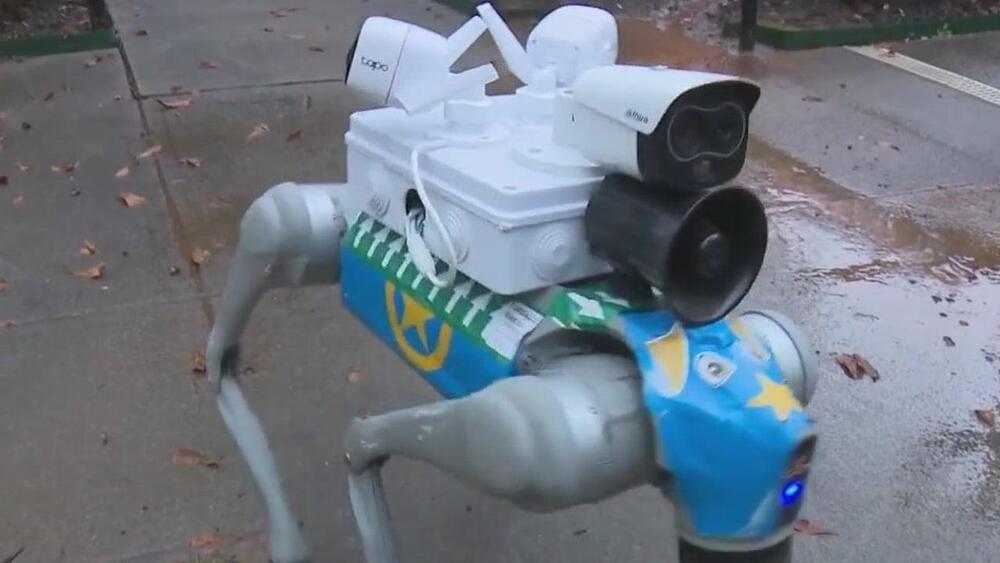
ATLANTA — An innovative approach to public safety is taking shape on Cleveland Avenue, where Atlanta City Councilman Antonio Lewis has partnered with the 445 Cleveland apartment complex to deploy AI-powered robotic dogs to deter crime.
The robotic dog, named “Beth,” is equipped with 360-degree cameras, a siren, and stair-climbing capabilities. Unlike other artificial intelligence robots like “Spunky” on Boulevard, Beth is monitored in real time by a human operator located in Bogotá, Colombia.
“Our operator who is physically watching these cameras needs to deploy the dog. It’s all in one system, and they are just controlling it, like a video game at home, except it’s not a video game—it’s Beth,” said Avi Wolf, the owner of 445 Cleveland.