from Erik Wernquist
Wanderers — a short film by Erik Wernquist from Erik Wernquist on Vimeo.
Quoted: “If you understand the core innovations around the blockchain idea, you’ll realize that the technology concept behind it is similar to that of a database, except that the way you interact with that database is very different.
The blockchain concept represents a paradigm shift in how software engineers will write software applications in the future, and it is one of the key concepts behind the Bitcoin revolution that need to be well understood. In this post, I’d like to explain 5 of these concepts, and how they interrelate to one another in the context of this new computing paradigm that is unravelling in front of us. They are: the blockchain, decentralized consensus, trusted computing, smart contracts and proof of work / stake. This computing paradigm is important, because it is a catalyst for the creation of decentralized applications, a next-step evolution from distributed computing architectural constructs.
Read the article here > http://startupmanagement.org/2014/12/27/the-blockchain-is-th…verything/

Written By: Jason Dorrier — Singularity Hub
Why blow billions of dollars on space exploration when billions of people are living in poverty here on Earth?
You’ve likely heard the justifications. The space program brings us useful innovations and inventions. Space exploration delivers perspective, inspiration, and understanding. Because it’s the final frontier. Because it’s there.
What you haven’t heard is anything to inspire a sense of urgency. Indeed, NASA’s struggle to defend its existence and funding testifies to how weak these justifications sound to a public that cares less about space than seemingly more pressing needs.
Quoted: “Ethereum will also be a decentralised exchange system, but with one big distinction. While Bitcoin allows transactions, Ethereum aims to offer a system by which arbitrary messages can be passed to the blockchain. More to the point, these messages can contain code, written in a Turing-complete scripting language native to Ethereum. In simple terms, Ethereum claims to allow users to write entire programs and have the blockchain execute them on the creator’s behalf. Crucially, Turing-completeness means that in theory any program that could be made to run on a computer should run in Ethereum.” And, quoted: “As a more concrete use-case, Ethereum could be utilised to create smart contracts, pieces of code that once deployed become autonomous agents in their own right, executing pre-programmed instructions. An example could be escrow services, which automatically release funds to a seller once a buyer verifies that they have received the agreed products.”
Read Part One of this Series here » Ethereum — Bitcoin 2.0? And, What Is Ethereum.
Read Part Two of this Series here » Ethereum — Opportunities and Challenges.
Read Part Three of this Series here » Ethereum — A Summary.
Preamble: Bitcoin 1.0 is currency — the deployment of cryptocurrencies in applications related to cash such as currency transfer, remittance, and digital payment systems. Bitcoin 2.0 is contracts — the whole slate of economic, market, and financial applications using the blockchain that are more extensive than simple cash transactions like stocks, bonds, futures, loans, mortgages, titles, smart property, and smart contracts
Bitcoin 3.0 is blockchain applications beyond currency, finance, and markets, particularly in the areas of government, health, science, literacy, culture, and art.
Read the article here » http://ieet.org/index.php/IEET/more/swan20141110
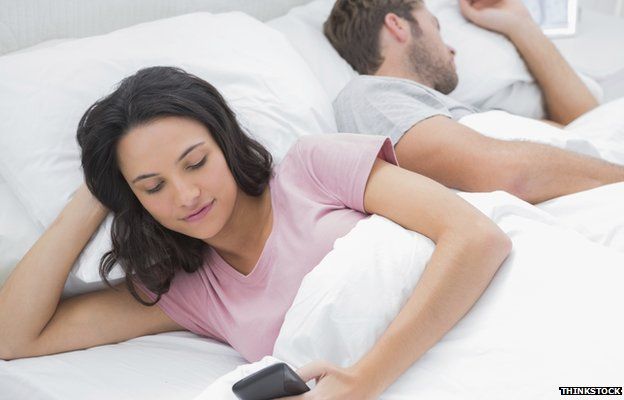

— BBC News
Communications regulator Ofcom said UK adults spend an average of eight hours and 41 minutes a day on media devices, compared with the average night’s sleep of eight hours and 21 minutes.
Almost four hours a day are spent watching TV according to Ofcom’s survey of 2,800 UK adults and children.
