It may do more for heart health than joint pain.


Glyphosate, the primary ingredient in Monsanto’s popular weed killer Roundup, has been linked to liver disease in animal models. In a new study, the first of its kind, researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine report an association between the herbicide and negative effects upon the human liver.
In a study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, a team led by Paul J. Mills, Ph.D., professor and chief in the Department of Family Medicine and Public Health at UC San Diego School of Medicine, examined glyphosate excretion in the urine samples of two patient groups—those with a diagnosis of NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, a type of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or NAFLD), and those without. The results, they found, were significant: Regardless of age, race, body mass index (BMI), ethnicity or diabetes status, glyphosate residue was significantly higher in patients with NASH than it was in patients with a healthier liver.
The findings, coupled with prior animal studies, said Mills, suggest a link between the use of commercial glyphosate in our food supply, which has increased significantly over the past 25 years, and the prevalence of NAFLD in the United States, which too has been on the rise for two decades.
In breast cancer, there are cases of women and men whose cancer returns in their bones 20–30 years after they were treated for their primary disease and thought they were cancer-free. This phenomenon always puzzled Jefferson researcher Karen Bussard, Ph.D. How is it possible that breast cancer cells from a primary tumor are able to reach the bones when a patient is deemed “cancer-free” after treatment? What was happening in bones that allowed the cancer cells to remain there for up to 30 years, alive but in a sleeping state, only to re-awaken decades later? In a step towards answering these questions, Dr. Bussard recently discovered a type of bone cell that can subdue cancer cells, slowing their growth, even in one of the most aggressive types of breast cancer: triple negative.
