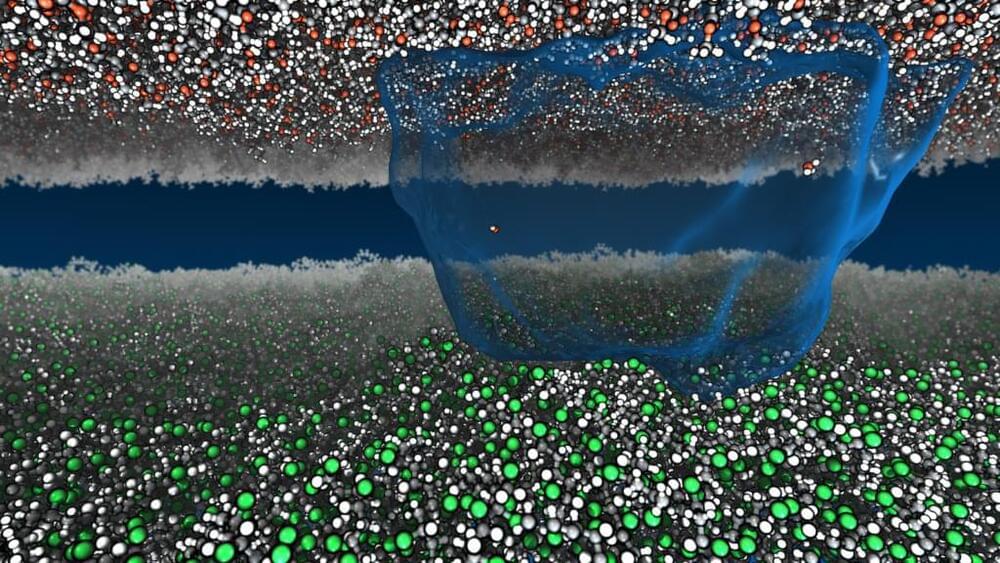
Now Princeton researchers have sparked new life into static. Using millions of hours of computational time to run detailed simulations, the researchers found a way to describe static charge atom-by-atom with the mathematics of heat and work. Their paper appeared in Nature Communications on March 23.
The study looked specifically at how charge moves between materials that do not allow the free flow of electrons, called insulating materials, such as vinyl and acrylic. The researchers said there is no established view on what mechanisms drive these jolts, despite the ubiquity of static: the crackle and pop of clothes pulled from a dryer, packing peanuts that cling to a box.
“We know it’s not electrons,” said Mike Webb, assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering, who led the study. “What is it?”