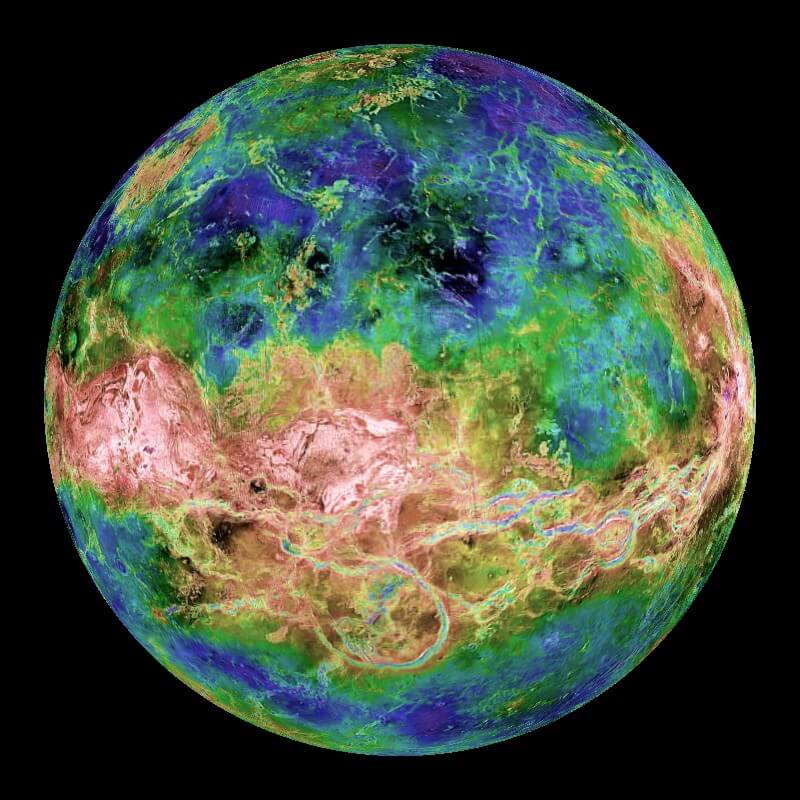
Terra Forming Venus & Mars by leveraging Asteroids
Inspired by: Lifeboat Foundation
Both Mars and Venus can be terra-formed to provide Earth-like gravity and atmospheres; Venus with an effort of about 100 years to terra-form the atmosphere, and Mars with an effort of about 2,000 years to terra-form the atmosphere. These are both potentially realized through the use of systems of solar sails. Asteroids provide many of the resources needed to seed related development.
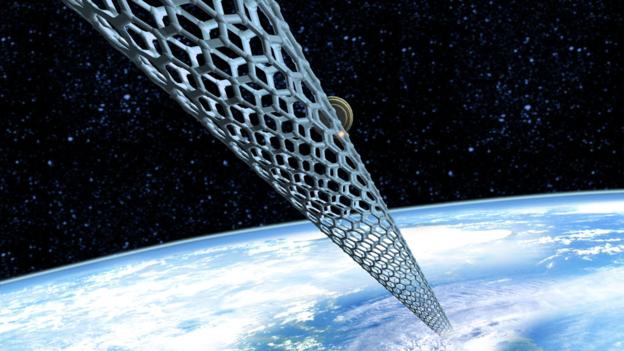
Conceptual Space Elevator
Mars is not the closest match to Earth within reach, Venus is. Venus is 90% of the mass of Earth and can hold an atmospheric pressure that can support human life after terra-forming the atmosphere.
Mars has 38% of the gravity of Earth and will never be able to support the atmospheric pressure needed to sustain human life without pressurized suits. The current atmosphere on Mars is like living at 125,000 feet above sea level here on Earth and has very limited resources in the atmosphere. The Sun continues to whisk away the atmosphere, and there is no protection from ionizing radiation. On Mars we will be required to live in pressurized caverns and bio-spheres to sustain life.

So why not just live in ventilated caverns here on Earth?
Mars is needed as an absolute necessity to test Space Elevator deployment before deploying a space elevator from space. The following details a potential deployment methodology that is ecosystem friendly, provides for recycling precious resources, and provides low-cost interplanetary transport.
The on-going Venus missions can remain in space and use the space-built harvesting of resources to provide sustainable life-long enterprise in space for hundreds of thousands of people. People who provide services and resource processing over the 100 years of terra-forming Venus, and the 2,000 years needed for terra-forming Mars. Provided the total system proposed, billions of people will support diverse industries related to the terra-forming of Venus, then Mars, then … the building of other planets.
