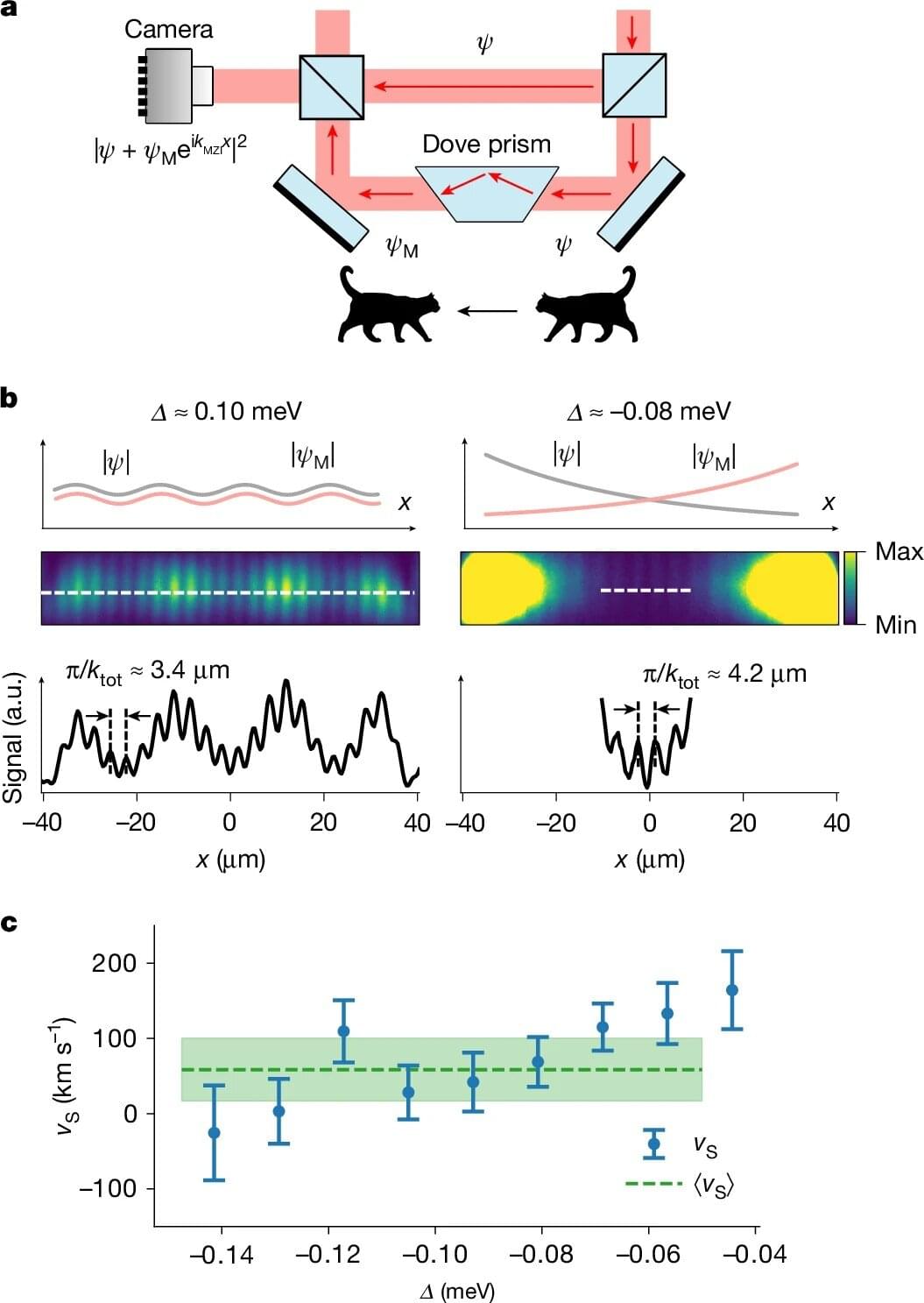
With so many people using devices that can be connected to the internet, reliably securing wireless communications and protecting the data they are exchanging is of growing importance. While computer scientists have devised increasingly advanced security measures over the past decades, the most effective techniques rely on complex algorithms and intensive computations, which can consume a lot of energy.
Researchers at Peking University, Southeast University, University of Sannio and other institutes recently introduced a new approach for securing communications both effectively and energy-efficiently, which relies on a reconfigurable metasurface with properties that are modulated by chaotic patterns.
This approach, outlined in a paper published in Nature Communications, is based on an idea conceived by the senior authors Vincenzo Galdi, Lianlin Li and Tie Jun Cui, who oversaw the project. The idea was then realized at Peking University and Southeast University by junior authors JiaWen Xu Menglin Wei and Lei Zhang.