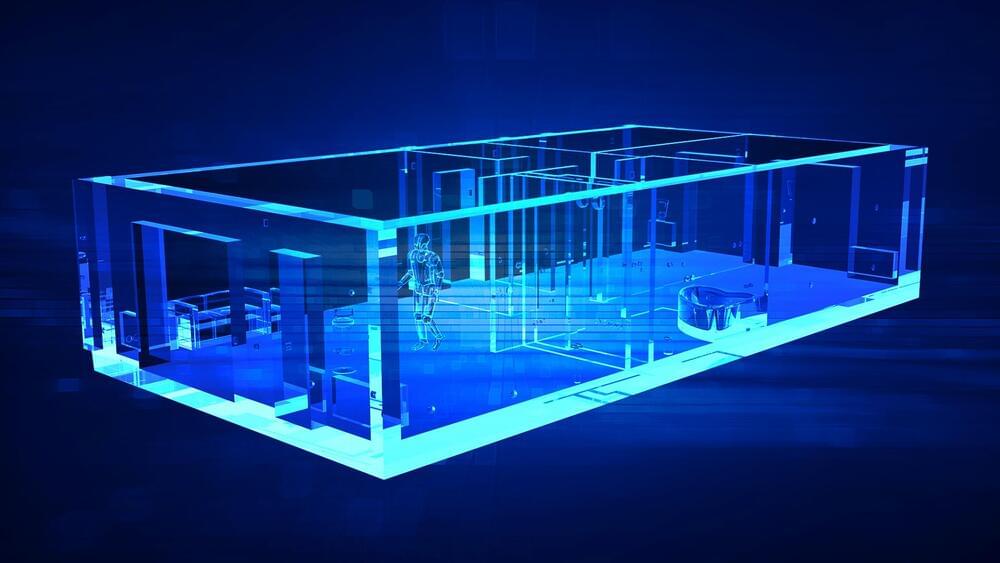
The method detects all the objects in the room and cancels out the static objects.
Researchers have been working on ways to “see” people without using cameras or expensive LiDAR hardware for years. In 2013, a team of researchers at MIT found a way to use cell phone signals to see through walls. In 2018, another MIT team used WiFi to detect people in another room and translate their movements into walking stick figures. Now, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Waterloo are advancing our ability to see through walls using WiFi.
Sauliakas/iStock.
The technology works by sending a low-powered WiFi signal through a wall, which reverberates around the room. It detects all the objects in the room, cancels out the static objects, and when the signal bounces back, uses the reflection of moving objects to generate a radar-like image. It can work through standard drywall, wooden fences, and even concrete walls, though the range and accuracy depend on the type of wall.