There are methods that can be developed to fraction larger planets into smaller planets, so that our solar system can potentially sustain 10 or more Earth-like planets in our Solar system. All without using fossil fuels for propulsion. Hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, methane, and other hydrocarbons used and converted to support diversity of life instead of wasted dilution as fuel byproducts lost and polluting space. Pollutants that cause frictional drag when a spacecraft impacts the pollutants and causing a change in course of spacecraft and asteroids and the needed extra fuel to compensate, and more fuel pollutants causing more expenditure of fuel.
Terra-forming Venus from Space
Venus can have its’ atmosphere terra-formed from space. The same technology to terra-form the Venus atmosphere creates both active Weather Control for Venus and Earth. The same structures can be used for solar sails to transfer people and resources between the inner planets and provide maintenance transport. The same systems can help provide for terra-watts of solar energy based utilities. All without fossil fuels.
Currently the atmosphere of Venus is very hot at the surface (molten lead temperatures), is poisonous to humans, and has a surface pressure about 90 times that of Earth. This can ALL feasibly be terra-formed to Earth-like conditions from space.
By creating large systems of solar sails, these solar energy based transports use large rotating sails that can also be used as “shade structures”. By positioning the shade structures between the Sun and Venus in elliptical orbits, this cools the atmosphere. As cooling continues, condensing vapors rain down upon the planet surface and related chemical interactions create systems of molecules on the surface.
These systems of molecules if strategically manipulated, provide the eventual materials to support vegetation and microbial life. Through pervasive influence, an Earth-like ecosystem is produced.
Being able to terra-form from space is desirable because of the costs and dangers related to transport to and from the surface.
Catalysts and energy differentials of the Venus atmosphere at different phases while cooling can convert the CO2 to oxygen and hydrocarbons. The atmospheres of both Mars and Venus are 97% CO2, but Venus has more atmospheric components to sustain catalyst based conversions.
The conversion and cooling processes lower the atmosphere pressures to designed final pressures and related atmospheric chemical distributions.
Systems related to Terra-Forming Venus
http://www.orionsarm.com/fm_store/TerraformingVenusQuickly.pdf
http://www.academia.edu/5367728/Terraforming_Venus_A_Synthes…Approaches
http://global-energy-system.pbworks.com
Sources of water:
http://nextbigfuture.com/2014/01/unlocking-solar-system-with-water-from.html
Moving Water Asteroids to Venus
Identifying and Seeding broad enterprise related to space-based initiatives
Pulverizing hydrogen rich asteroids and seeding cooled Venus atmosphere
https://journals.uair.arizona.edu/index.php/maps/article/viewFile/14865/14836
Seeding H2O catalysts
http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Physical_Chemistry/Kinetics/Case…Converters
Recurrent catalytic processes
Creating fuels from CO2
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ie3007962
There are better systems, but these just support an example.
Space elevator Deployed from Space
Terra-forming Venus does not mean that Mars is not an important initial pathway to start terra-forming planetoids. Mars is critical for testing the viability of deploying Space Elevators. Mars has an atmosphere (thin) and significant gravity (but much less than Earth) that can be used to test the stresses and predicted nature of all parts to attain a stable space deployed space elevator. Until the Space Elevator deployed from space is tested on Mars, absolutely no one on Earth should want an asteroid steered anywhere near close to Earth.
Mars has the potential of having rich ore deposits and mineral compounds that do not exist here on Earth. For processing that needs gravity to facilitate processes, Mars may provide a unique environment in that region of space to support processing and manufacturing. But as yet, there are no fuels available on Mars to get off the planet. The depletion of Earth’s resources are presently necessary to be able to escape the Mars gravity to return to Earth.
The mining of the Moons of Saturn and Jupiter during the process of merging them with Mars is facilitated by producing space deployed Space Elevators. Nano-tube cables produced in space that are attached between two shaped and sized asteroids. The system is precisely rotated on a controlled trajectory so that one asteroid is controllably lowered to anchor the space elevator tether. A cable climbing tractor then controllably raises and lowers materials to and from planetoids.
The building of space elevators using this process may become the initial main industry for early missions. The combination of a planet that has numerous space elevators (every country; or shared by several small countries) and the low-cost solar sail structures described, provides an inexpensive means for almost any country to carry-on interplanetary space-based commerce.
To prevent contributing to, or otherwise disturbing the natural wobble of the Earth over long periods, the positioning of space elevators needs to be logically determined in advance. As economic systems change, small countries not previously thought to have the potential to engage in a space-based economy may purchase a space elevator. To prevent global ecological destruction of micro-ecosystems (diversity of life that contributes to overall resistance to pervasive pathogens), a balancing in support of our stable wobble must consider potentially positioning space elevators in locations not intended to be used, to position a space elevator where it is desired.