The results, published in Breast Cancer Research, raise intriguing questions about how these bone cells exert their sleep-inducing influence, and whether it’s possible to replicate and permanently turn cancers dormant.
“Cancer has this uncanny ability to turn other cell types it comes in contact with to the cancer cell’s advantage,” says Dr. Bussard, Assistant Professor of Cancer Biology at Thomas Jefferson University and a researcher at the Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center—Jefferson Health. “For example, cancer cells can turn the immune cells that should kill it, into its own guards. However, we have now found a population of bone cells that not only resists, but subdues the cancer. It’s fascinating.”
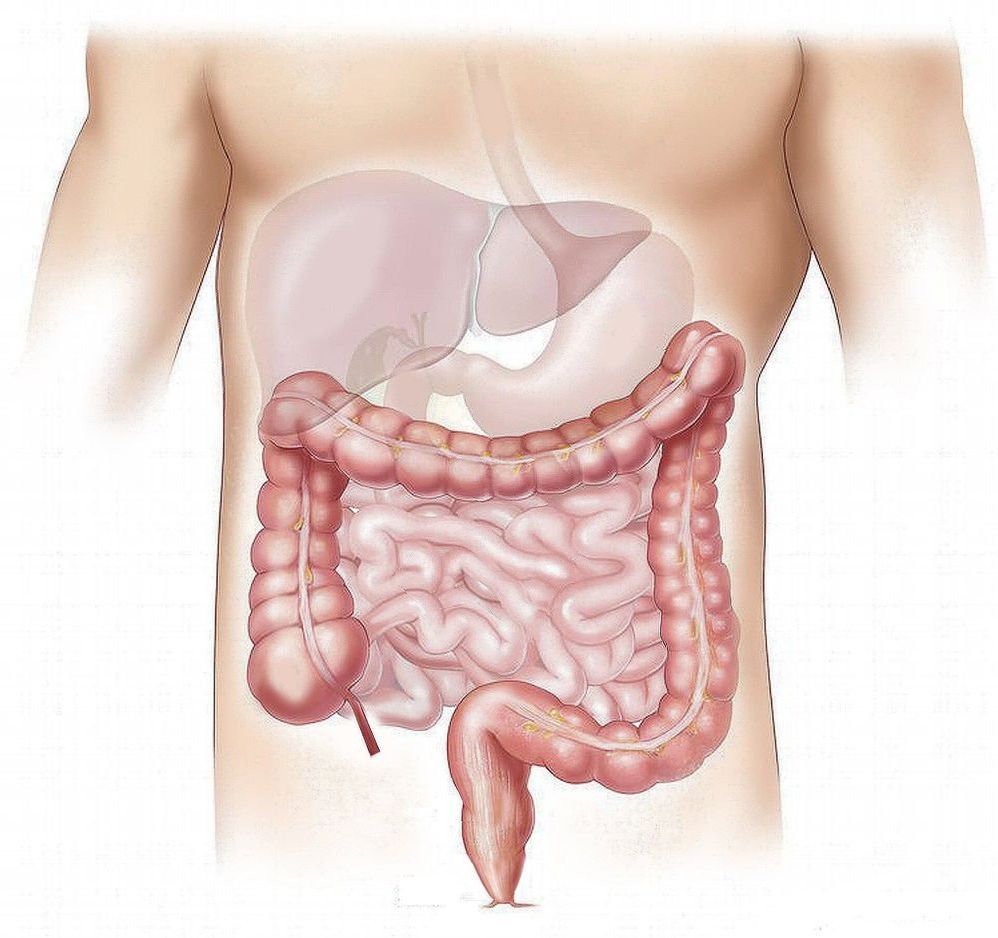
University of Sydney research provides new evidence that nanoparticles, which are present in many food items, may have a substantial and harmful influence on human health.
The study investigated the health impacts of food additive E171 (titanium dioxide nanoparticles) which is commonly used in high quantities in foods and some medicines as a whitening agent. Found in more than 900 food products such as chewing gum and mayonnaise, E171 is consumed in high proportion everyday by the general population.
Published in Frontiers in Nutrition, the mice study found that consumption of food containing E171 has an impact on the gut microbiota (defined by the trillions of bacteria that inhabit the gut) which could trigger diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases and colorectal cancer.
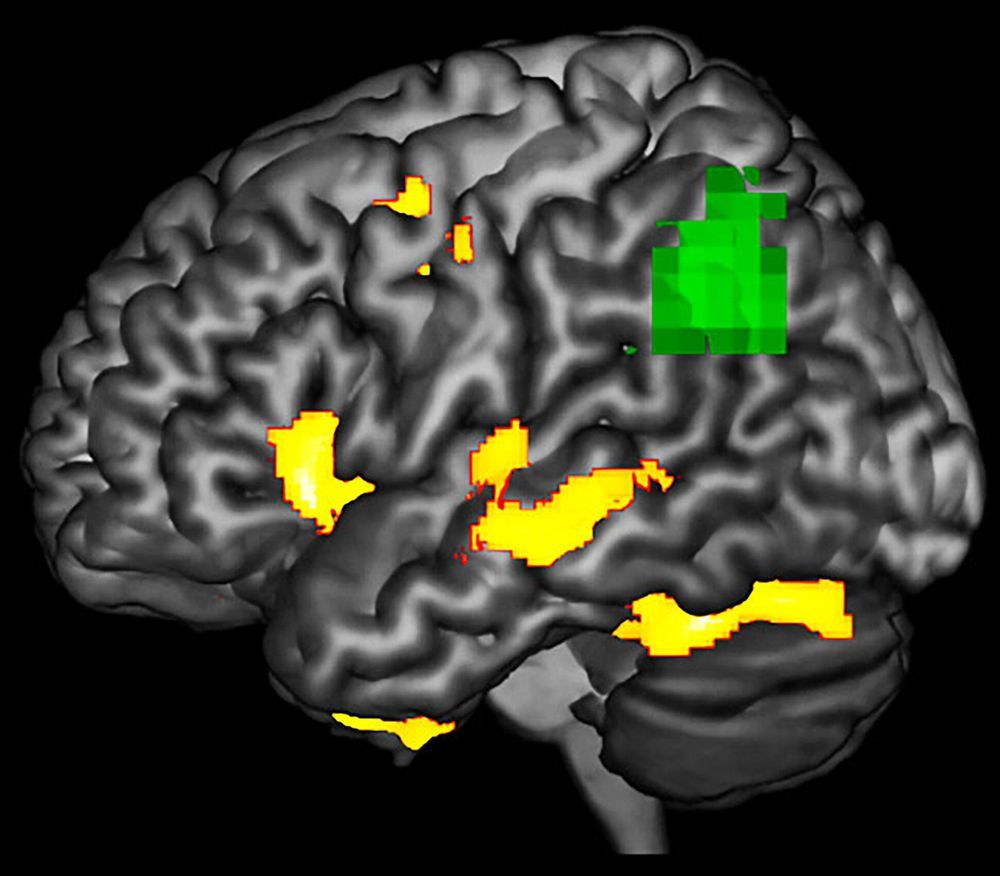
Scientists might have found an early detection method for some forms of dementia, according to new research by the University of Arizona and the University of Toronto’s Baycrest Health Sciences Centre.
