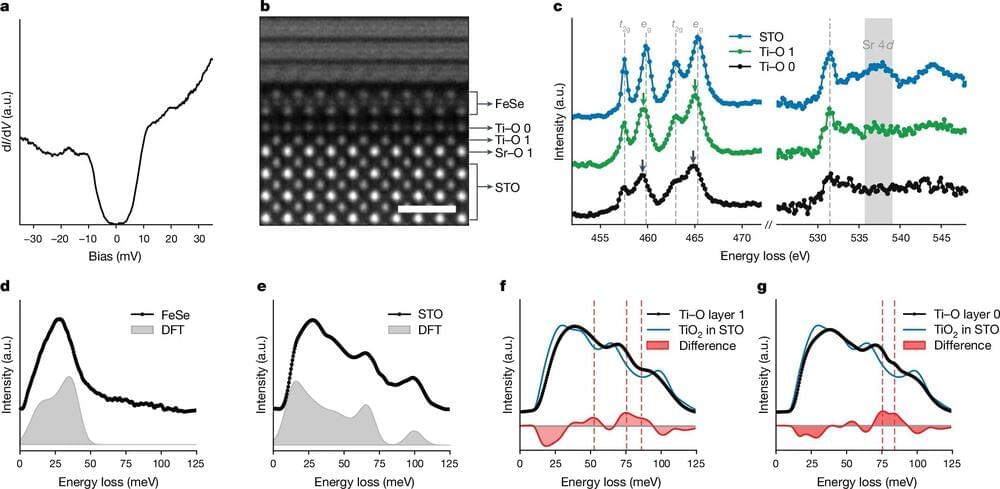
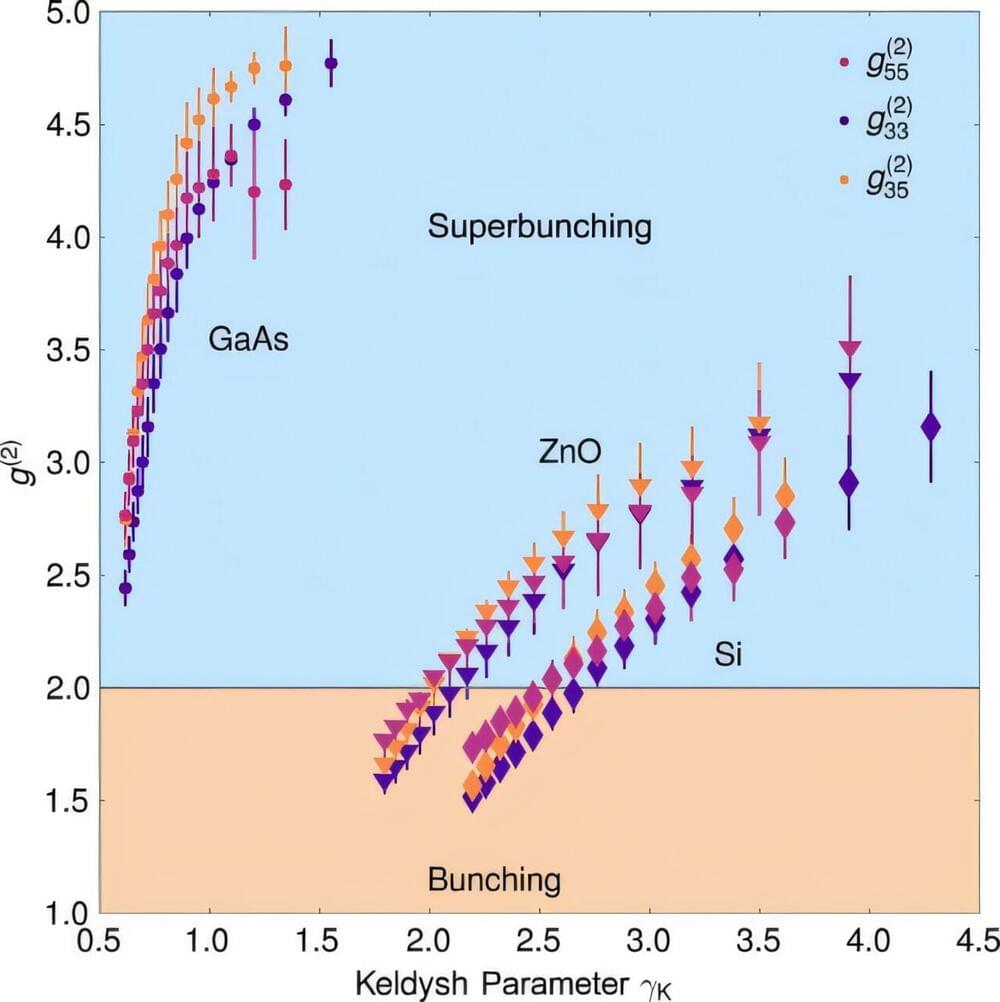
High harmonic generation (HHG) is a highly non-linear phenomenon where a system (for example, an atom) absorbs many photons of a laser and emits photons of much higher energy, whose frequency is a harmonic (that is, a multiple) of the incoming laser’s frequency. Historically, the theoretical description of this process was addressed from a semi-classical perspective, which treated matter (the electrons of the atoms) quantum-mechanically, but the incoming light classically. According to this approach, the emitted photons should also behave classically.
Despite this evident theoretical mismatch, the description was sufficient to carry out most of the experiments, and there was no apparent need to change the framework. Only in the last few years has the scientific community begun to explore whether the emitted light could actually exhibit a quantum behavior, which the semi-classical theory might have overlooked. Several theoretical groups, including the Quantum Optics Theory group at ICFO, have already shown that, under a full quantum description, the HHG process emits light with quantum features.
However, experimental validation of such predictions remained elusive until, recently, a team led by the Laboratoire d’Optique Appliquée (CNRS), in collaboration with ICREA Professor at ICFO Jens Biegert and other multiple institutions (Institut für Quantenoptik—Leibniz Universität Hannover, Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering IOF, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena), demonstrated the quantum optical properties of high-harmonic generation in semiconductors. The results, appearing in PRX Quantum, align with the previous theoretical predictions about HHG.