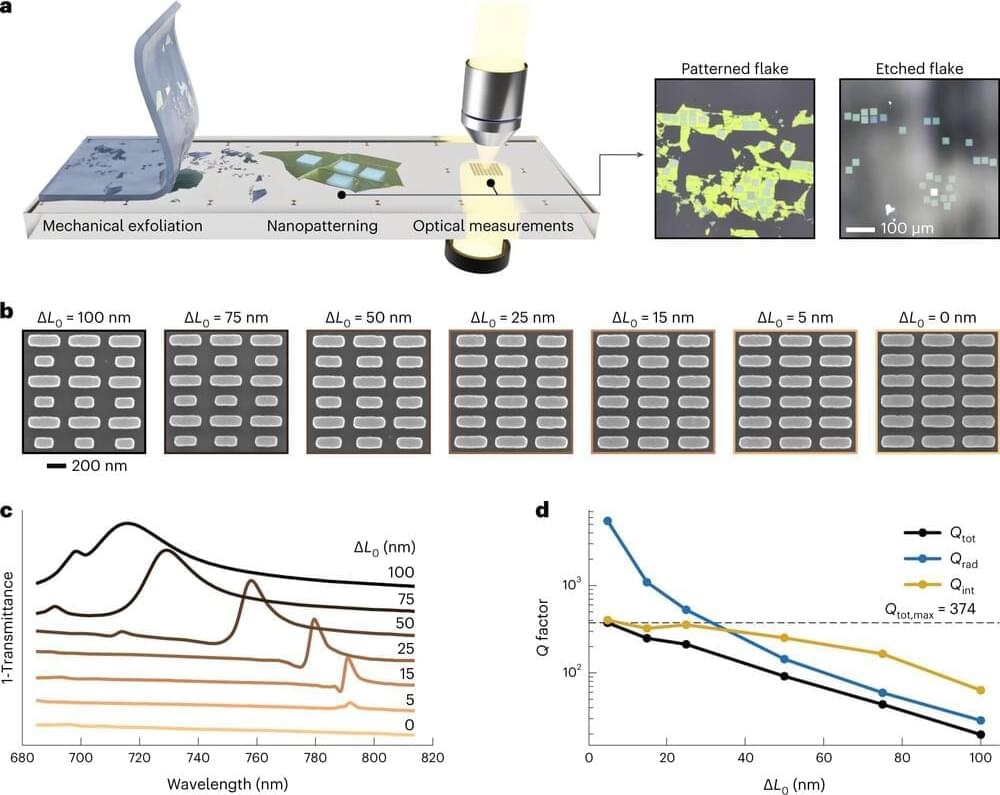
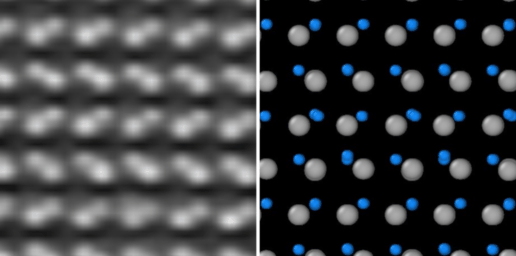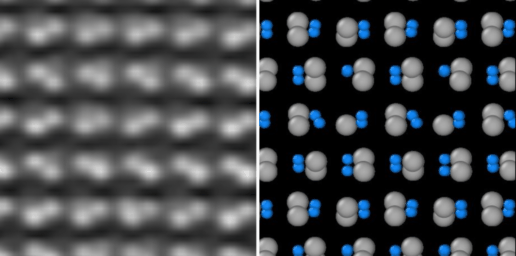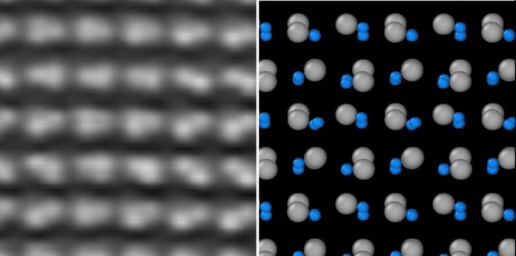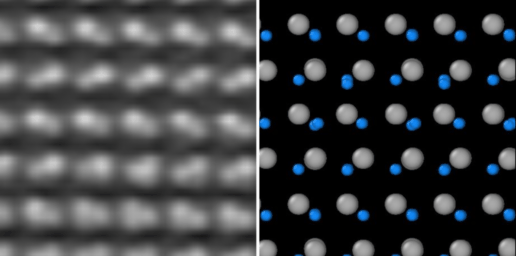
The interaction of light and matter on the nanoscale is a vital aspect of nanophotonics. Resonant nanosystems allow scientists to control and enhance electromagnetic energy at volumes smaller than the wavelength of the incident light. As well as allowing sunlight to be captured much more effectively, they also facilitate improved optical wave-guiding and emissions control. The strong coupling of light with electronic excitation in solid-state materials generates hybridized photonic and electronic states, so-called polaritons, which can exhibit interesting properties such as Bose-Einstein condensation and superfluidity.