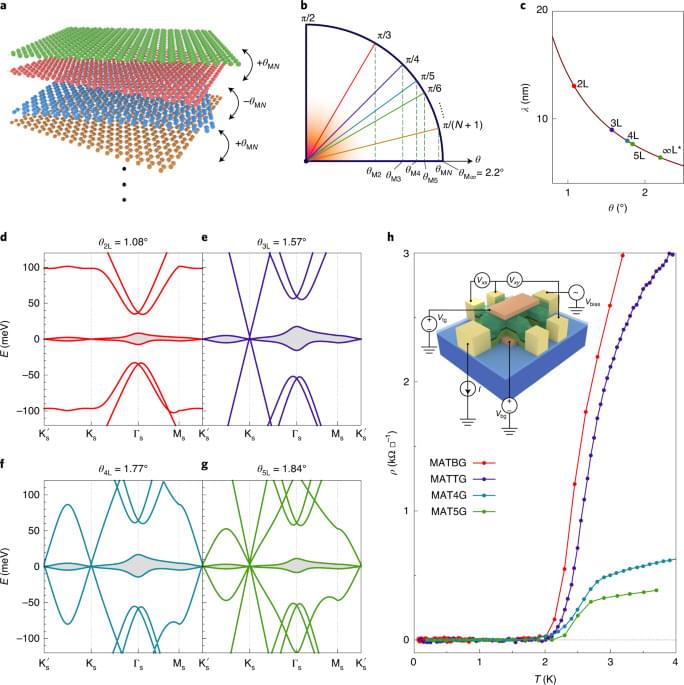
When an ordinary electrical conductor—such as a metal wire—is connected to a battery, the electrons in the conductor are accelerated by the electric field created by the battery. While moving, electrons frequently collide with impurity atoms or vacancies in the crystal lattice of the wire, and convert part of their motional energy into lattice vibrations. The energy lost in this process is converted into heat that can be felt, for example, by touching an incandescent light bulb.