PORTLAND, Ore. (KOIN) — Hundreds of thousands of customers are still without power in several counties throughout Oregon and Washington.


A team of engineers has developed a new device that you can wear like a ring or bracelet and that harvests energy from your own body heat.
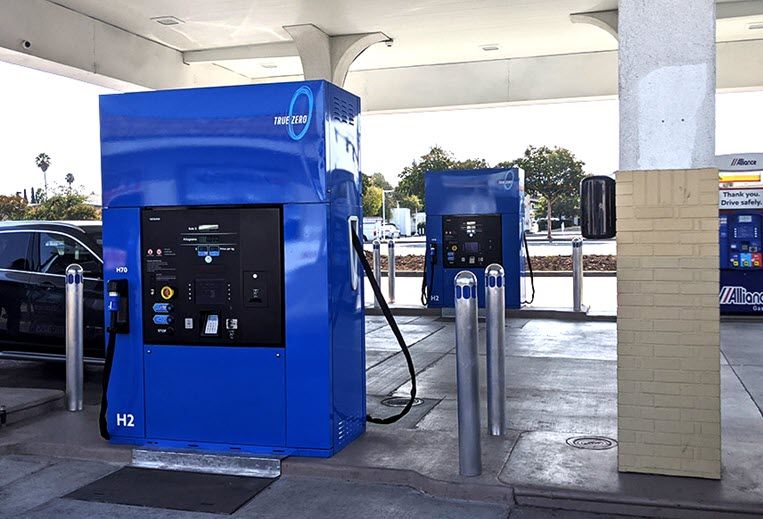

The Sunnyvale True Zero station, located in Silicon Valley, was developed by FirstElement Fuel. It will be open 24 hours a day and is located at 1296 Sunnyvale Saratoga Road, Sunnyvale, CA 94087. The price of hydrogen is $13.08 per kilogram.
The Sunnyvale hydrogen station capacity is 1600 kilograms and has four fueling positions with a total of five nozzles (four H70 nozzles and one H35 nozzle). It is one of the first hydrogen stations in California serving passenger cars to have four fueling positions and capacity up to six times the size of earlier hydrogen stations. The next-largest stations for passenger cars are similar include the True Zero station in Fountain Valley that opened in July and the True Zero station in Oakland, with more than 800 kilograms. It opened in late 2019.
This station will be able to fuel three cars simultaneously, increasing the number of vehicles served in a shorter time. This and future stations like it will help meet the needs of the growing fuel cell passenger car market in Silicon Valley and the greater Bay areas and across California.

😃
These guys developed a super yacht that scoops up plastic trash from the ocean and then uses it as FUEL! 🤯 @theseacleaners’ Mantra concept is seriously effective… See More.


😃
Canadian YouTuber Linus Sebastián reviewed SpaceX’s Starlink Internet on his Linus Tech Tips channel (video below). SpaceX currently operates approximately 1085 internet-beaming Starlink satellites in low Earth orbit that will be part of a constellation of over 4400 satellites designed to connect the planet to the world wide web. To connect to space-based internet Starlink customers use a dish antenna and Wi-Fi router device. The company says the dish antenna is more advanced than what is currently in-use aboard fighter jets. The dish features a phased-array antenna, capable of transmitting and receiving signal from all directions as the satellites move across the sky. This week SpaceX started to accept preorders of the service via Starlink.com.
Linus Tech Tips created a great review video in which he tests Starlink’s speed and also talks about important aspects of the Starlink constellation, including a brief discussion on how the network works. In the video, Linus unboxes the Starlink Kit that costs $499USD, it includes a dish antenna, mounting equipment, power supply, and Wi-Fi router/modem device. The Starlink broadband internet service has no data cap, priced at $99USD per month. Linus and his team install the dish outdoors on top of the roof and connect to the network. First, he used the service to play multiple 4K YouTube videos at once, with good results. He just noticed a small lag when trying to load YouTube thumbnails and comments as four high-definition videos played simultaneously. Then Linus ran an online speed test, Starlink provided him with internet download speed of around 138 megabits per second (Mbps) and latency of 27 milliseconds (ms).