According to the study published in the journal Neuropsychologia last month, patients with a rare neurodegenerative brain disorder called Primary Progressive Aphasia, or PPA, show abnormalities in brain function in areas that look structurally normal on an MRI scan.
“We wanted to study how degeneration affects function of the brain,” said Aneta Kielar, the study’s lead author and assistant professor in the UA Department of Speech, Language and Hearing Sciences.

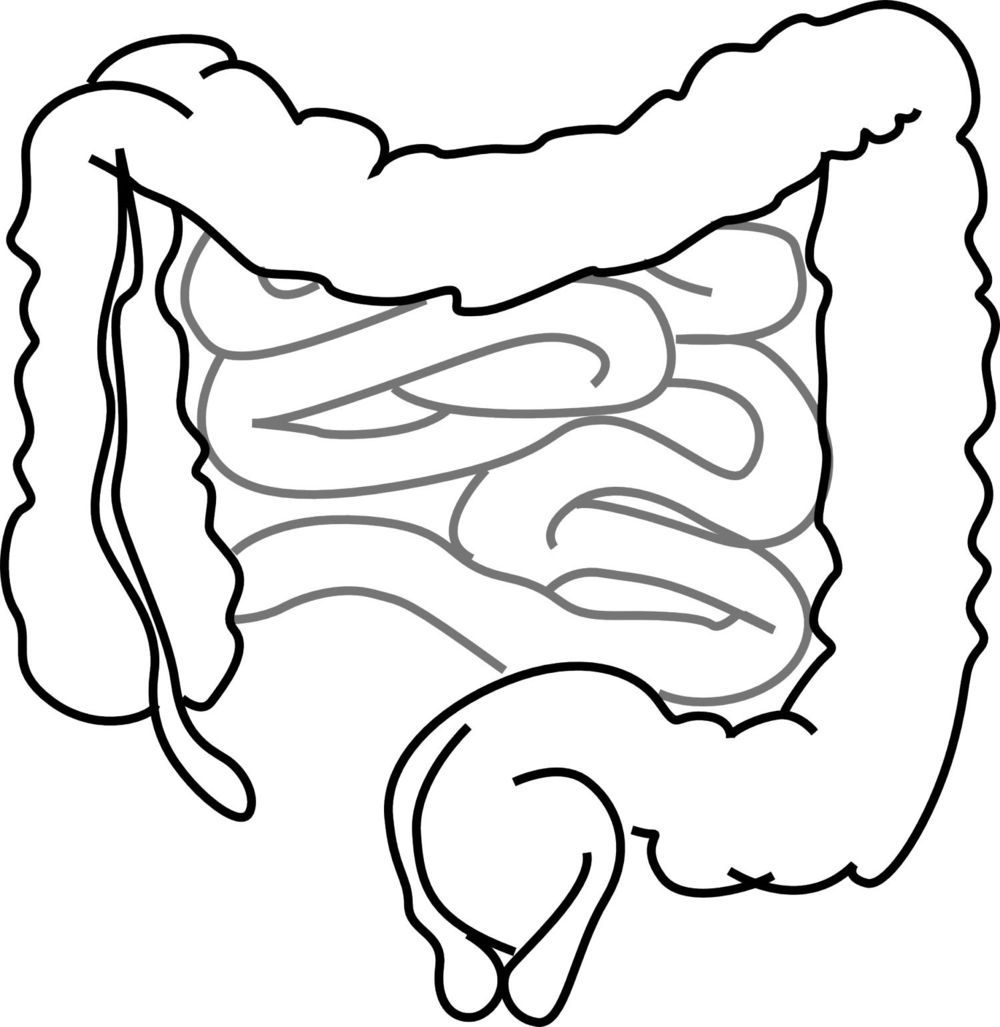
University of Sydney research provides new evidence that nanoparticles, which are present in many food items, may have a substantial and harmful influence on human health.
