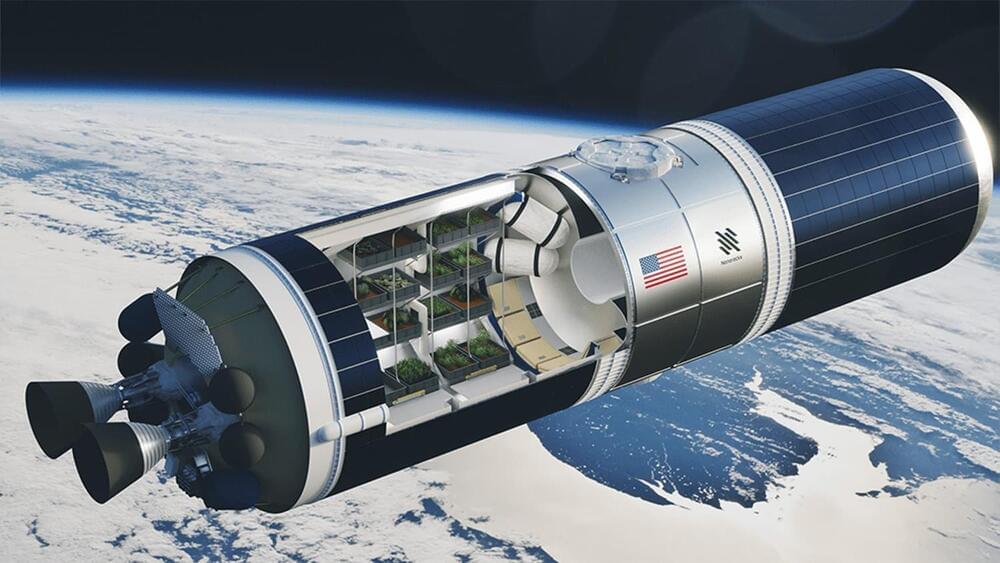
Nanoracks is using space to improve life on Earth.


Sometimes, good things come in small packages. Extremely tiny packages such as a microrobot that can pollinate fields of crops, help rescue people, and so on. Researchers at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) are already working on that and they’re making significant progress.
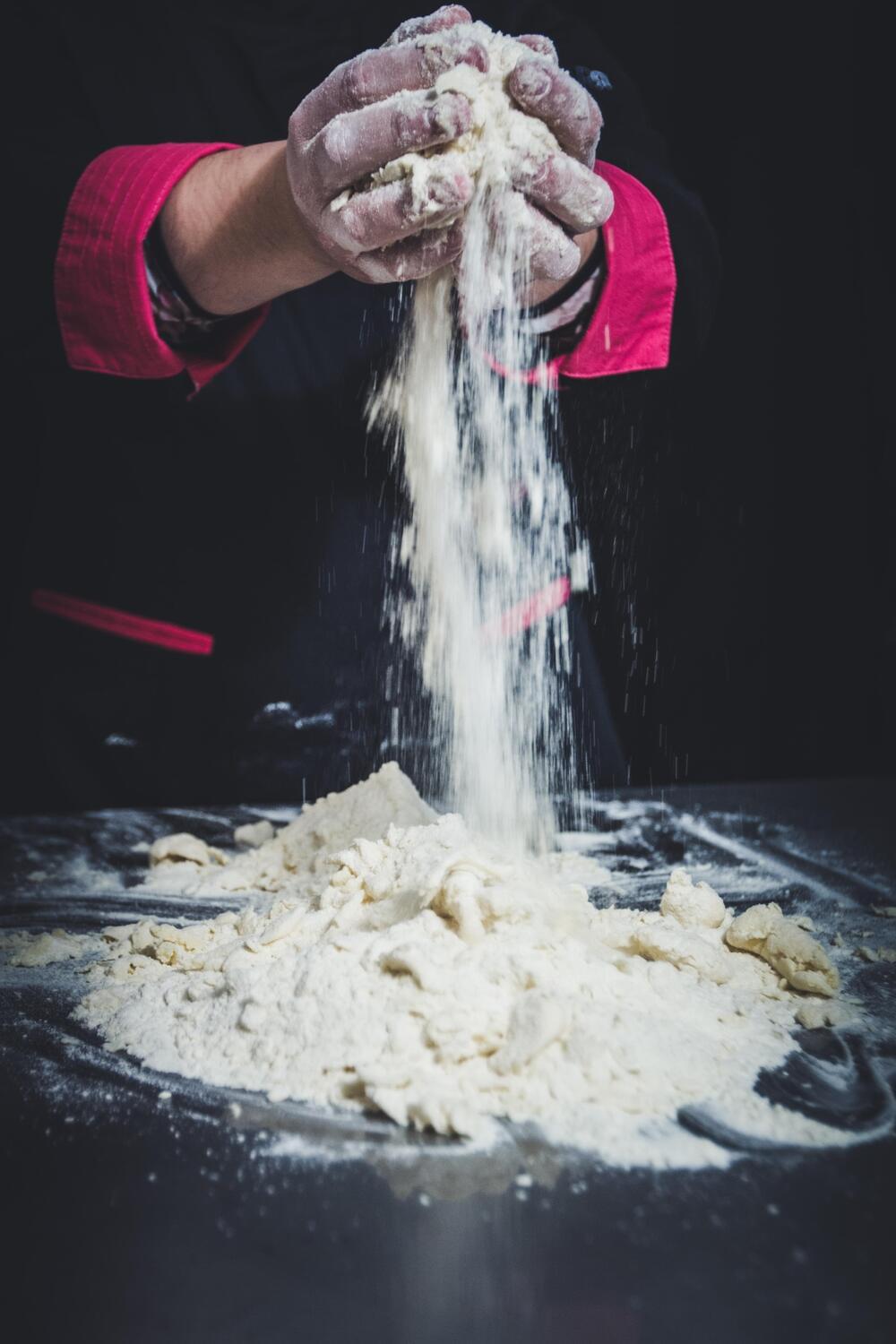


At a massive vertical farm in Denmark, food tech startup Nordic Harvest is demonstrating the benefits of moving agriculture indoors.
