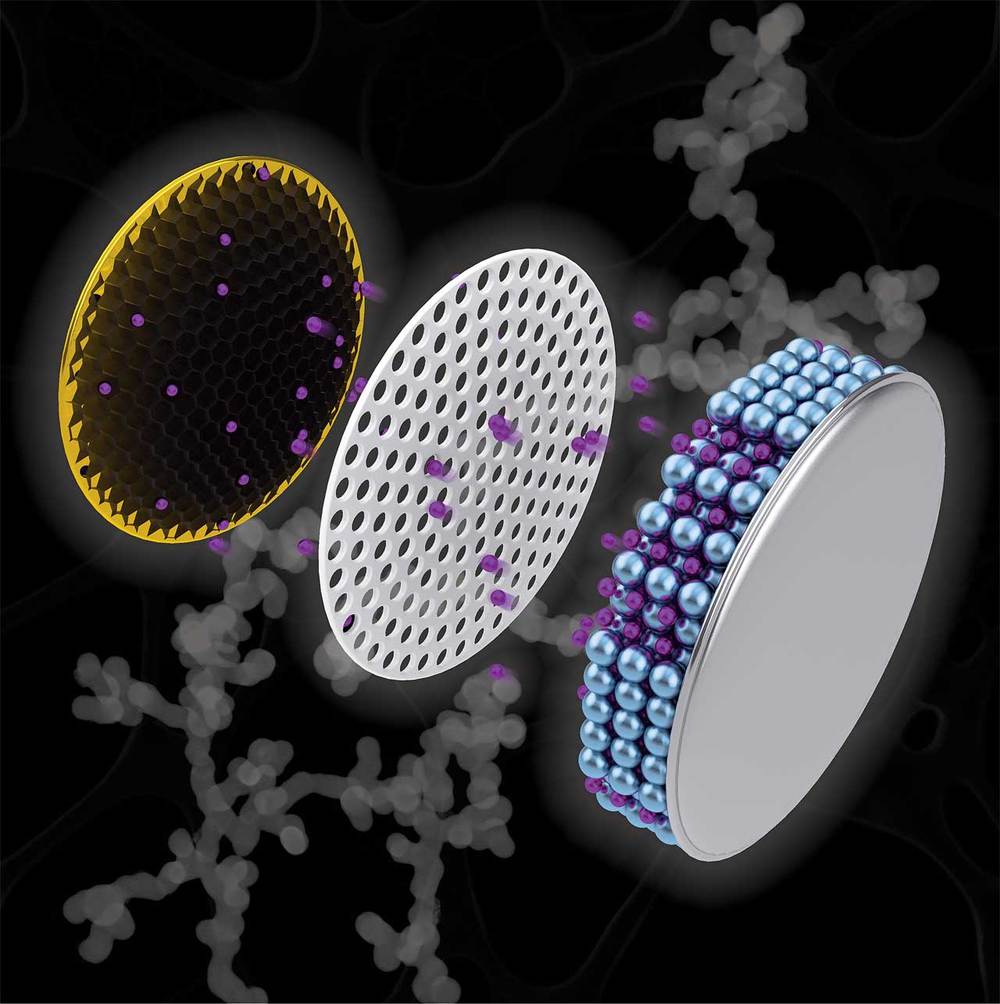
Researchers at Purdue University have announced a breakthrough that could have a significant impact on batteries of the future. The team says that the runtime for the battery in a phone or computer depends on how many lithium-ions can be stored in the negative electrode material inside the battery. When those ions are depleted, the battery is unable to deliver an electrical current.