The study investigated the health impacts of food additive E171 (titanium dioxide nanoparticles) which is commonly used in high quantities in foods and some medicines as a whitening agent. Found in more than 900 food products such as chewing gum and mayonnaise, E171 is consumed in high proportion everyday by the general population.
Published in Frontiers in Nutrition, the mice study found that consumption of food containing E171 has an impact on the gut microbiota (defined by the trillions of bacteria that inhabit the gut) which could trigger diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases and colorectal cancer.
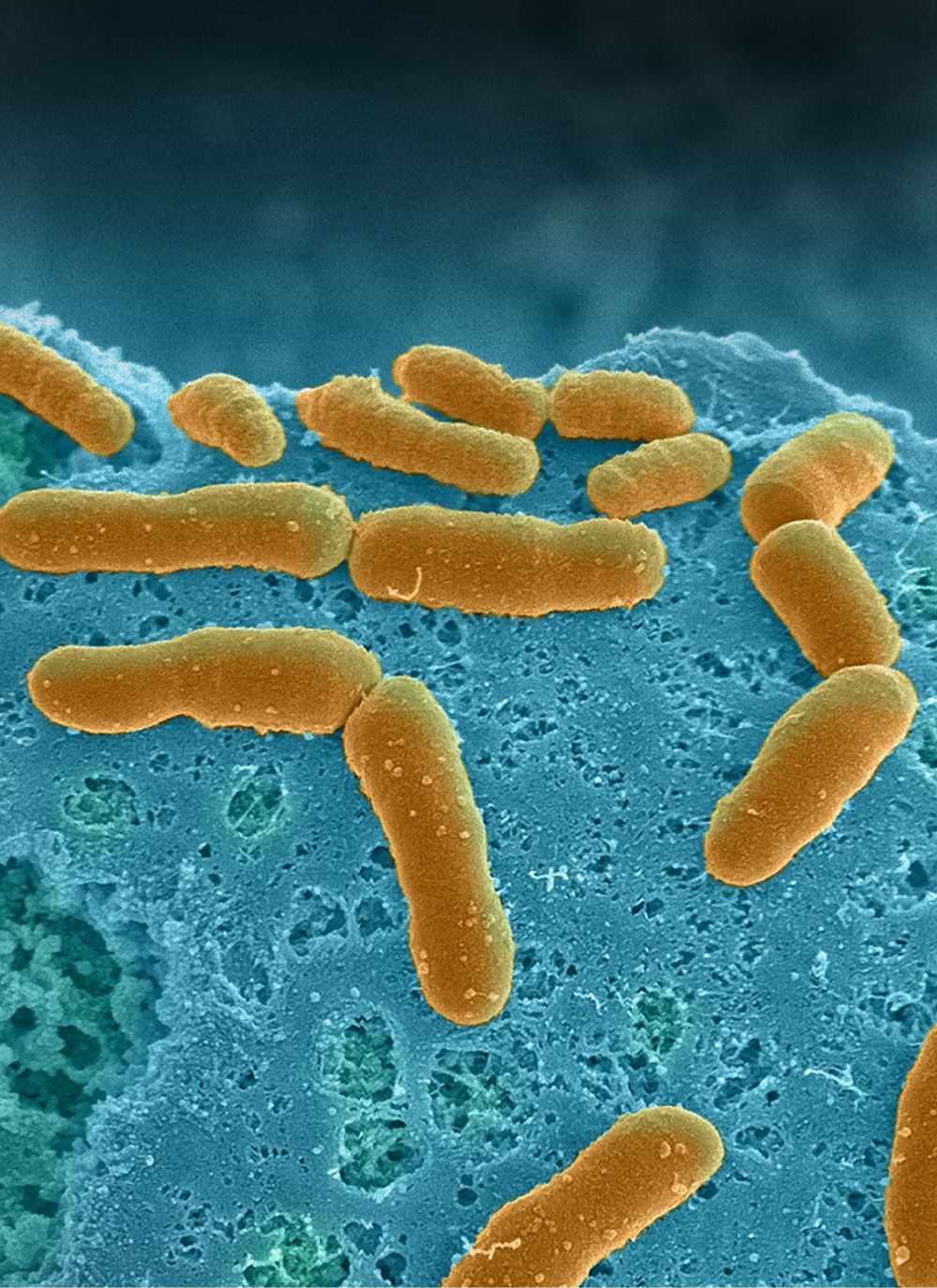
The human microbiome, the huge collection of microbes that live inside and on our body, profoundly affects human health and disease. The human gut flora in particular, which harbor the densest number of microbes, not only break down nutrients and release molecules important for our survival but are also key players in the development of many diseases including infections, inflammatory bowel diseases, cancer, metabolic diseases, autoimmune diseases, and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Most of what we know about human–microbiome interactions is based on correlational studies between disease state and bacterial DNA contained in stool samples using genomic or metagenomic analysis. This is because studying direct interactions between the microbiome and intestinal tissue outside the human body represents a formidable challenge, in large part because even commensal bacteria tend to overgrow and kill human cells within a day when grown on culture dishes. Many of the commensal microbes in the intestine are also anaerobic, and so they require very low oxygen conditions to grow which can injure human cells.
