Non-destructive testing allows engineers to evaluate the integrity of structures such as pipelines, tanks, bridges, and machinery without dismantling them. Conventional approaches rely on loudspeakers, lasers, or electric sparks. While effective, these systems can be difficult or dangerous to use in flammable or confined areas and require considerable power to function effectively.
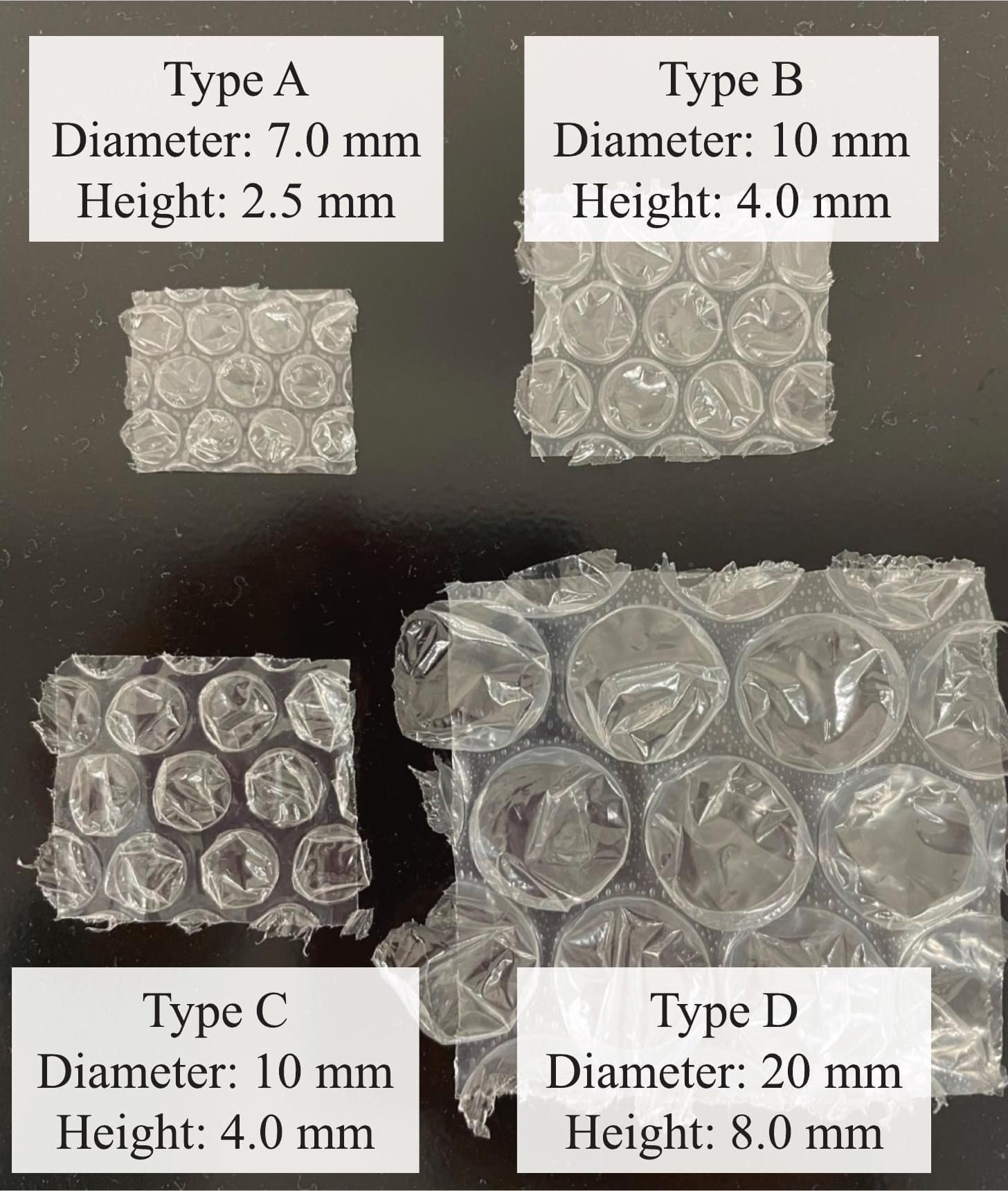
Now, a new study from Japan, available online in Measurement, shows how a common packaging material can replace power-hungry devices in non-destructive testing. The team, led by Professor Naoki Hosoya, along with Shuichi Yahagi from Tokyo City University, Toshiki Shimizu and Seiya Inadera from the Shibaura Institute of Technology, and Itsuro Kajiwara of Hokkaido University, found a simple way to test pipes for hidden flaws by using bubble wrap.
The researchers discovered that the sharp crack of a bubble burst can be a viable substitute for the expensive, energy-dependent tools usually employed in non-destructive testing. The researchers claim the method can detect objects inside a pipe within a 2% error margin, without requiring electricity or heavy equipment.