An existing drug currently used to treat glaucoma, altitude sickness, and seizures may also have the potential to prevent relapse in opioid use disorder, according to a study by researchers at University of Iowa Health Care. The work is published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
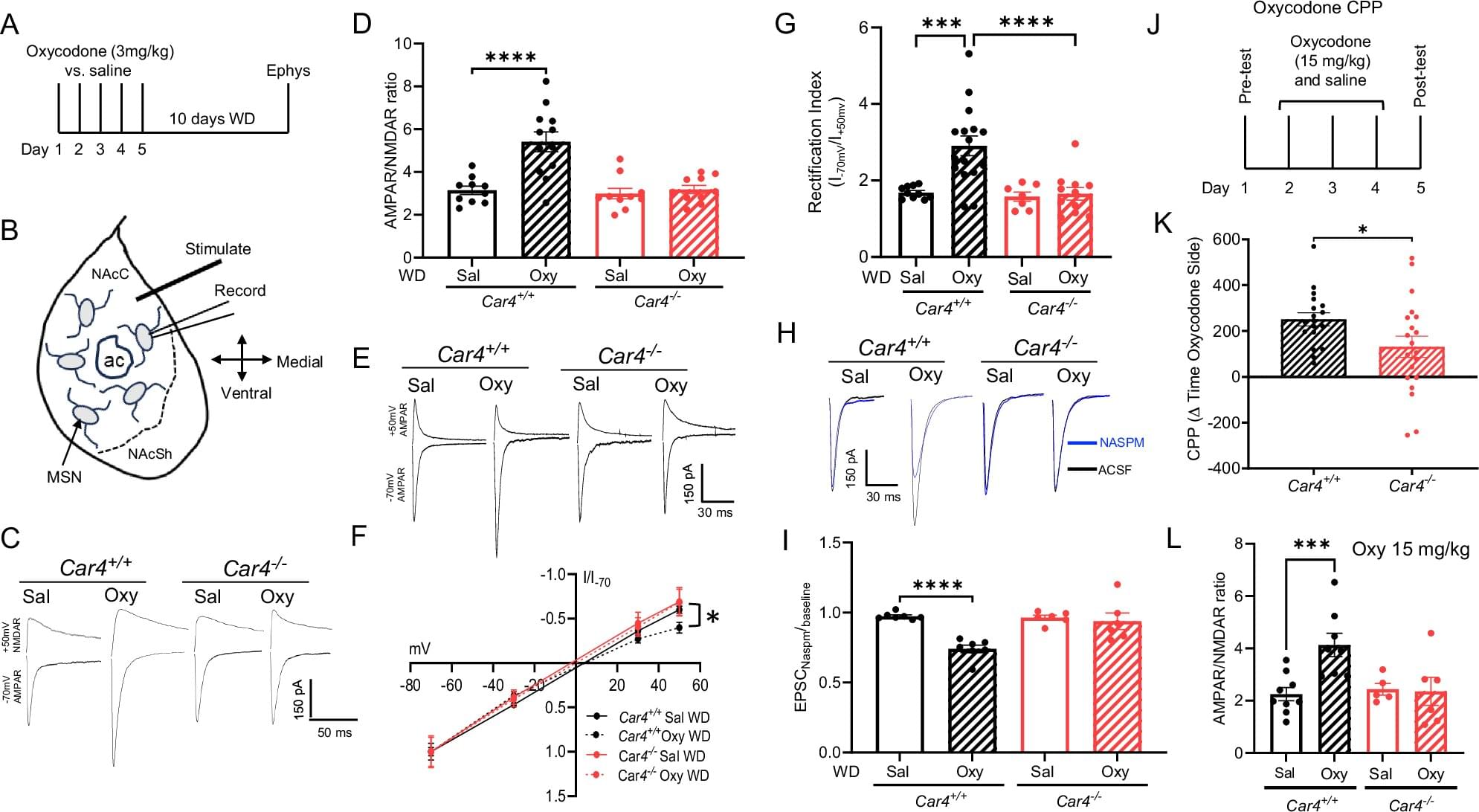
The UI researchers led by John Wemmie, MD, Ph.D., focused on the drug known as acetazolamide (AZD) because it blocks the activity of a brain enzyme called carbonic anhydrase 4 (CA4). Wemmie’s team had previously discovered that inhibiting CA4 in the whole brain, or just in its reward center (the nucleus accumbens), of mice, significantly reduced the brain changes that occurred after cocaine withdrawal. In addition, blocking the CA4 enzyme reduced drug-seeking behavior and relapse in the mice.
“What makes this approach promising is that it works in a completely different way from current treatments,” says Wemmie, a professor of psychiatry in the UI Carver College of Medicine. “Instead of targeting opioid receptors, AZD targets a different pathway involved in drug-induced synaptic changes and drug-seeking behavior. This could open the door to new therapies that help people stay in recovery by addressing the brain’s long-term response to drug use.”