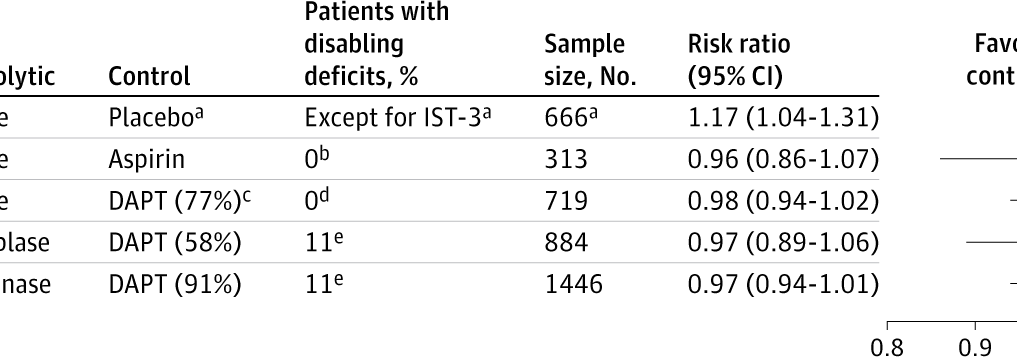
Eating more high-fat cheese and high-fat cream may be linked to a lower risk of developing dementia, according to a new study published in Neurology. This study does not prove that eating high-fat cheese and high-fat cream lowers the risk of dementia, it only shows an association.
High-fat cheeses contain more than 20% fat and include varieties such as cheddar, Brie and Gouda. High-fat creams typically contain 30–40% fat and include whipping cream, double cream and clotted cream. These are commonly labeled as “full-fat” or “regular” versions in stores.
“For decades, the debate over high-fat versus low-fat diets has shaped health advice, sometimes even categorizing cheese as an unhealthy food to limit,” said Emily Sonestedt, Ph.D., of Lund University, Sweden.