Analog computers are systems that perform computations by manipulating physical quantities such as electrical current, that map math variables, instead of representing information using abstraction with discrete binary values (i.e., 0 or 1), like digital computers.
While analog computing systems can perform well on general-purpose tasks, they are known to be susceptible to noise (i.e., background or external interferences) and less precise than digital devices.
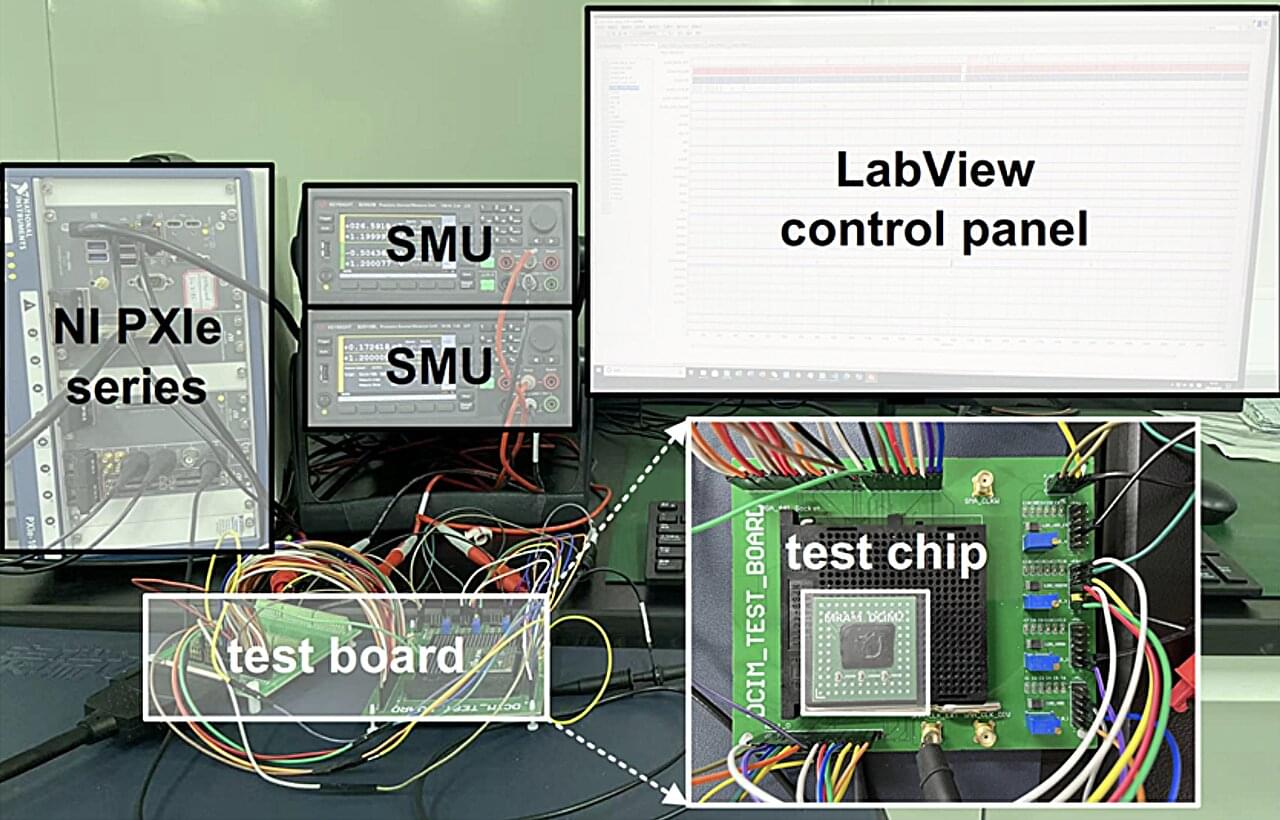
Researchers at Peking University and the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Integrated Circuits have developed a scalable analog computing device that can solve so-called matrix equations with remarkable precision. This new system, introduced in a paper published in Nature Electronics, was built using tiny non-volatile memory devices known as resistive random-access memory (RRAM) chips.