A research team at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering led by the Institute’s Founding Director Donald Ingber has developed a solution to this problem using ‘organ-on-a-chip’ (Organ Chip) microfluidic culture technology. His team is now able to culture a stable complex human microbiome in direct contact with a vascularized human intestinal epithelium for at least 5 days in a human Intestine Chip in which an oxygen gradient is established that provides high levels to the endothelium and epithelium while maintaining hypoxic conditions in the intestinal lumen inhabited by the commensal bacteria. Their “anaerobic Intestine Chip” stably maintained a microbial diversity similar to that in human feces over days and a protective physiological barrier that was formed by human intestinal tissue. The study is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
In the months since, China’s scientists and regulators have been going through a period of soul-searching. We, our colleagues and our government agencies, such as the Ministry of Science and Technology and the National Health Commission, have reflected on what the incident says about the culture and regulation of research in China. We’ve also thought about what long-term strategies need to be put in place to strengthen the nation’s governance of science and ethics.
The shocking announcement of genetically modified babies creates an opportunity to overhaul the nation’s science, argue Ruipeng Lei and colleagues.
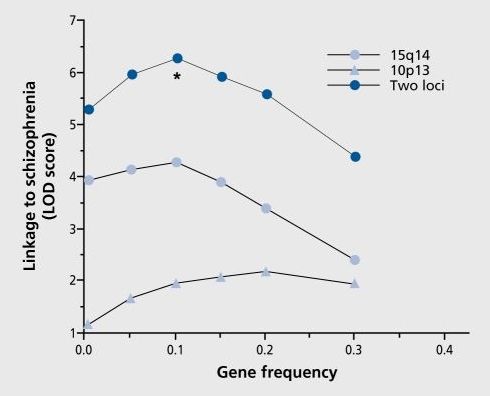
Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2005;7:17–29.
Freedman R, Ross R, Leonard S, Myles-Worsley M, Adams CE, Waldo M, Tregellas J, Martin L, Olincy A, Tanabe J, Kisley MA, Hunter S, Stevens KE.
1Department of Psychiatry C-268–71, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, CO 80262, USA. Robert. [email protected]
