face_with_colon_three year 2022.
It’s all in the power of kinetic energy. Oh, and batteries.

Sharpshooters eliminate up to 300 times their body weight in liquid waste each day, and save energy through a phenomenon called superpropulsion.

Physicists in West Virginia have announced a potential breakthrough that could help upend a longstanding constraint imposed by the first law of thermodynamics.
The discovery, involving how energy is converted in plasmas in space, was described in new research published in the journal Physical Review Letters, and could potentially require scientists to have to rethink how plasmas are heated both in the lab and in space.
The first law of thermodynamics, an expression of the law of conservation of energy albeit styled with relation to thermodynamic processes, conveys that the total energy within a system will remain constant, but that it can be converted from one form of energy into another. More simply, the idea is commonly expressed as “energy can neither be created or destroyed.”
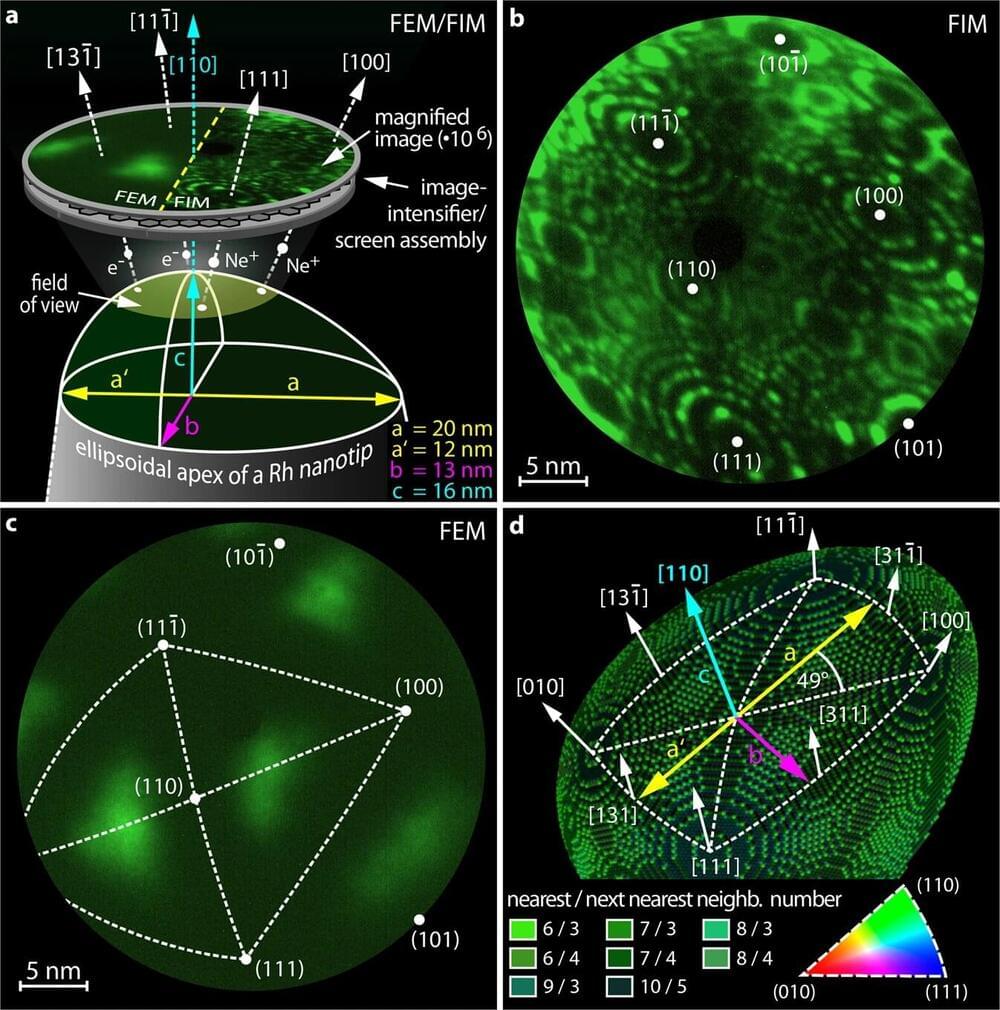
Chaotic behavior is typically known from large systems: for example, from weather, from asteroids in space that are simultaneously attracted by several large celestial bodies, or from swinging pendulums that are coupled together. On the atomic scale, however, one does normally not encounter chaos—other effects predominate.
Now, for the first time, scientists at TU Wien have been able to detect clear indications of chaos on the nanometer scale—in chemical reactions on tiny rhodium crystals. The results have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
The chemical reaction studied is actually quite simple: with the help of a precious metal catalyst, oxygen reacts with hydrogen to form water, which is also the basic principle of a fuel cell. The reaction rate depends on external conditions (pressure, temperature). Under certain conditions, however, this reaction shows oscillating behavior, even though the external conditions are constant.
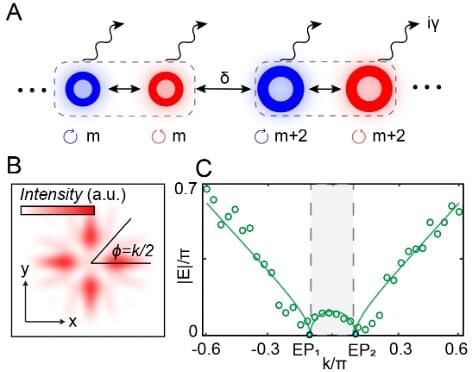
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Guo Guangcan from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) constructed a non-Hermiticity (NH) synthetic orbital angular momentum (OAM) dimension in a degenerate optical cavity and observed the exceptional points (EPs). This study was published in Science Advances.
In topological physics, the NH systems depict open systems with complex energy spectra. Exceptional points are one of the unique features of NH systems. To study EPs, the team had constructed synthetic one-dimensional lattices and established topological simulation platform in a degenerate optical cavity. Based on this platform, an additional pseudomomentum was introduced as a parameter to construct the Dirac point in the two-dimensional momentum space. A pair of EPs can be obtained by introducing non-Hermitian perturbation around the Dirac point.
The detection of complex energy spectra in NH systems can be troublesome for traditional means. The research group developed a method which is referred to as wave front angle–resolved band structure spectroscopy to investigate complex energy spectra based on synthetic OAM. Using this method, the team not only detected EPs in momentum space, but also the key features of EPs like bulk Fermi arcs, parity-time symmetry-breaking transition, energy swapping and half-integer band windings.

