Australian researchers have developed a high‑performance coating made from peppermint essential oil that can be applied to the surfaces of many commonly used medical devices, offering a safer way to protect patients from infection and inflammation.
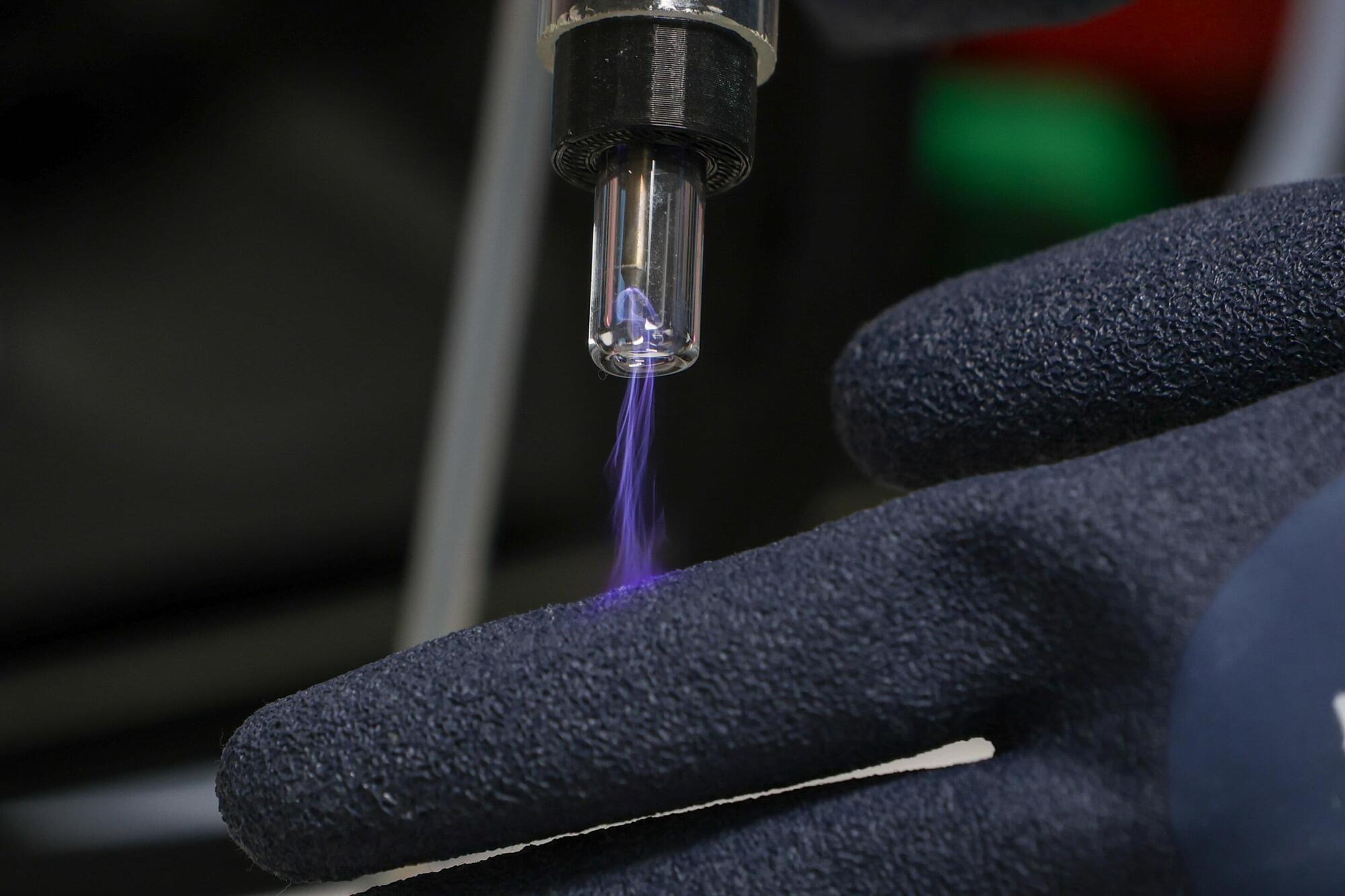
Matthew Flinders Professor and senior author of the new study, Professor Krasimir Vasilev, says the idea emerged after noticing that eating peppermint leaves from his drink significantly relieved his sore throat, inspiring him to explore whether its bioactivity could be converted into a durable coating using plasma technology—something he has been researching for more than two decades.