Delivering rich ore asteroids to the surface of the Earth
A slightly different version of the space elevator provides a means of delivering and extracting large masses from Earth’s gravity. In largely the same manner that a space elevator is created using the Bola method of deploying space elevators, large amounts of mass can both be deposited and extracted without the use of fossil fuels.
A heavier built carbon nano-tube cable delivers an ore-rich asteroid to Earth as an anchor. The tether is transferred from the anchor to the payload to be extracted from Earth. The near-orbit tethered mass in space has a latching/hinge mechanism where another carbon nano-tube cable that extends out into space at some angle from tangent to the Earth’s atmosphere to a far-orbit mass with twice the total mass of both the near-orbit tethered mass and anchor. At the mid-point between the far-orbit and near-orbit tethered masses, is a latch/hinge structure that a larger asteroid attaches to and pulls with increasing velocity (not sudden stresses) both the anchor payload and far-orbit masses along a trajectory out toward a delivery destination. The mid-point attached acceleration method is necessary to prevent catastrophic failure forces from building up during the extraction process.
This method of using asteroids and solar sail structures provides for low-cost interplanetary commerce.
Extending commerce to the resources of the Kuiper Belt.
The Kuiper Belt has significant volitile gas resources. Volitile elements are frozen. There are vast resources of water and hydrocarbons to use for terra-forming Venus, Mars and other planets that we build. There is presently 20 to 200 times as much known mass in the Kuiper Belt as there is in the Asteroid Belt. These resources provide elements needed to support biological life.
Another reason for providing a presence in the Kuiper Belt is to detect masses on a trajectory toward Earth. We want masses to be on a trajectory that spirals into Earth’s orbit around the Sun so we can harvest resources, not tangent to Earth’s orbit where an impact causes potential global extinction from impact on Earth. The Kuiper Belt is expansive. By having a presence we can not just detect impending events, we can cultivate them into beneficial mining outcomes.
Automated systems of solar sails can systematically guide thousands of objects on trajectories that will eventually form an orbit around the Sun between Venus and Earth. However, because of the reduced photon pressures from the Sun the time needed is much longer. But, tend to stop the orbit of anything around the Sun and it will start moving toward the Sun. The timing and trajectory within the complex gravitational fields of the solar system scheduled so that the trajectory and orbit entered never intersects Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Materials stored in its own orbit around the Sun between Venus and Earth. Accelerate the orbit to deliver it to Earth, slow the orbit to deliver it to Venus.
Ethics related to the deployment of Space Elevators
Space Elevator strands are quite small for human eye detection at a distance. The extreme hazards for flight safety and related economic upheaval related to space-based trade, must be taken into account and planned for in advance. Terrorists, either from intellectually deprived puppets of economic aggressors (undeclared economic coalitions that instigate destruction for self-serving purposes), or countries at war in dispute of access to natural resources, the danger is that a single person has the capacity to disrupt an entire nations primary source of economic sovereignty.
See http://eliminate-all-corruption.pbworks.com to see how global society can both Maximize Freedoms and at the same time Maximize Security, not having to sacrifice one to have the other. To include providing an environment to maximize economic development globally.
Realize that all science and technology based products are transitory; they only exist until something better comes along. Doors based upon latches and hinges have largely gone unchanged for many thousands of years. But with the potential tools of space-time manipulation at our near-future door step, the potential is that housing and doors may take on a form that is an entirely different form of technology; will producing living environments where doors and housing are not like anything we can presently reference physically. Perhaps a living space directly accessible without having to physically travel from anywhere. Transportation similarly may become unnecessary as physical movements evolve with other technological capabilities.
These changes in technology largely motivate the directions we choose to socially participate with others (money) to support development of related technologies.
Money is a social tool that provides the ability to efficiently connect resources and opportunities to act toward diverse pathways of development.
Evolving along a broadly sustainable pathway toward a set of desirable outcomes, the social processes incrementally change and use technology to generate the related economic processes; i.e. interconnected loops of cash flows.
For most, this is the primary importance of ethics, to broadly promote a sharing of resources and opportunities that overall deliver vast systems of mutually beneficial outcomes; global economic and time pervasive prosperity. This is the common short-sighted purpose of ethical consideration.
The longer-sighted purpose is to “Broadly promote the diversity of life”; only through diversity does plague-like conditions meet local barriers to prevent broad destruction (extinction events).
