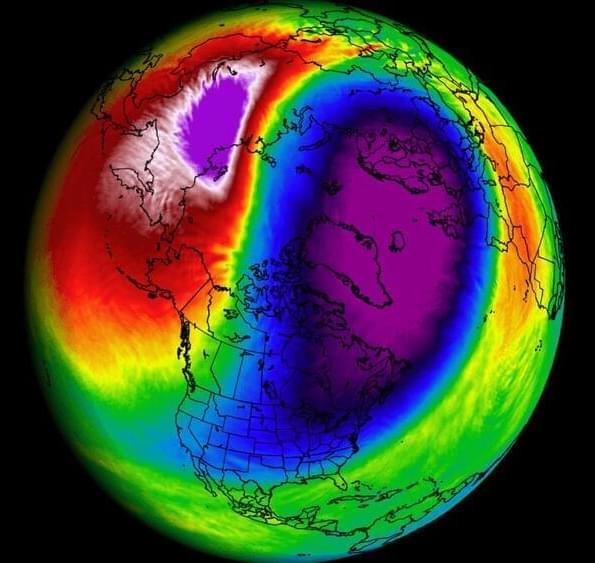
The Polar Vortex is starting to power up and will drive a weather pattern change in the coming days, creating warm conditions over the United States and Europe. But its power-up will be quickly followed by a disruption event. A strong stratospheric warming wave is forecast to emerge, putting a question mark on the weather patterns for the rest of the Winter season.
Weather and the stratospheric Polar Vortex are strongly connected, especially in Winter. So it matters greatly in what shape or form the Polar Vortex is as we go through the season.
We will look at the important role of the Polar Vortex during the Winter season and how it played into the recent cold outbreaks. But more importantly, we will look closely at the latest forecasts and why the Polar Vortex might be the deciding factor for the weather patterns for the rest of the Winter season.