“This is real physics, not science fiction”.
A group of researchers essentially pulled energy out of nothing using a quirk of quantum mechanics. Two different physics experiments proved the feat is possible when they drew energy out of an energy vacuum by teleporting energy across microscopic distances.
The new experiments drew on a 2008 theory from theoretical physicist Masahiro Hotta at Tohoku University, as per a report from Quanta Magazine.
Masahiro Hotta’s energy teleportation theory.
Koto_feja / iStock.
Two different physics experiments proved the feat is possible when they drew energy out of an energy vacuum by teleporting energy across microscopic distances.

The BMW Group on Monday launched a pilot fleet of hydrogen vehicles, with the German automotive giant’s CEO referring to hydrogen as “the missing piece in the jigsaw when it comes to emission-free mobility.”
The BMW iX5 Hydrogen, which uses fuel cells sourced from Toyota and has a top speed of more than 112 miles per hour, is being put together at a facility in Munich.
Described by the International Energy Agency as a “versatile energy carrier,” hydrogen has a variety of applications and can be deployed in sectors such as industry and transport.
BMW is one of several automotive firms continuing to look into the potential of hydrogen. Others include Toyota and Hyundai, while smaller businesses such as Riversimple are also working on hydrogen-powered cars.
Hydrogen may have its backers, but some high-profile figures from the automotive industry are not so sure.
A shelved theory seems to have given new life to energy teleportation, a concept that pulls energy from one location to another. The notion might sound like science fiction, but some scientists demonstrated that it is possible to generate energy out of thin air.
According to The Space Academy, scientists were able to extract energy and filled a vacuum through two separate experiments. It has indeed opened a fresh world of quantum energy physics.