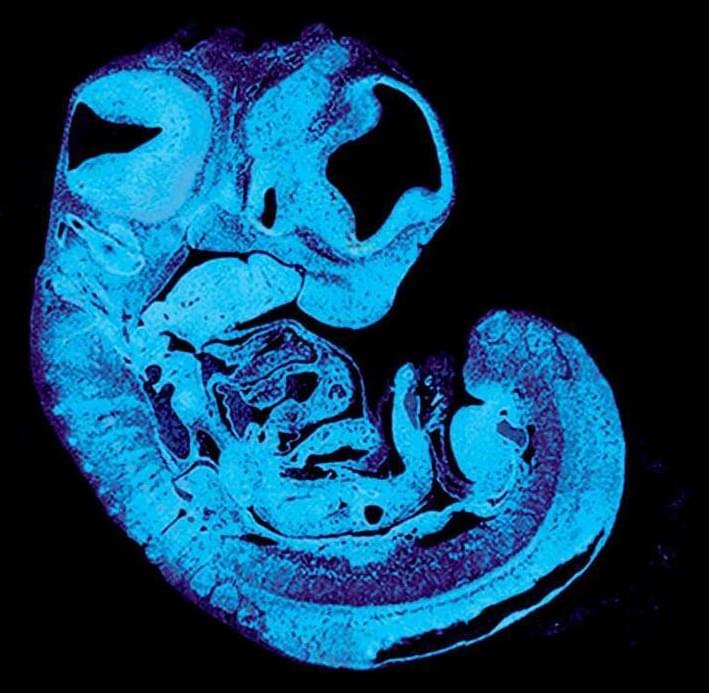
Cambridge scientists have identified a key signal that the fetus uses to control its supply of nutrients from the placenta, revealing a tug-of-war between genes inherited from the father and from the mother. The study, carried out in mice, could help explain why some babies grow poorly in the womb.
As the fetus grows, it needs to communicate its increasing needs for food to the mother. It receives its nourishment via blood vessels in the placenta, a specialized organ that contains cells from both baby and mother.
Between 10% and 15% of babies grow poorly in the womb, often showing reduced growth of blood vessels in the placenta. In humans, these blood vessels expand dramatically between mid and late gestation, reaching a total length of approximately 320 kilometers at term.
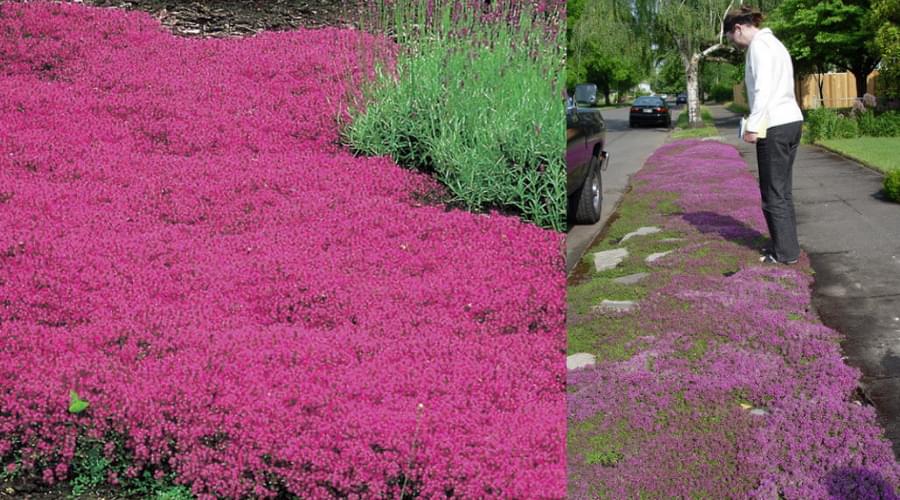

Lawns are becoming less and less popular these days. Besides being high-maintenance, they are terrible for the environment. The mono-crop grasses require lots of watering, fertilizing and “herbiciding.” With mounting water shortages around the world, should we really be dumping clean water on non-edible grass?
