Bots are now tackling tricky and dangerous jobs to help the environment, from clearing invasive species to fighting wildfires.
Category: employment – Page 84

This Economic Model Organized Asia for Decades. Now It’s Broken
Pan’s company is at the vanguard of a trend that could have devastating consequences for Asia’s poorest nations. Low-cost manufacturing of clothes, shoes, and the like was the first rung on the economic ladder that Japan, South Korea, China, and other countries used to climb out of poverty after World War II. For decades that process followed a familiar pattern: As the economies of the early movers shifted into more sophisticated industries such as electronics, poorer countries took their place in textiles, offering the cheap labor that low-tech factories traditionally required. Manufacturers got inexpensive goods to ship to Walmarts and Tescos around the world, and poor countries were able to provide mass industrial employment for the first time, giving citizens an alternative to toiling on farms.
Automation threatens to block the ascent of Asia’s poor. Civil unrest could follow.
This fast robot will make Adidas shirts cheaper — and kill hundreds of jobs
A Chinese garment company is partnering with American robotics to use Sewbots in manufacturing. How many people will this new innovation put out of work?
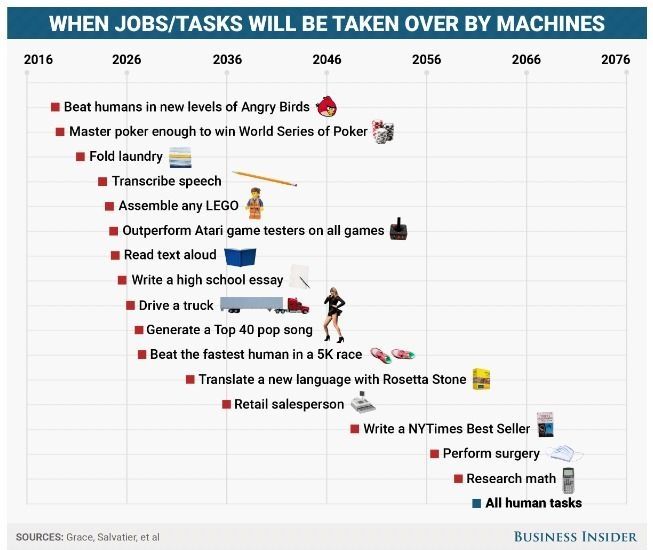
This is when robots will start beating humans at every task
According to a new study from Oxford and Yale University researchers, those are the years artificial intelligence is slated to take over each of those tasks. And so it will go for millions of other jobs over the next 50 years, researchers find.
The Scary AI Revolution Will Decimate Jobs and Might Cause World War III: Jack Ma
Jack Ma, founder of Chinese e-commerce behemoth Alibaba and one of the world’s most successful entrepreneurs, says he worries about the scary Artificial Intelligence revolution. Artificial Intelligence could decimate middle-class jobs and might cause World War III, but it could also be the opportunities to build new companies and change the current status quo of Africa. He believes that AI will be smarter than human and in the future we will make robot more like human.
He spoke to young African at the University of Nairobi and encourage African Entrepreneurs “When I arrived, I found the internet speed in Kenya is faster than in United states, and you will build even better infrastructure and build the future of Africa because entrepreneurship is the best philanthropy to help the society.”
How humans will stay competitive in the age of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is conquering an increasing number of jobs. How can humans keep the edge as robots become smarter?

Most Exponential Law Firms 2025
Exponential Fever. The business world is currently gripped by exponential fever. The concept came to prominence with Moore’s law — the doubling every 18–24 months of the amount of computer power available for $1,000. The phenomenon has since been replicated in many fields of science and technology. We now see the speed, functionality and performance of a range of technologies growing at an exponential rate – encompassing everything from data storage capacity and video download speed to the time taken to map a genome and the cost of producing a laboratory grown hamburger.
New Pretenders. A wave of new economy businesses has now brought exponential thinking to bear in transforming assumptions about how an industry works. For example, AirBnB handles roughly 90 times more bedroom listings per employee than the average hotel group, while Tangerine Bank can service seven times more customers than a typical competitor. In automotive, by adopting 3D printing, Local Motors can develop a new car model 1,000 times cheaper than traditional manufacturers, with each car coming ‘off the line’ 5 to 22 times faster. In response, businesses in literally every sector are pursuing exponential improvement in everything from new product development and order fulfillment through to professional productivity and the rate of revenue growth.
Stepping Up. For law firms, the transformation of other sectors and their accompanying legal frameworks creates a massive growth opportunity, coupled with the potential to bring similar approach to rethinking the way law firms operate. While some might be hesitant about applying these disruptive technologies internally, there is a clear opportunity to be captured from helping clients respond to these developments and from the creation of the industries of the future. To help bring to life the possibilities within legal, we highlight seven scenarios that illustrate how exponential change could transform law firms over the next 5 to 10 years.
Rise of the ‘Exponential Circle’. Our continuing programme of research on the future of law firms suggests that we will see exponential growth for those firms who can both master the legal implications of these technologies for their clients and become adept at their application within the firm. By 2025, we could indeed have witnessed the emergence of an Exponential Circle of law firms who have reached ‘escape velocity’ and left the rest behind.
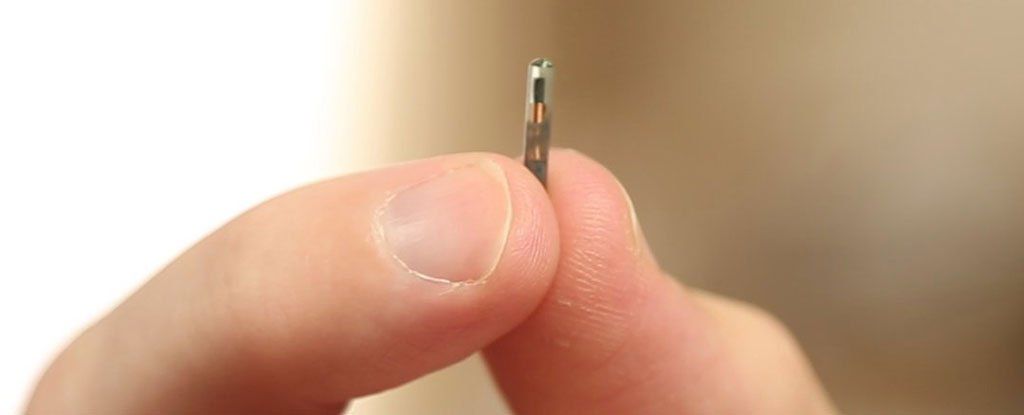

For The First Time, a US Company Is Implanting Microchips in Its Employees
We’re always hearing how robots are going to take our jobs, but there might be a way of preventing that grim future from happening: by becoming workplace cyborgs first.
A company in Wisconsin has become the first in the US to roll out microchip implants for all its employees, and says it’s expecting over 50 of its staff members to be voluntarily ‘chipped’ next week.
The initiative, which is entirely optional for employees at snack stall supplier Three Square Market (32M), will implant radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips in staff members’ hands in between their thumb and forefinger.

The future of work: will humans remain employed in an era of AI and robotics?
New Report Predicts Over 100,000 Legal Jobs Will Be Lost To Automation
An extensive new analysis by Deloitte estimates that over 100,000 jobs will be lost to technological automation within the next two decades. Increasing technological advances have helped replace menial roles in the office and do repetitive tasks.
To paraphrase the Bard’s famous quote: “The first thing we do, let’s replace all the lawyers with automated algorithms.”