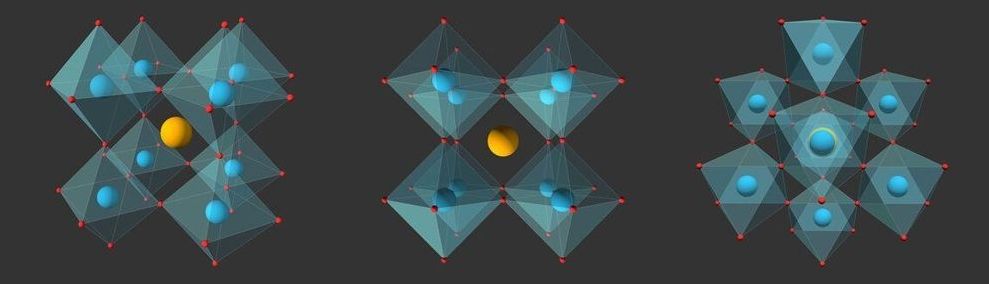
A lead-free ceramic that could be used in applications ranging from optical sensors and switches to creams for protecting against ultraviolet (UV) light has been developed by A*STAR researchers.
Ceramics made from potassium sodium niobate (KNN) are promising alternatives to lead-based ceramics in electro-optical applications. However, it is both challenging and costly to improve KNN’s performance by ensuring it has a high density, fine-grained, chemically uniform microstructure.
Known as PLZT, lanthanum modified lead zirconate titanate is one of the most widely used electro-optic ceramics. Yet there are serious ecological concerns regarding toxicity to the environment and living organisms once devices made with it are discarded; PLZT contains around 60 per cent of lead (by weight). The search is on to find lead-free replacements for PLZT.