Space Elevators provide the opportunities to both create sustainable environments for humans, but also other species. If we focus upon creating environments just for human habitats, then a plague in the form of economic depression, biological virus, genetically evolved sterility .… will eventually cause the extinction of humans; in the not so distant future. If we ourselves desire to survive, and/or evolve, then required is that the environments we create are also broadly diverse to include every known form of life that has its’ boundaries limited by resources and synergy with other diverse forms of life.
Mining the Asteroids between Mars and Jupiter
The total mass of the asteroid belt is about 1/35th the size of our Moon. About 1/2 the total mass of the asteroid belt are in the four largest asteroids called Ceres, Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea. Most asteroids are one of three groups in composition: carbonaceous (C-type), silicate (S-type), and metal-rich (M-type). These are the primary purpose of
Terra-forming Mars from Space
Mars can be terra-formed to become an Earth-like eco-system, but it takes a more involved effort. With Earth’s present atmospheric components, the pressure on Mars would be too sparse to both prevent ionized losses of water introduced, and provide the pressures needed by humans to survive without a pressurized suit. By maneuvering three of the largest Moons of Jupiter (Ganymede, Europa, and Calisto) to merge with Mars on specific trajectories that incrementally bring Mars to a new sustainable orbit around the Sun, enough mass can be added to Mars to provide an atmospheric pressure needed to sustainably support human life and the related ecosystems. Moving Moons sounds far fetched, but the continuous force applied by solar sails to precisely cause a track through the gravity distributions imposed on the Moons, and not just the dominant influences (a form of finite element analysis), provides a practical method by which the Moons can be accelerated along intentional trajectories over long periods of time.
The Moons due to the gravitational fluctuations of Jupiter have sufficient friction to produce heat; and water is present. Therefore it is possible that life may be present. If so than this form of terra-forming is not ethically plausible because the evolution of those life forms and their potential future will be extinguished by the act of merging the Moon with Mars. There are other related ethical issues to consider.
Planetary bodies are considered sacred by many cultures, and the ethics related to inhabiting those planetary bodies is an ethical issue. Merging them becomes an even greater social issue.
But given a finding that life does not exist on the Moons, then as mass is merged with Mars and the orbit is changed to reflect a stable new orbit, then the crushing of those large masses together creates heat that must dissipate before providing a habitable environment for life. The act of crushing the last of three Moons, the water-rich Moon, with Mars is to produce an atmosphere. The crushing exposes core materials of all three Moons and Mars.
This process will produce a jagged landscape that will produce planetary quakes for millions of years. By reversing the process the non-uniform gravity of Jupiter can be used to accelerate the process of annealing the planetary structures. By moving Mars to orbit Jupiter, as Moons are merged in with Mars the gravitational forces can anneal the merged structures to largely stabilize them before the intentionally unstable orbit casts Mars out toward a new orbit around the Sun. The solar sail systems guiding the path of the now larger Mars to seek a stable orbit. The now larger Mars that is about the same size as Venus will have far less quakes and terra-forming the atmosphere provides the components needed for using catalysts to produce the needed balances in atmospheric and soil components.
Needed calculation will need to be done to determine the losses in atmosphere and chemical make-up due to the processes involved and the interaction with Jupiter’s annealing gravity influences. All of the incremental gravitational interactions of all solar system gravitational and electromagnetic influences will need to be modeled for millions of years so that long term stability is supported during all translations in mass.
The total process has continuous opportunities to harvest unique resources to use in support of the business systems needed to support a 2,000 year effort. Sixty generations of people continuously supporting a long term business initiative. Not as attractive as terra-forming Venus, but providing a third largely independent ecosystem within our solar system.
Maximizing the Diversity of Life in Independent Ecosystems
With three largely independent ecosystems, three forms of evolution can be promoted to provide diverse outcomes. For example, Mars can evolve technology based evolutionary systems that promote a diversity of life that is uniquely technology interconnected and dependent; technological evolution. Earth can largely remove its technology and dominantly provide support or the evolving of already established ecosystems and related animal and vegetation life; natural evolution. While Venus can support human-centric evolution; building Venus as the resources and imagination provide for the most interesting place for humans to live. While distributed out in space on asteroids, other planets, space stations… is a mix of all parts of the three independent ecosystems. The purpose of which is to sustainably support a maximized diversity of life.
Deploying Space Elevators from Space
The most expensive part of producing products for space based efforts, is the transport between the ground of planetary bodies and space. To deploy space elevators from Earth requires transporting large amounts of materials, and related burning of fossil fuels.
