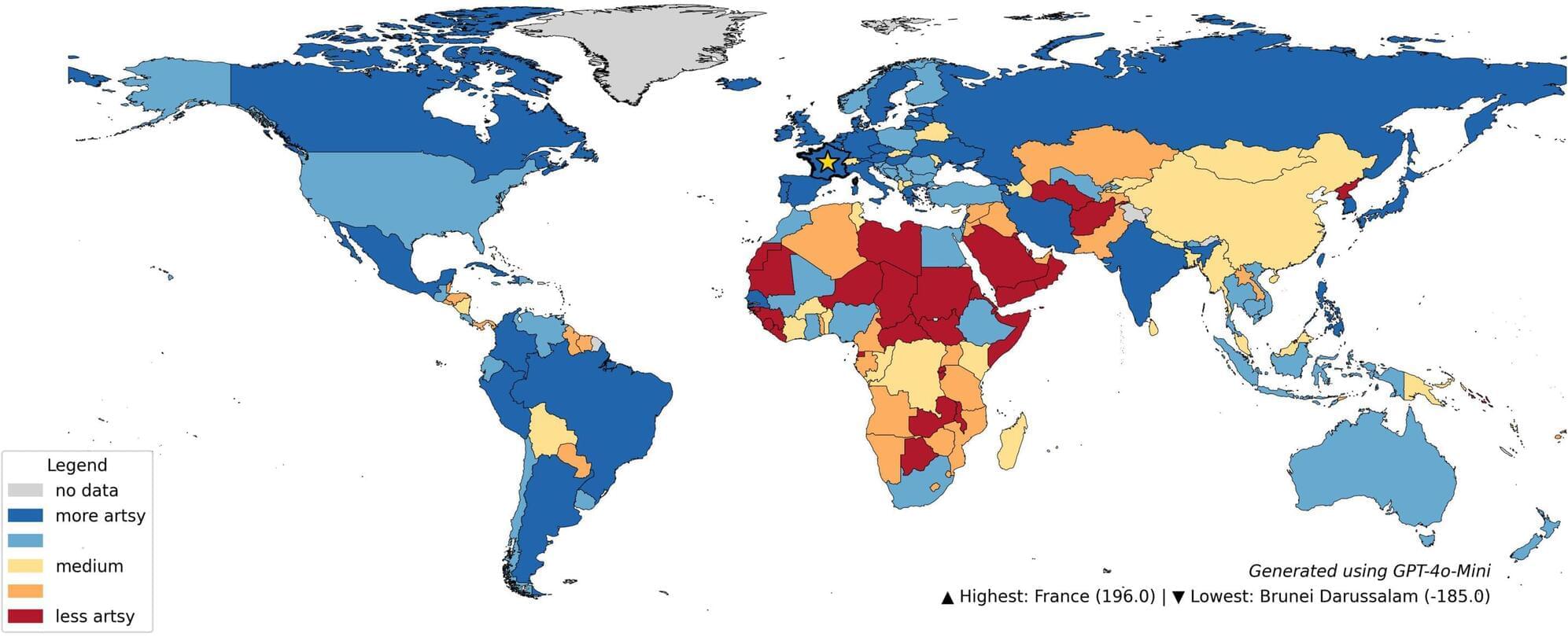
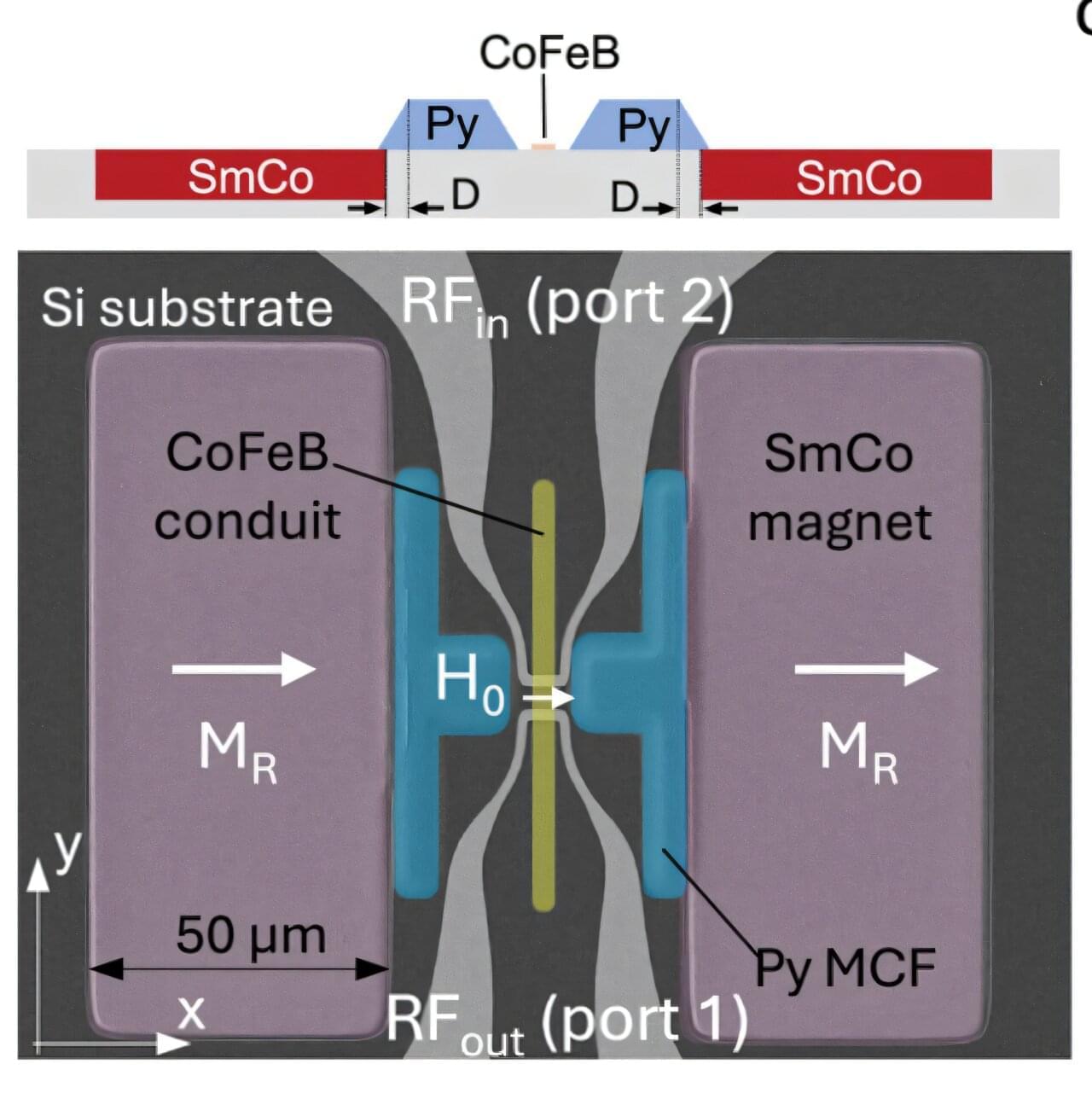
At first glance, some scientific research can seem, well, impractical. When physicists began exploring the strange, subatomic world of quantum mechanics a century ago, they weren’t trying to build better medical tools or high-speed internet. They were simply curious about how the universe worked at its most fundamental level.
Yet without that “curiosity-driven” research—often called basic science—the modern world would look unrecognizable.
“Basic science drives the really big discoveries,” says Steve Kahn, UC Berkeley’s dean of mathematical and physical sciences. “Those paradigm changes are what really drive innovation.”