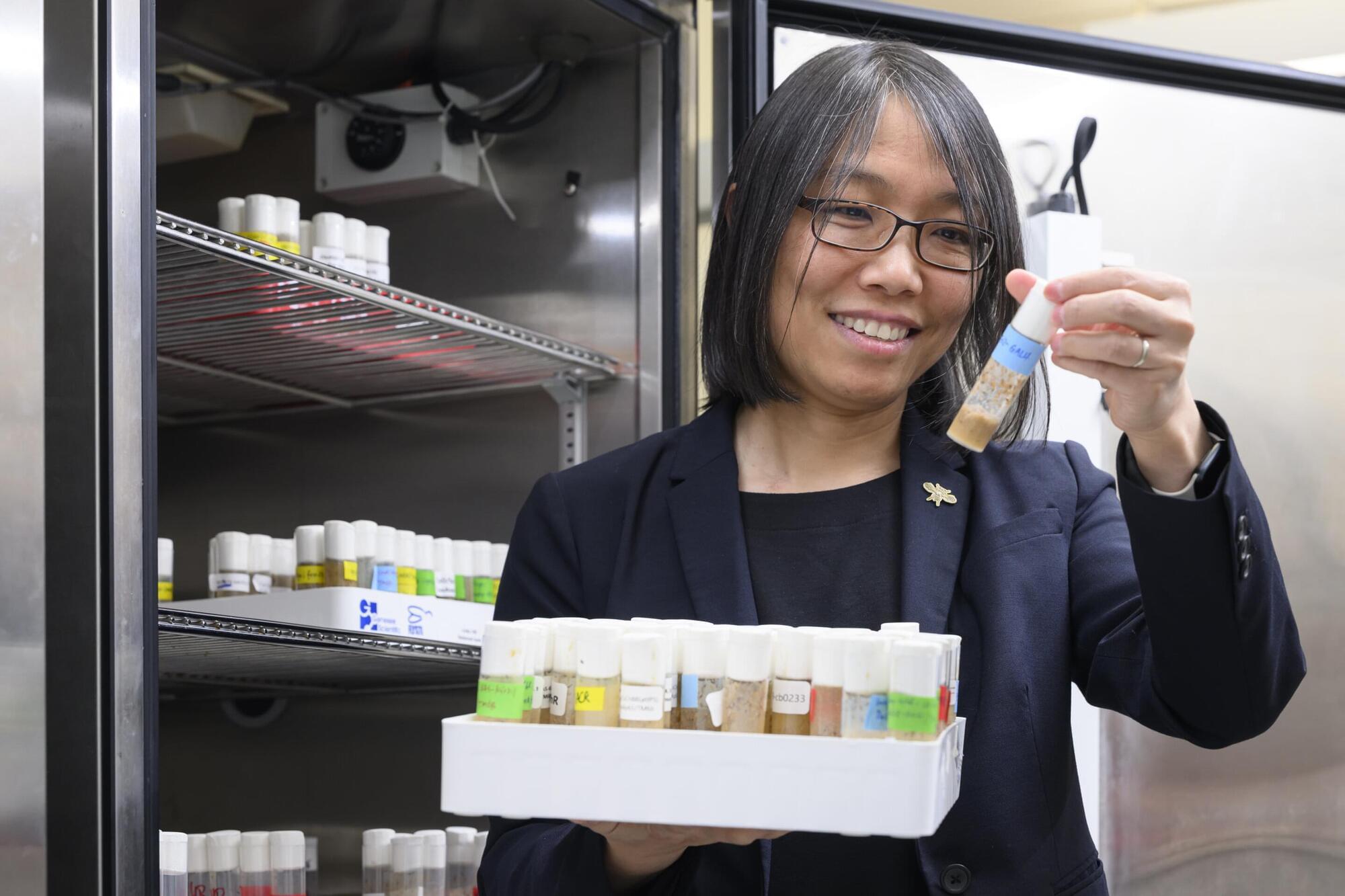
The team from Flinders’s Biomedical Nanoengineering Laboratory—including Professor Vasilev (Director), Associate Professor Vi‑Khanh Truong, Dr. Andrew Hayes, and Ph.D. candidates Trong Quan Luu and Tuyet Pham—created a nanoscale peppermint‑oil coating that protects against infection, inflammation and oxidative stress, while remaining compatible with human tissue and suitable for medical materials.