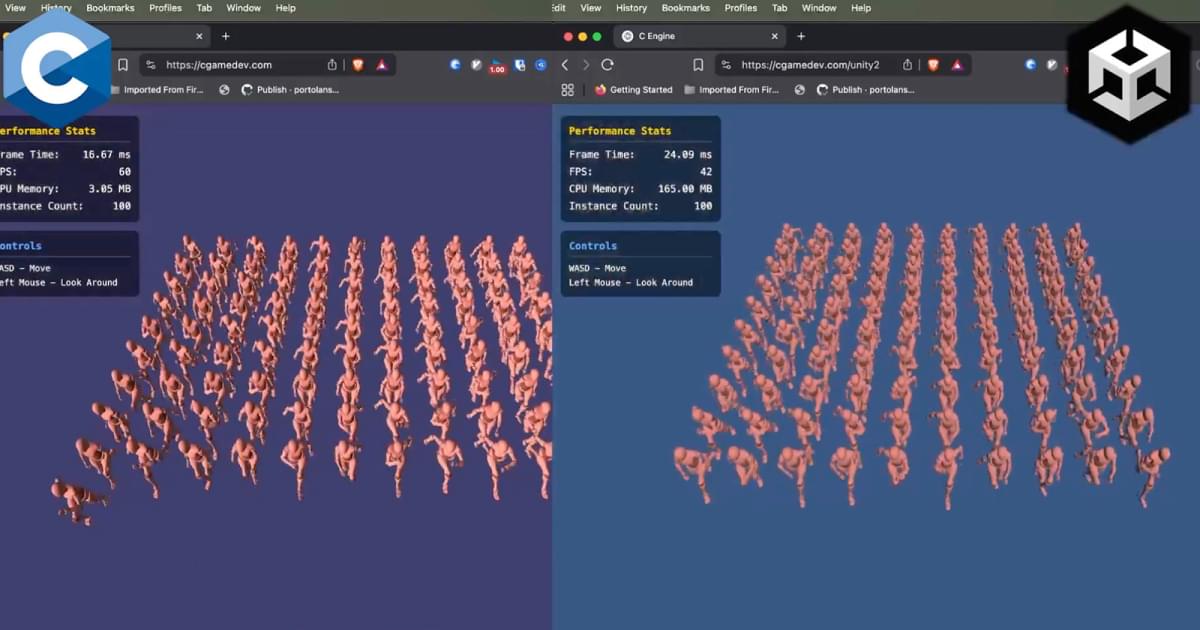
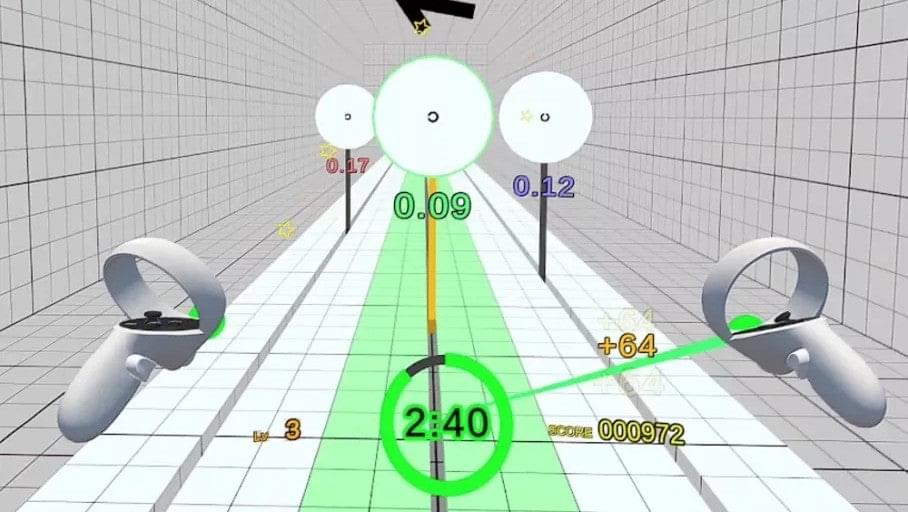
This is something that I often wonder about, because a model’s hardcore reasoning ability doesn’t necessarily translate into a fun, informative, and creative experience. Most queries from average users are probably not going to be rocket science. There isn’t much research yet on how to effectively evaluate a model’s creativity, but I’d love to know which model would be the best for creative writing or art projects.
Human preference testing has also emerged as an alternative to benchmarks. One increasingly popular platform is LMarena, which lets users submit questions and compare responses from different models side by side—and then pick which one they like best. Still, this method has its flaws. Users sometimes reward the answer that sounds more flattering or agreeable, even if it’s wrong. That can incentivize “sweet-talking” models and skew results in favor of pandering.
AI researchers are beginning to realize—and admit—that the status quo of AI testing cannot continue. At the recent CVPR conference, NYU professor Saining Xie drew on historian James Carse’s Finite and Infinite Games to critique the hypercompetitive culture of AI research. An infinite game, he noted, is open-ended—the goal is to keep playing. But in AI, a dominant player often drops a big result, triggering a wave of follow-up papers chasing the same narrow topic. This race-to-publish culture puts enormous pressure on researchers and rewards speed over depth, short-term wins over long-term insight. “If academia chooses to play a finite game,” he warned, “it will lose everything.”