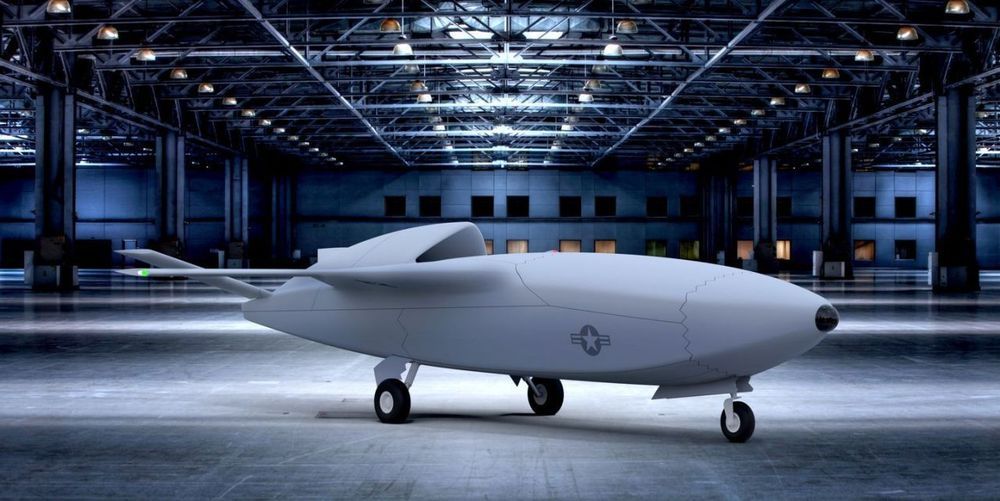
The drones would fly alongside Air Force warplanes, doing jobs too dangerous or dull for pilots.



“I do believe there’s great potential to bring in artificial intelligence to provide early warning of future problems” such as disease outbreaks, Air Force Lt. Gen. John N.T. “Jack” Shanahan, director of the Pentagon’s Joint Artificial Intelligence Center, said in an interview.
Artificial intelligence could spot and track earlier outbreaks of disease around the world, the Pentagon’s AI chief says as he retires from service.
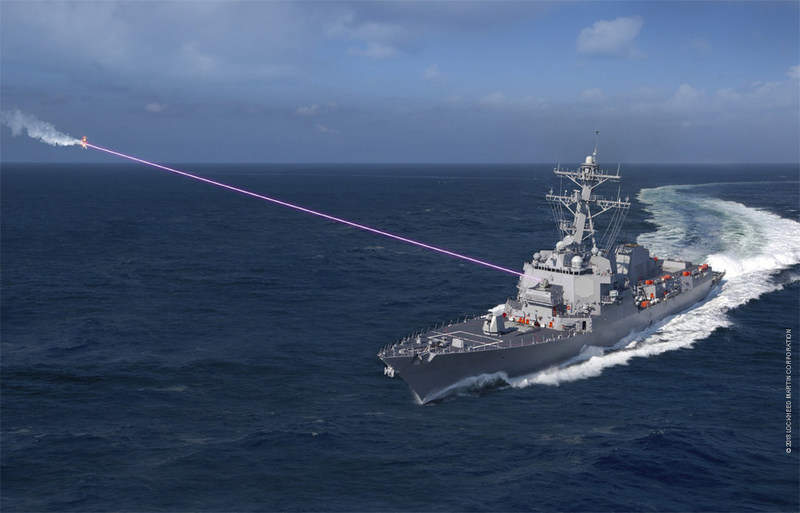

The US Navy has installed its first Optical Dazzling Interdictor, Navy (ODIN), a laser weapon designed to counter unmanned aerial systems (UAS).
The first ODIN laser system was installed on the Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyer USS Dewey during a recent dry-docking.
Unlike hard-kill laser systems already deployed by the US Navy on vessels, ODIN uses a dazzling laser to confuse systems sensors and cameras or, in manned systems, potentially cause glare in a pilot’s vision.
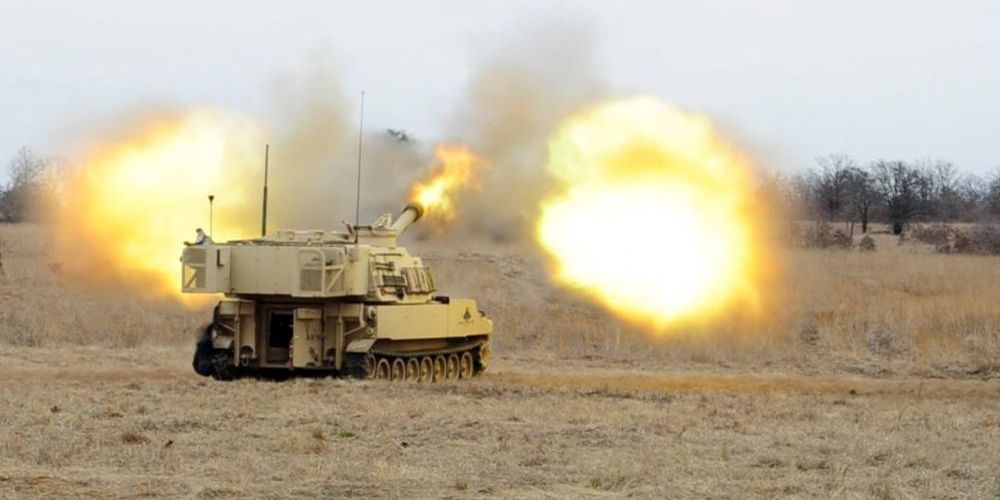

