Quantum computers hold great promise for exciting applications in the future, but for now they keep presenting physicists and engineers with a series of challenges and conundrums. One of them relates to decoherence and the errors that result from it: bit flips and phase flips. Such errors mean that the logical unit of a quantum computer, the qubit, can suddenly and unpredictably change its state from “0” to “1,” or that the relative phase of a superposition state can jump from positive to negative.
These errors can be held at bay by building a logical qubit out of many physical qubits and constantly applying error correction protocols. This approach takes care of storing the quantum information relatively safely over time. However, at some point it becomes necessary to exit storage mode and do something useful with the qubit—like applying a quantum gate, which is the building block of quantum algorithms.
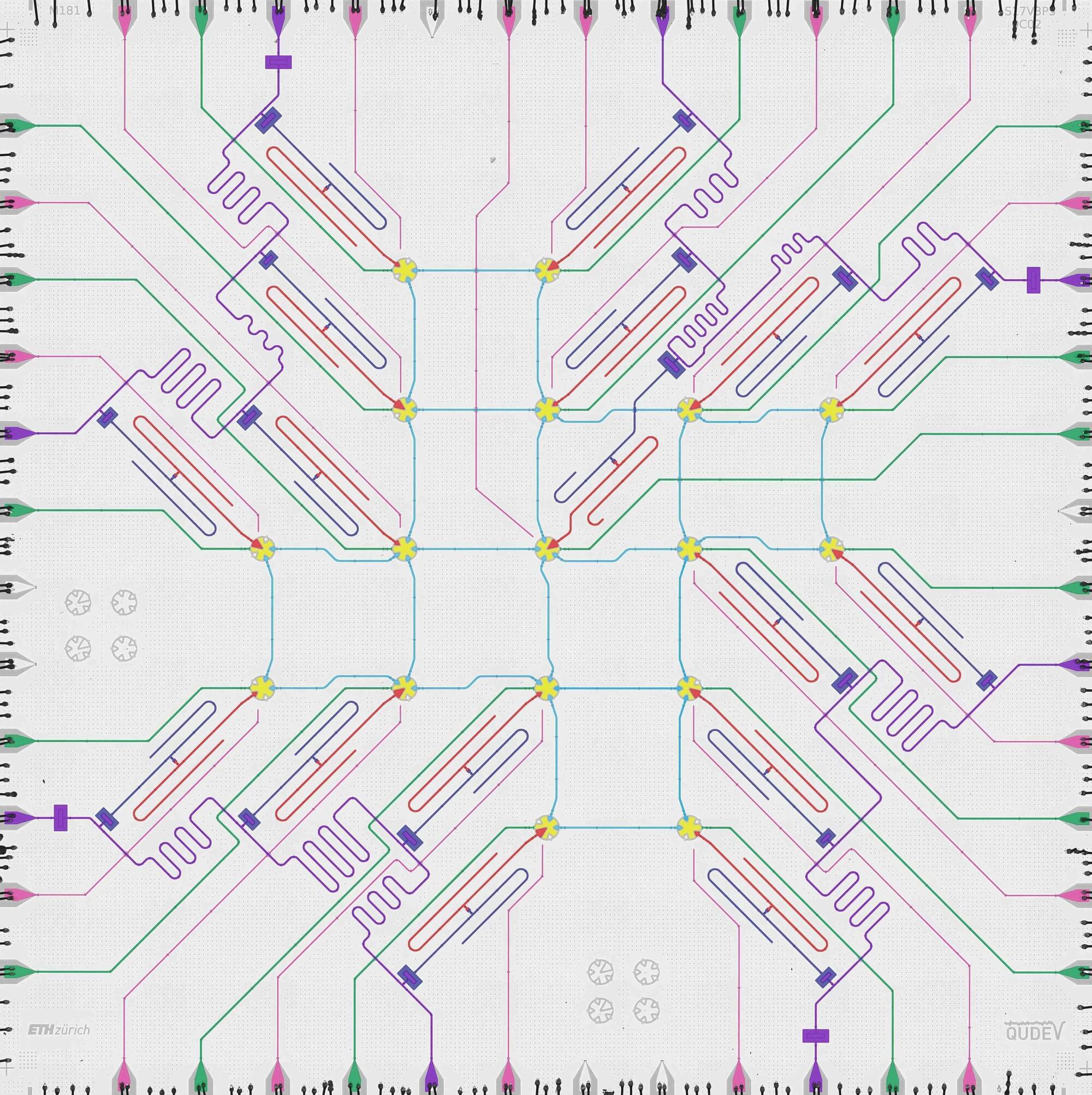
The research group led by D-PHYS Professor Andreas Wallraff, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the theory team of Professor Markus Müller at RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich, has now demonstrated a technique that makes it possible to perform a quantum operation between superconducting logical qubits while correcting for potential errors occurring during the operation. The researchers have just published their results in Nature Physics.