Naturally, people are looking for alternatives. Some are planting edible gardens, some are planting prairie grasses and flowers for pollinators, and some are planting eco-friendly clover lawns, for a look and feel more similar to a regular lawn.
And now we’ve found another alternative — creeping red thyme. Like clover, the fast-growing cover crop can take over your whole lawn like a carpet.
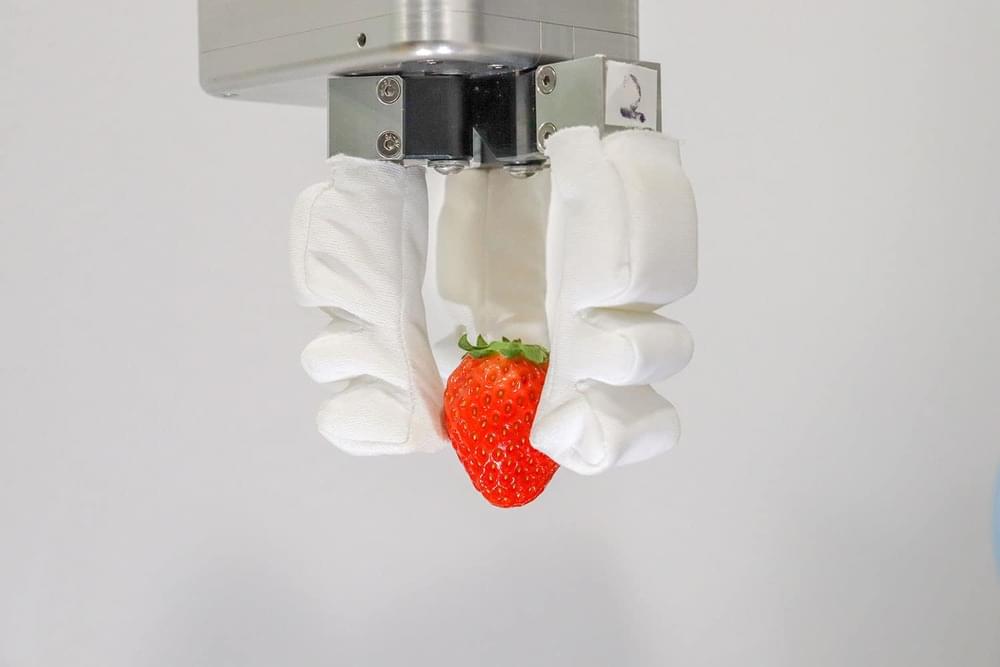


Engineers from National University of Singapore (NUS) have built a robotics system they say can grip various objects, ranging from soft and delicate to bulky and heavy. Designed to be configurable, the robotic hand is touted to address the needs of sectors such as vertical farming, food assembly, and fast-moving consumer goods packaging, and with a 23% improvement in efficiency.
These industries increasingly were automating more of their operations, but currently required manual handling for some processes, according to NUS. The human hand’s natural dexterity remained necessary for these tasks.
Rave Yeow, associate professor from NUS Advanced Robotics Centre and Department of Biomedical Engineering, said: “An object’s shape, texture, weight, and size affect how we choose to grip them. This is one of the main reasons why many industries still heavily rely on human labour to package and handle delicate items.”
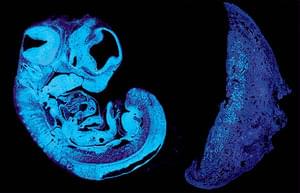
Cambridge scientists have identified a key signal that the fetus uses to control its supply of nutrients from the placenta, revealing a tug-of-war between genes inherited from the father and from the mother. The study, carried out in mice, could help explain why some babies grow poorly in the womb.
As the fetus grows, it needs to communicate its increasing needs for food to the mother. It receives its nourishment via blood vessels in the placenta, a specialised organ that contains cells from both baby and mother.
Between 10% and 15% of babies grow poorly in the womb, often showing reduced growth of blood vessels in the placenta. In humans, these blood vessels expand dramatically between mid and late gestation, reaching a total length of approximately 320 kilometres at term.