The U.S. Army is working on a new artillery shell capable of locating enemy targets, including moving tanks and armored vehicles. The shell, called Cannon-Delivered Area Effects Munition (C-DAEM), is designed to replace older weapons that leave behind unexploded cluster bomblets on the battlefield that might pose a threat to civilians. The shell is designed to hit targets even in situations where GPS is jammed and friendly forces are not entirely sure where the enemy is.
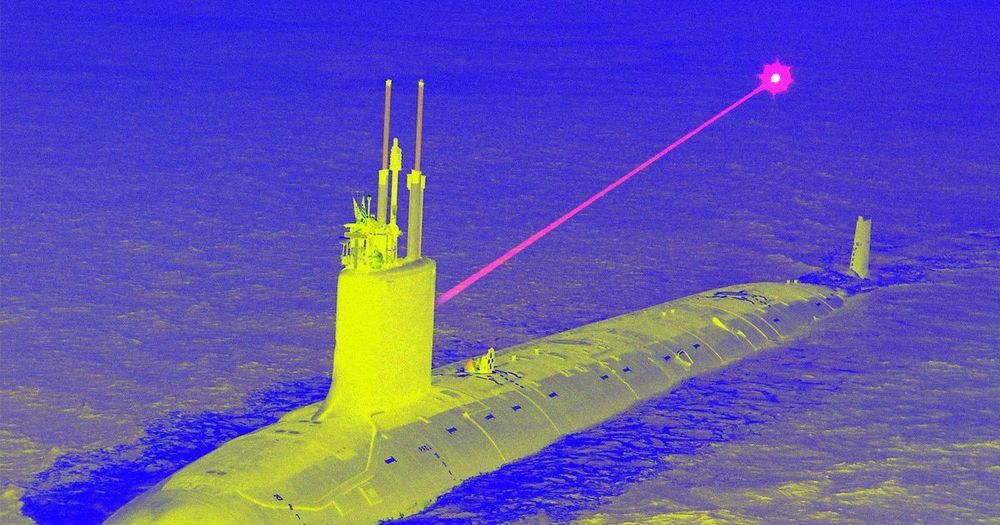

But there’s just one problem, according to the magazine: Laser weapons basically don’t work underwater, where laser light scatters and gets absorbed almost immediately.
Top Secret
While public documents reveal certain details about the designs the Navy has been testing since at least 2011, the Navy has remained tight-lipped about the execution or purpose of such a system, PopMech reports. One theory, according to the magazine, is that the Navy plans to integrate the lasers into the submarines’ periscopes and use them as surface weapons.