To deploy space elevators from space requires a source of carbon (atmosphere of Venus), a heat source (Sun), processing system (relatively small from Earth), and two small asteroids. By shaping and sizing two asteroids and connecting a fully developed nano-tube space elevator tractor cable between them, the two asteroids can incrementally be rotated around one another connected together by the nano-tube cable. The resulting rotating masses are carefully guiding in trajectory and rotation such that the counter rotation of one asteroid end entering the atmosphere slows rotation and gently transitions to the total system into geosynchronous orbit with the planetary body.
This business of creating space elevators can deploy space elevators throughout the solar system.
Care must be made to deploy mating space elevators balanced across the same hemisphere such that noticeable increasing planet wobble does not occur over long periods of time.
Synergy with Native American Robotics Mars Yard
NASA is funding an educational initiative to encourage students to engage STEM education. Employment opportunities in rural areas are very sparse. To prepare students for engaging in opportunities accessible through use of the internet, STEM programs are being taught. STEM is an acronym for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. More recently the effort has been to produce STEEM, or Science, Technology, Enterprise, Engineering, and Mathematics.
The Robotics Mars Yard is in a building with dimensions of 50 feet by 60 feet that intends to house automated system of robots and self-configuring landscape to be used by native American students throughout the United States. Simulators are to be built to allow most students, anywhere globally, to participate in related activities. Coursework already in use by teachers are intended to be modified to provide greater contact time with each student, and at the same time free instructor time so that they have more time to thoughtfully interact with the unique needs of each student.
The broad use of the Mars Yard is centered in its user interface, that matches form and function of most programming user interfaces. Students are able to engage programming beginning as early as Elementary School, and use the system throughout Post-Doctoral industry and related research efforts. Developing the ability to engage diverse related technologies, followed by developing the ability to produce market driven enterprise.
Contributors include Dr. Nader Vadiee (SIPI.edu), Dr. Larry Crumple (NM Museum Curator), Dr. Zhang (transportation science) … and a host of others.
Synergy with Lifeboat Foundation
Lifeboat Foundation (LF) at www.lifeboat.com is a non-profit organization dedicated to identifying and developing resources for mitigating mass extinction events. Those in review are currently considered to be existential because of low probability, but more often because of no current practical method of mitigation.
NASA recently selected Lifeboat Foundation as a contributor in an upcoming event to help provide insights related to asteroid centered enterprise in space.
ALL development requires sustainable business support or the effort never gets off the ground (pun intended), or the effort dies without significant useful outcomes. “Not” listed below are the concepts for business systems of development submitted to Lifeboat Foundation for review and potential inclusion in their managed effort with NASA.
What follows is my position piece for London’s FutureFest 2013, the website for which no longer exists.
Medicine is a very ancient practice. In fact, it is so ancient that it may have become obsolete. Medicine aims to restore the mind and body to their natural state relative to an individual’s stage in the life cycle. The idea has been to live as well as possible but also die well when the time came. The sense of what is ‘natural’ was tied to statistically normal ways of living in particular cultures. Past conceptions of health dictated future medical practice. In this respect, medical practitioners may have been wise but they certainly were not progressive.
However, this began to change in the mid-19th century when the great medical experimenter, Claude Bernard, began to champion the idea that medicine should be about the indefinite delaying, if not outright overcoming, of death. Bernard saw organisms as perpetual motion machines in an endless struggle to bring order to an environment that always threatens to consume them. That ‘order’ consists in sustaining the conditions needed to maintain an organism’s indefinite existence. Toward this end, Bernard enthusiastically used animals as living laboratories for testing his various hypotheses.
Historians identify Bernard’s sensibility with the advent of ‘modern medicine’, an increasingly high-tech and aspirational enterprise, dedicated to extending the full panoply of human capacities indefinitely. On this view, scientific training trumps practitioner experience, radically invasive and reconstructive procedures become the norm, and death on a physician’s watch is taken to be the ultimate failure. Humanity 2.0 takes this way of thinking to the next level, which involves the abolition of medicine itself. But what exactly would that mean – and what would replace it?
The short answer is bioengineering, the leading edge of which is ‘synthetic biology’. The molecular revolution in the life sciences, which began in earnest with the discovery of DNA’s function in 1953, came about when scientists trained in physics and chemistry entered biology. What is sometimes called ‘genomic medicine’ now promises to bring an engineer’s eye to improving the human condition without presuming any limits to what might count as optimal performance. In that case, ‘standards’ do not refer to some natural norm of health, but to features of an organism’s design that enable its parts to be ‘interoperable’ in service of its life processes.
