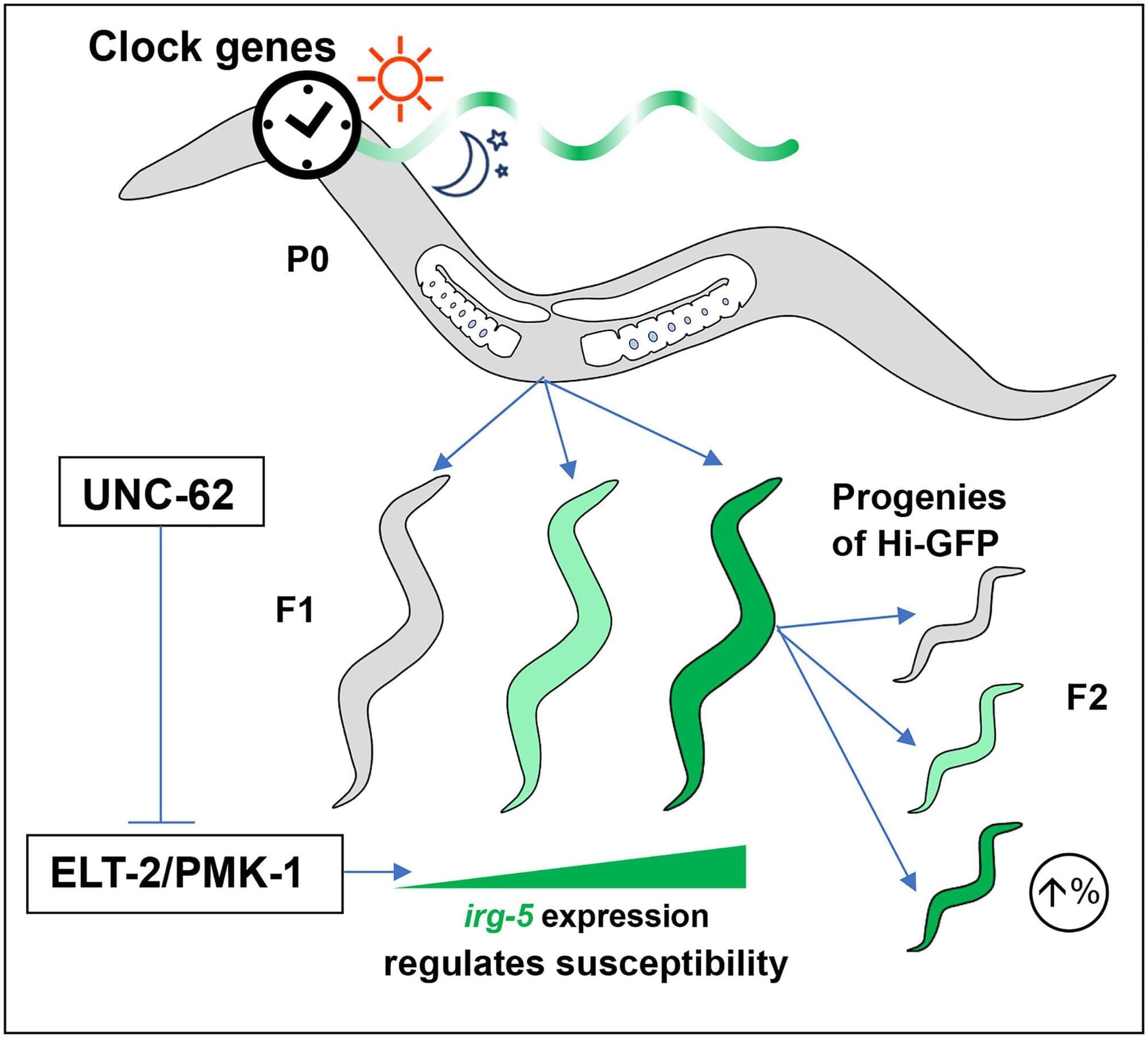
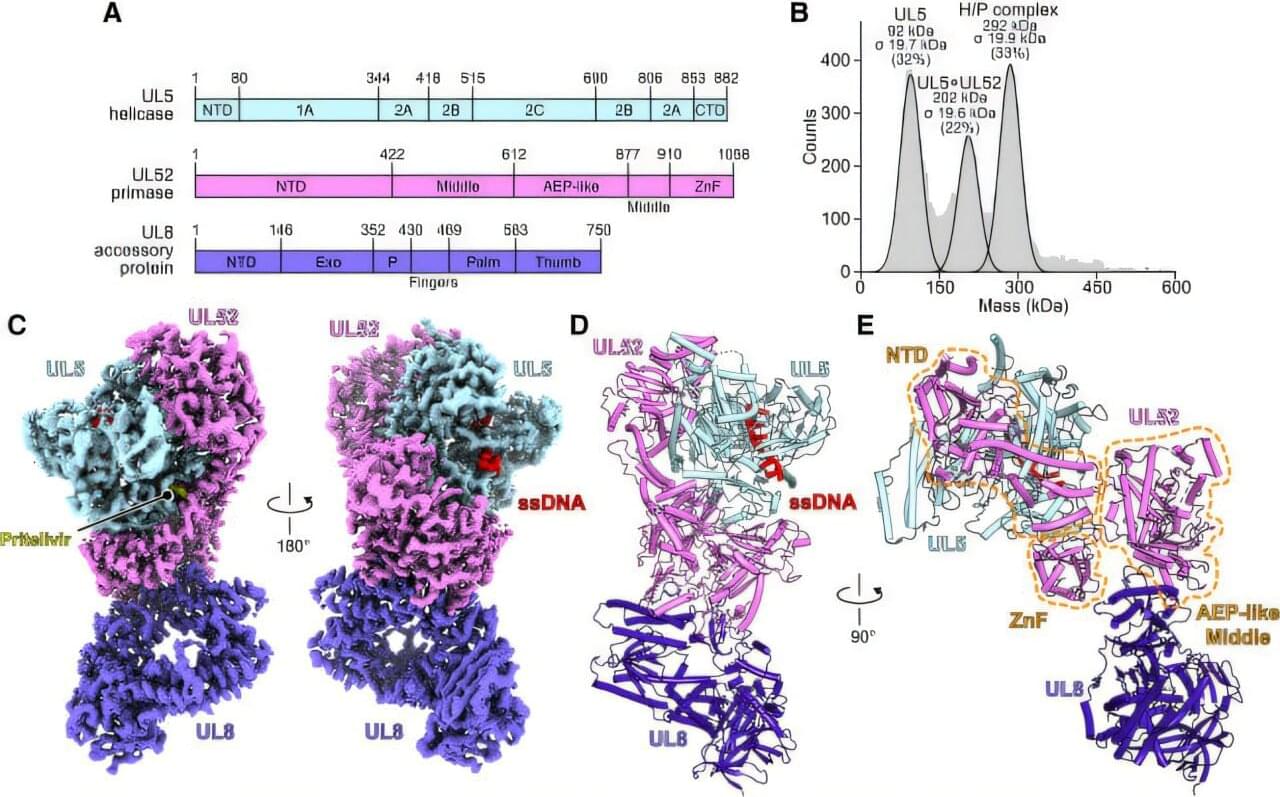
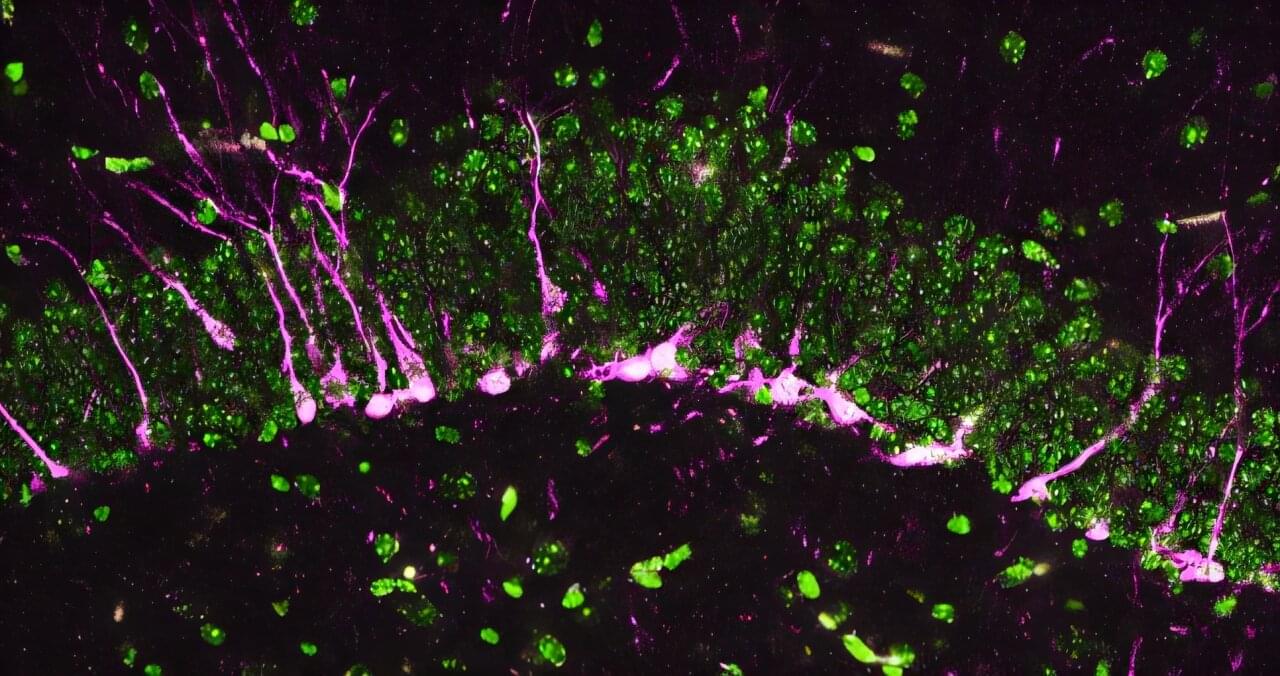
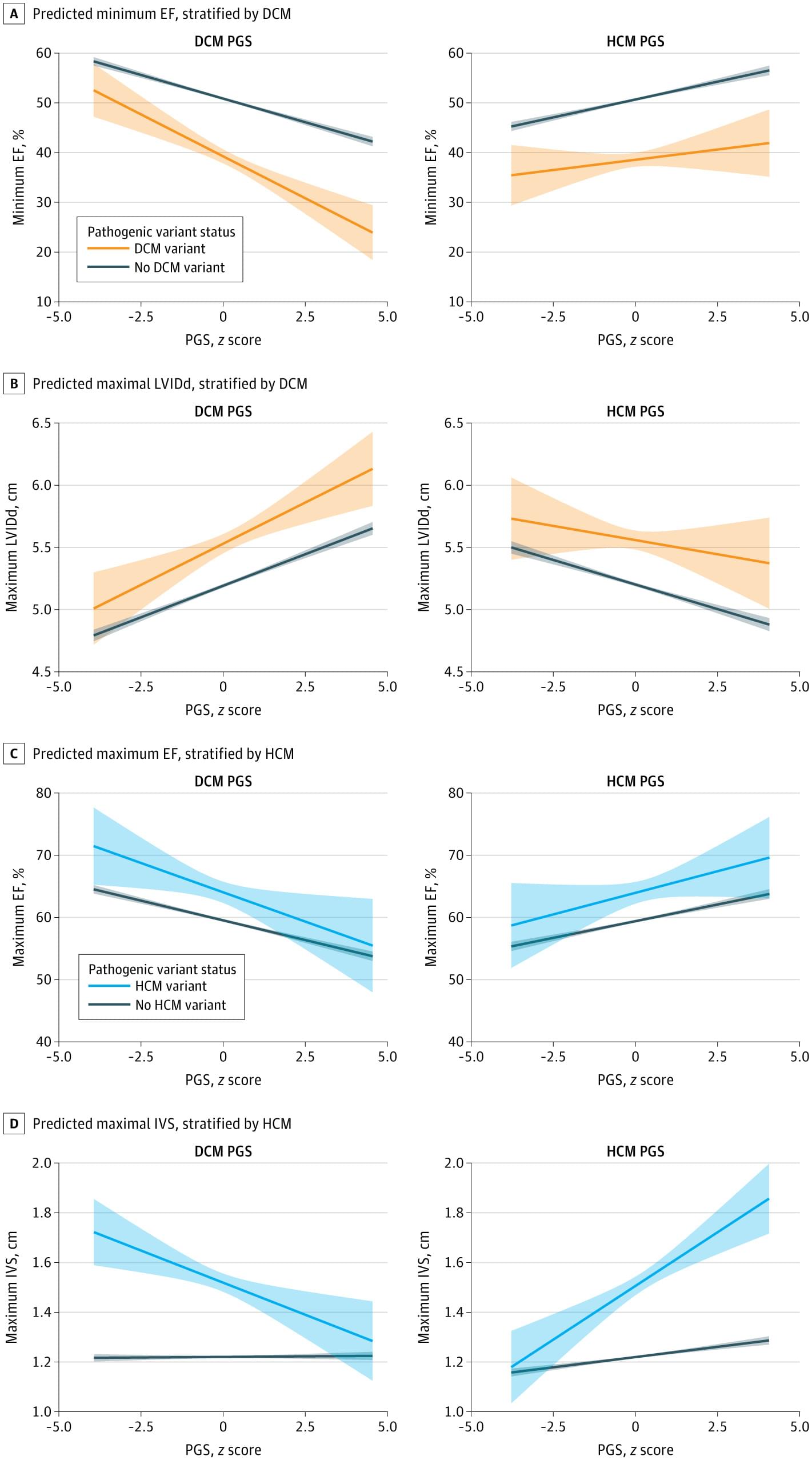
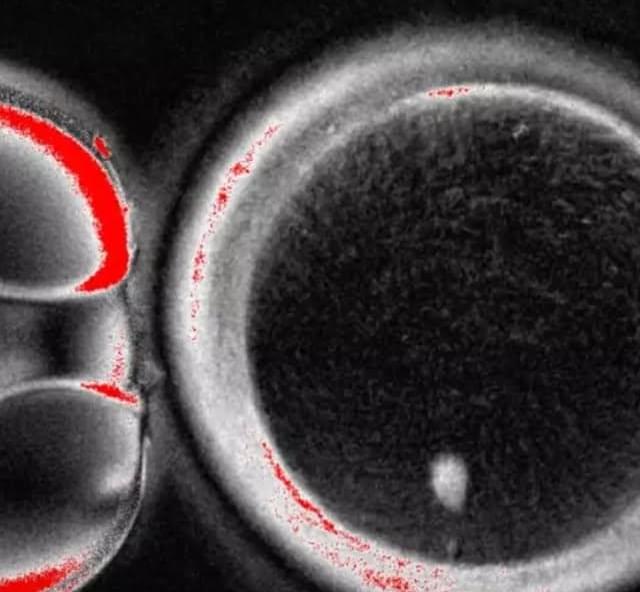
In laboratory models, researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center discovered that a mother’s circadian rhythms, or internal body clock, can influence the immune system states of her offspring, which can accurately predict the risk of bacterial infection.
These findings offer novel insights into non-genetic factors shaping immune defenses and provide a framework to study circadian rhythms as a possible reason why some patients might be more vulnerable to getting infections during disease treatment. The study, published in Science Advances, was led by Alejandro Aballay, Ph.D., professor of Genetics and dean of the UTHealth Houston Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences.
“These findings reveal a circadian mechanism that can create significant differences in infection outcomes even when genetics and environment are similar,” Aballay said. “This circadian control may help explain why patients with comparable risk profiles often experience very different responses to infection.”