Samsung has a hardened version of the Galaxy S20, but don’t reach for your credit card — it’s not what you were expecting, and you probably can’t get one. The company has introduced a Galaxy S20 Tactical Edition that, as the name suggests, is designed to meet the needs of the US military and federal government. It touts two layers of encryption strong enough to handle top secret data and connects to tactical radios and mission systems out of the box.
There are combat-related conveniences, too. One mode can turn the display on and off while you’re wearing night vision goggles, while a stealth mode turns off LTE and and mutes all RF broadcasts to eliminate even the slightest chance of eavesdropping. It’s also easy to unlock the phone in landscape mode so that you can quickly launch an app while the device is mounted to your chest.
This is otherwise a run-of-the-mill Galaxy S20 with a 6.2-inch, 1440p display, a Snapdragon 865 processor, 12GB of RAM, 128GB of expandable storage, a 4,000mAh battery and the usual arrays of front and rear cameras. Although Samsung shows the Tactical Edition in a rugged casing, there’s no mention of the phone itself being rugged.
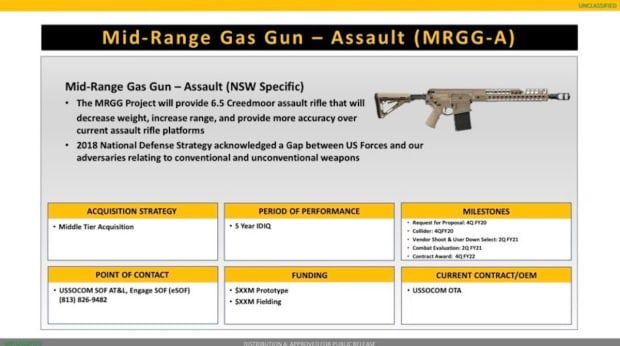
U.S. Special Operations Command will wait for the Army’s 6.8mm rifle and automatic rifle, but it’s moving forward to adopt a new sniper support weapon chambered in the longer-range 6.5mm Creedmoor round.
If all goes well with the Army’s 6.8mm Next Generation Squad Weapon (NGSW) effort, special-ops weapons officials plan to field both variants to units such as the 75th Ranger Regiment after the service begins its planned fielding in fiscal 2023.
Technology related to sending power via a microwave beam down to Earth could potentially be applied to taking out hostile targets in space.

The contracting giant will provide the JAIC with “data labeling, data management, data conditioning, AI product development, and the transition of AI products into new and existing fielded programs,” according to the GSA news release.
“The delivered AI products will leverage the power of DoD data to enable a transformational shift across the Department that will give the U.S. a definitive information advantage to prepare for future warfare operations,” the release said.
The contract will support the JAIC’s new joint warfighting mission initiative, launched earlier this year. The initiative includes “Joint All-Domain Command and Control; autonomous ground reconnaissance and surveillance; accelerated sensor-to-shooter timelines; operations center workflows; and deliberate and dynamic targeting solutions,” said JAIC spokesperson Arlo Abrahamson told C4ISRNET in January.
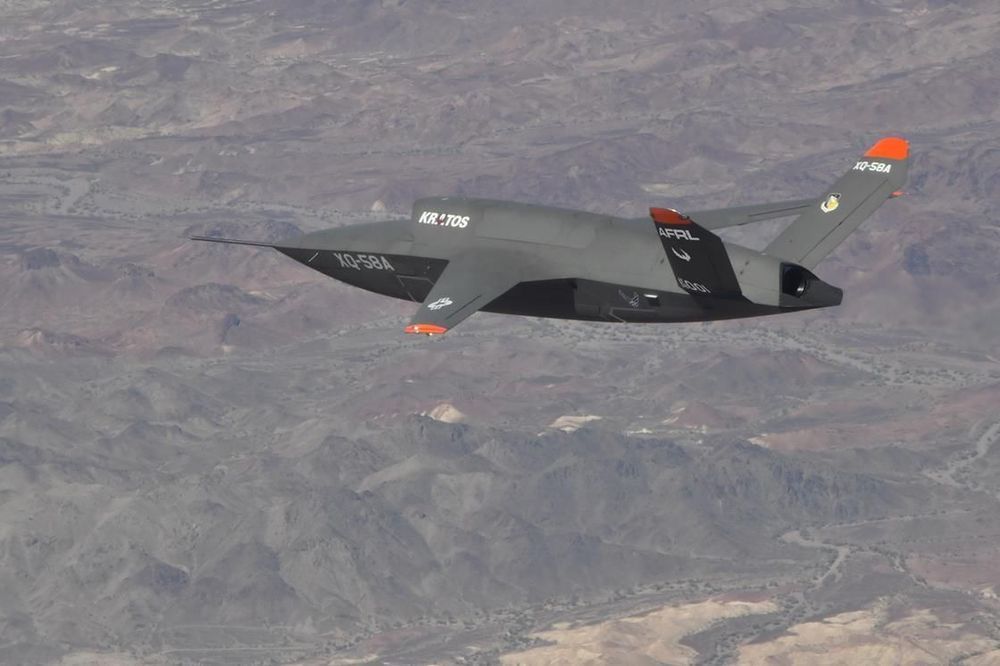

The US Air Force (USAF) has launched a competition to design the artificially intelligent software, called Skyborg, that would control its planned fleet of loyal wingman unmanned air vehicles (UAV).
The service intends to grant indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity contracts worth $400 million per awardee to develop the software and related hardware, it says in a request for proposals released on 15 May. The USAF is looking for technical and cost proposals from companies by 15 June 2020 and intends to award multiple companies contracts, though it may award just one contract or no contracts, based on proposals.