In this brave new ‘post-medical’ world, there is always room for improvement and, in that sense, everyone may be seen as ‘underperforming’ if not outright disabled. The prospect suggests a series of questions for both the individual and society: (1) Which dimensions of the human condition are worth extending – and how far should we go? (2) Can we afford to allow everyone a free choice in the matter, given the likely skew of the risky decisions that people might take? (3) How shall these improvements be implemented? While bioengineering is popularly associated with nano-interventions inside the body, of course similarly targeted interventions can be made outside the body, or indeed many bodies, to produce ‘smart habitats’ that channel and reinforce desirable emergent traits and behaviours that may even leave long-term genetic traces.
However these questions are answered, it is clear that people will be encouraged, if not legally required, to learn more about how their minds and bodies work. At the same time, there will no longer be any pressure to place one’s fate in the hands of a physician, who instead will function as a paid consultant on a need-to-know and take-it-or-leave-it basis. People will take greater responsibility for the regular maintenance and upgrading of their minds and bodies – and society will learn to tolerate the diversity of human conditions that will result from this newfound sense of autonomy.
Among transhumanists, Nick Bostrom is well-known for promoting the idea of ‘existential risks’, potential harms which, were they come to pass, would annihilate the human condition altogether. Their probability may be relatively small, but the expected magnitude of their effects are so great, so Bostrom claims, that it is rational to devote some significant resources to safeguarding against them. (Indeed, there are now institutes for the study of existential risks on both sides of the Atlantic.) Moreover, because existential risks are intimately tied to the advancement of science and technology, their probability is likely to grow in the coming years.
Contrary to expectations, Bostrom is much less concerned with ecological suicide from humanity’s excessive carbon emissions than with the emergence of a superior brand of artificial intelligence – a ‘superintelligence’. This creature would be a human artefact, or at least descended from one. However, its self-programming capacity would have run amok in positive feedback, resulting in a maniacal, even self-destructive mission to rearrange the world in the image of its objectives. Such a superintelligence may appear to be quite ruthless in its dealings with humans, but that would only reflect the obstacles that we place, perhaps unwittingly, in the way of the realization of its objectives. Thus, this being would not conform to the science fiction stereotype of robots deliberately revolting against creators who are now seen as their inferiors.
I must confess that I find this conceptualisation of ‘existential risk’ rather un-transhumanist in spirit. Bostrom treats risk as a threat rather than as an opportunity. His risk horizon is precautionary rather than proactionary: He focuses on preventing the worst consequences rather than considering the prospects that are opened up by whatever radical changes might be inflicted by the superintelligence. This may be because in Bostrom’s key thought experiment, the superintelligence turns out to be the ultimate paper-clip collecting machine that ends up subsuming the entire planet to its task, destroying humanity along the way, almost as an afterthought.
But is this really a good starting point for thinking about existential risk? Much more likely than total human annihilation is that a substantial portion of humanity – but not everyone – is eliminated. (Certainly this captures the worst case scenarios surrounding climate change.) The Cold War remains the gold standard for this line of thought. In the US, the RAND Corporation’s chief analyst, Herman Kahn — the model for Stanley Kubrick’s Dr Strangelove – routinely, if not casually, tossed off scenarios of how, say, a US-USSR nuclear confrontation would serve to increase the tolerance for human biological diversity, due to the resulting proliferation of genetic mutations. Put in more general terms, a severe social disruption provides a unique opportunity for pursuing ideals that might otherwise be thwarted by a ‘business as usual’ policy orientation.
Here it is worth recalling that the Cold War succeeded on its own terms: None of the worst case scenarios were ever realized, even though many people were mentally prepared to make the most of the projected adversities. This is one way to think about how the internet itself arose, courtesy the US Defense Department’s interest in maintaining scientific communications in the face of attack. In other words, rather than trying to prevent every possible catastrophe, the way to deal with ‘unknown unknowns’ is to imagine that some of them have already come to pass and redesign the world accordingly so that you can carry on regardless. Thus, Herman Kahn’s projection of a thermonuclear future provided grounds in the 1960s for the promotion of, say, racially mixed marriages, disability-friendly environments, and the ‘do more with less’ mentality that came to characterize the ecology movement.
