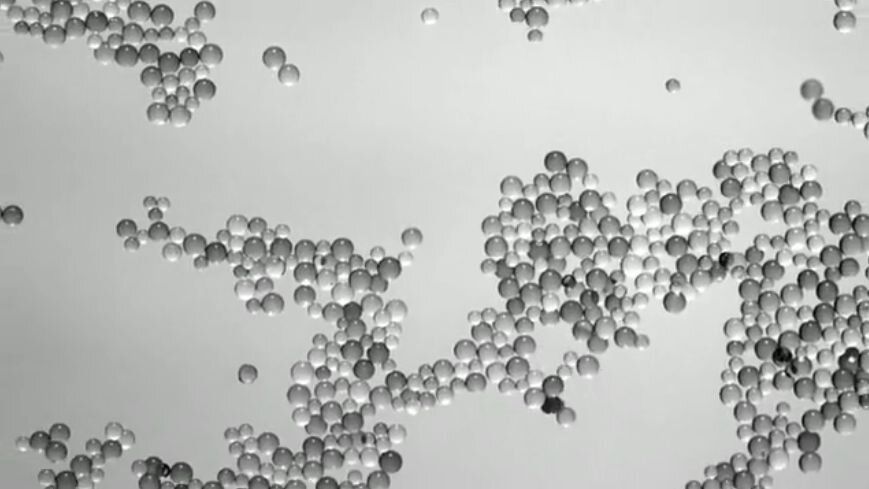
A team of mathematicians from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Brown University has discovered a new phenomenon that generates a fluidic force capable of moving and binding particles immersed in density-layered fluids. The breakthrough offers an alternative to previously held assumptions about how particles accumulate in lakes and oceans and could lead to applications in locating biological hotspots, cleaning up the environment and even in sorting and packing.
How matter settles and aggregates under gravitation in fluid systems, such as lakes and oceans, is a broad and important area of scientific study, one that greatly impacts humanity and the planet. Consider “marine snow,” the shower of organic matter constantly falling from upper waters to the deep ocean. Not only is nutrient-rich marine snow essential to the global food chain, but its accumulations in the briny deep represent the Earth’s largest carbon sink and one of the least-understood components of the planet’s carbon cycle. There is also the growing concern over microplastics swirling in ocean gyres.
Ocean particle accumulation has long been understood as the result of chance collisions and adhesion. But an entirely different and unexpected phenomenon is at work in the water column, according to a paper published Dec. 20 in Nature Communications by a team led by professors Richard McLaughlin and Roberto Camassa of the Carolina Center for Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics in the College of Arts & Sciences, along with their UNC-Chapel Hill graduate student Robert Hunt and Dan Harris of the School of Engineering at Brown University.