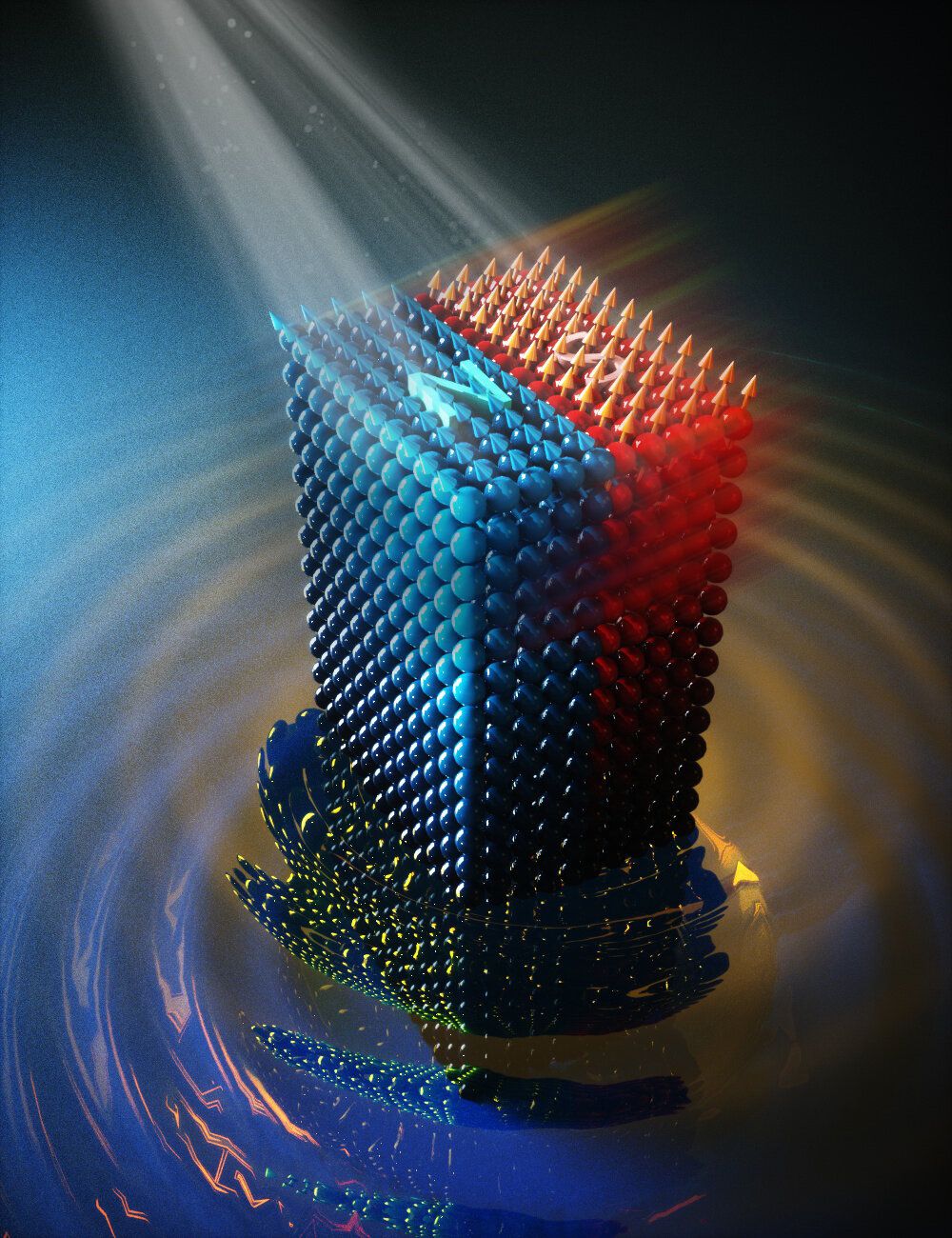
An international team led by researchers of Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) has managed to manipulate the magnetic state of a magnetic material by optically shaking it. The whole process happens within an extremely short time frame of less than a few picoseconds. In times of stalling efficiency trends of current technology, such atomically-driven ultrafast control of magnetism opens broad new vistas for information technology. The results, which have been published in Nature Materials, could eventually lead to fast and energy-efficient data processing technologies, which are essential to keep up with our data hunger.
