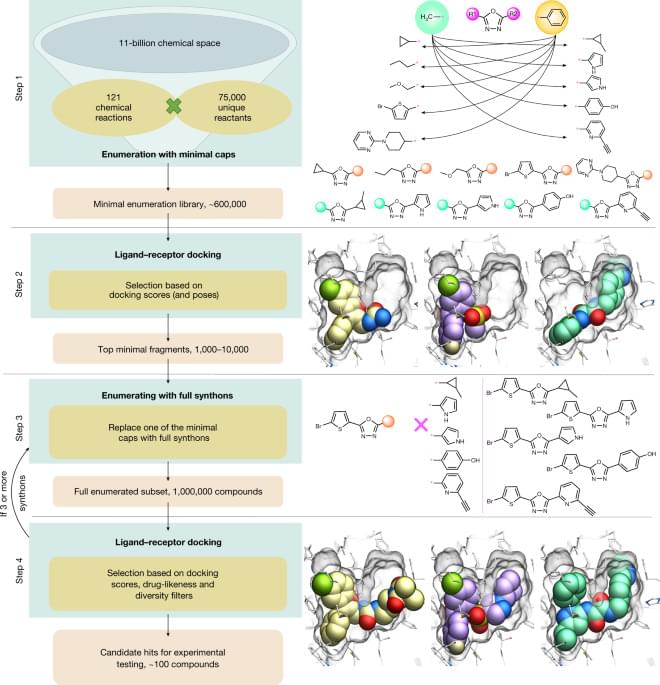
“This trial has changed the lives of people with mesothelioma, allowing us to live longer,” said one of the patients who benefited from the drug. The 80-year-old, who wished to remain anonymous, won compensation from his former employer after being exposed to asbestos in a factory in the 1970s.
He was given four months to live, but thanks to the trial is still alive five years later. “I have five grandchildren and two great-grandchildren now – I wouldn’t want to miss all that,” he said.
The breakthrough is significant, experts say, because mesothelioma has one of the lowest survival rates of any cancer. The new drug, ADI-PEG20 (pegargiminase), is the first of its kind to be successfully combined with chemotherapy in 20 years.