Tokamak Energy has announced a more efficient design for the cryogenic electronics in fusion reactors. This provides a 50% reduction in the power needed for the cooling of high-temperature superconducting magnets.
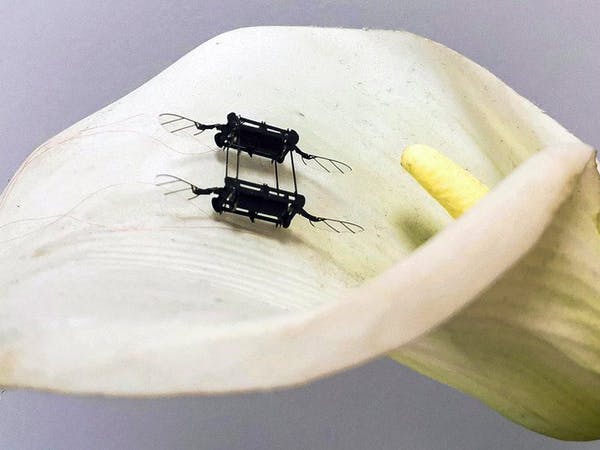



Bill Gates’ multibillion-dollar clean-tech initiative Breakthrough Energy Ventures has completed a $65 million funding round for the reusable rocket developer called Stoke Space, according to a Wednesday press release.
So don’t look away, because you might miss the makings of humanity’s future.
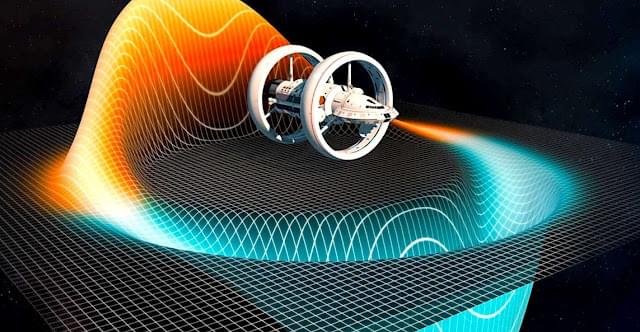
A team from the Limitless Space Institute (LSI), funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and led by Dr. Harold “Sonny” White, a former NASA specialist, pioneer in warp drive or warp drive, has reported that he has discovered a veritable warp bubble in the real world. The event marks a breakthrough for scientists trying to develop a spacecraft capable of going faster than light.
The concept offers a glimpse into the future that premium wine growers with narrow vineyards can aspire to.
Breakthrough Starshot’s ultra-lightweight spacecraft will have to travel four light-years to reach Alpha Centauri. To put it another way, our nearest neighboring star system is a mind-shattering 40,208,000,000,000 (40 trillion) km away from Earth.
As a point of reference, our fastest and most reliable technology today for long-range space travel is the ion thruster, which is powering NASA’s DART mission to a nearby asteroid at speeds of 15,000 mph (24,000 km/h). However, according to NASA, with the ion thruster, it would take 18,000 years, or approximately 2,700 human generations, to get to Alpha Centauri.
Impressively, the Breakthrough Starshot team believes its spacecraft, with the help of lasers located on Earth, will be able to reach unprecedented speeds, allowing it to travel the distance to Alpha Centauri in only 20 years. If it does reach its destination, the probe spacecraft will then send back the first-ever images taken from another solar system, allowing a never-before-seen window to distant planets that may or may not resemble Earth.
This year has witnessed a breakout for India’s startups. Companies going public in 2021 have raised record cash. But they also face unique challenges to grow even bigger.
For exclusive insights from Bloomberg’s technology reporters around the world, sign up for Fully Charged, a daily newsletter from Bloomberg Technology: https://www.bloomberg.com/account/newsletters/technology?utm…=quicktake.
#India+ #Tech #BloombergQuicktake.
——-
Like this video? Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/Bloomberg?sub_confirmation=1
Become a Quicktake Member for exclusive perks: https://www.youtube.com/bloomberg/join.
QuickTake Originals is Bloomberg’s official premium video channel. We bring you insights and analysis from business, science, and technology experts who are shaping our future. We’re home to Hello World, Giant Leap, Storylines, and the series powering CityLab, Bloomberg Businessweek, Bloomberg Green, and much more.
Subscribe for business news, but not as you’ve known it: exclusive interviews, fascinating profiles, data-driven analysis, and the latest in tech innovation from around the world.


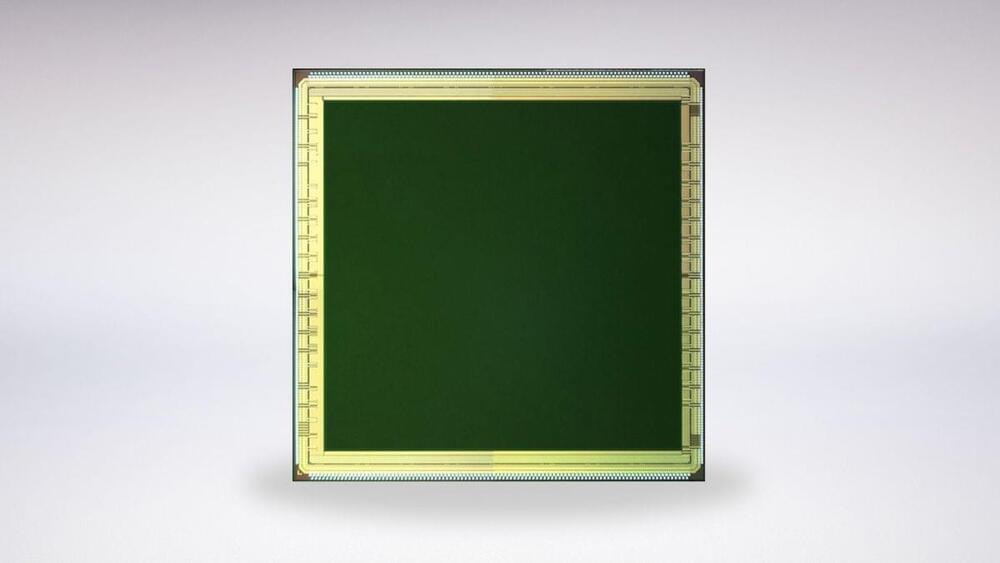
On Friday, Alibaba Cloud announced in a social media post that its DAMO Academy has successfully developed a 3D stacked In-Memory Computing (IMC) chip.
Alibaba Cloud claims this is a breakthrough that can help overcome the von Neumann bottleneck, a limitation on throughput caused by the standard personal computer architecture. It meets the needs of artificial intelligence (AI) and other scenarios for high bandwidth, high capacity memory and extreme computing power. In the specific AI scenario tested by Alibaba, the performance of the chip is improved by more than 10 times.
With the outbreak of AI applications, the shortcomings of the existing computer system architecture are gradually revealed. The main problems are that, on the one hand, processing data brings huge energy consumption. Under the traditional architecture, the power consumption required for data transmission from memory unit to computing unit is about 200 times of that of computing itself, so the real energy consumption and time used for computing are very low.