Kahn was a true proactionary thinker. For him, the threat of global nuclear war raised Joseph Schumpeter’s idea of ‘creative destruction’ to a higher plane, inspiring social innovations that would be otherwise difficult to achieve by conventional politics. Historians have long noted that modern warfare has promoted spikes in innovation that in times of peace are then subject to diffusion, as the relevant industries redeploy for civilian purposes. We might think of this tendency, in mechanical terms, as system ‘overdesign’ (i.e. preparing for the worst but benefitting even if the worst doesn’t happen) or, more organically, as a vaccine that converts a potential liability into an actual benefit.
In either case, existential risk is regarded in broadly positive terms, specifically as an unprecedented opportunity to extend the range of human capability, even under radically changed circumstances. This sense of ‘antifragility’, as the great ‘black swan’ detector Nicholas Taleb would put it, is the hallmark of our ‘risk intelligence’, the phrase that the British philosopher Dylan Evans has coined for a demonstrated capacity that people have to make step change improvements in their lives in the face of radical uncertainty. From this standpoint, Bostrom’s superintelligence concept severely underestimates the adaptive capacity of human intelligence.
Perhaps the best way to see just how much Bostrom shortchanges humanity is to note that his crucial thought experiment requires a strong ontological distinction between humans and superintelligent artefacts. Where are the cyborgs in this doomsday scenario? Reading Bostrom reminds me that science fiction did indeed make progress in the twentieth century, from the world of Karl Čapek’s Rossum’s Universal Robots in 1920 to the much subtler blending of human and computer futures in the works of William Gibson and others in more recent times.
Bostrom’s superintelligence scenario began to be handled in more sophisticated fashion after the end of the First World War, popularly under the guise of ‘runaway technology’, a topic that received its canonical formulation in Langdon Winner’s 1977 Autonomous Technology: Technics out of Control, a classic in the field of science and technology of studies. Back then the main problem with superintelligent machines was that they would ‘dehumanize’ us, less because they might dominate us but more because we might become like them – perhaps because we feel that we have invested our best qualities in them, very much like Ludwig Feuerbach’s aetiology of the Judaeo-Christian God. Marxists gave the term ‘alienation’ a popular spin to capture this sentiment in the 1960s.
Nowadays, of course, matters have been complicated by the prospect of human and machine identities merging together. This goes beyond simply implanting silicon chips in one’s brain. Rather, it involves the complex migration and enhancement of human selves in cyberspace. (Sherry Turkle has been the premier ethnographer of this process in children.) That such developments are even possible points to a prospect that Bostrom refuses to consider, namely, that to be ‘human’ is to be only contingently located in the body of Homo sapiens. The name of our species – Homo sapiens – already gives away the game, because our distinguishing feature (so claimed Linnaeus) had nothing to do with our physical morphology but with the character of our minds. And might not such a ‘sapient’ mind better exist somewhere other than in the upright ape from which we have descended?
The prospects for transhumanism hang on the answer to this question. Aubrey de Grey’s indefinite life extension project is about Homo sapiens in its normal biological form. In contrast, Ray Kurzweil’s ‘singularity’ talk of uploading our consciousness into indefinitely powerful computers suggests a complete abandonment of the ordinary human body. The lesson taught by Langdon Winner’s historical account is that our primary existential risk does not come from alien annihilation but from what social psychologists call ‘adaptive preference formation’. In other words, we come to want the sort of world that we think is most likely, simply because that offers us the greatest sense of security. Thus, the history of technology is full of cases in which humans have radically changed their lives to adjust to an innovation whose benefits they reckon outweigh the costs, even when both remain fundamentally incalculable. Success in the face such ‘existential risk’ is then largely a matter of whether people – perhaps of the following generation – have made the value shifts necessary to see the changes as positive overall. But of course, it does not follow that those who fail to survive the transition or have acquired their values before this transition would draw a similar conclusion.

Dylan Love — Business Insider
“Today there’s no legislation regarding how much intelligence a machine can have, how interconnected it can be. If that continues, look at the exponential trend. We will reach the singularity in the timeframe most experts predict. From that point on you’re going to see that the top species will no longer be humans, but machines.”
These are the words of Louis Del Monte, physicist, entrepreneur, and author of “The Artificial Intelligence Revolution.” Del Monte spoke to us over the phone about his thoughts surrounding artificial intelligence and the singularity, an indeterminate point in the future when machine intelligence will outmatch not only your own intelligence, but the world’s combined human intelligence too.