Riz Virk, the author of the new book The Simulated Multiverse, talks with GamesBeat’s Dean Takahashi about sci-fi and reality.
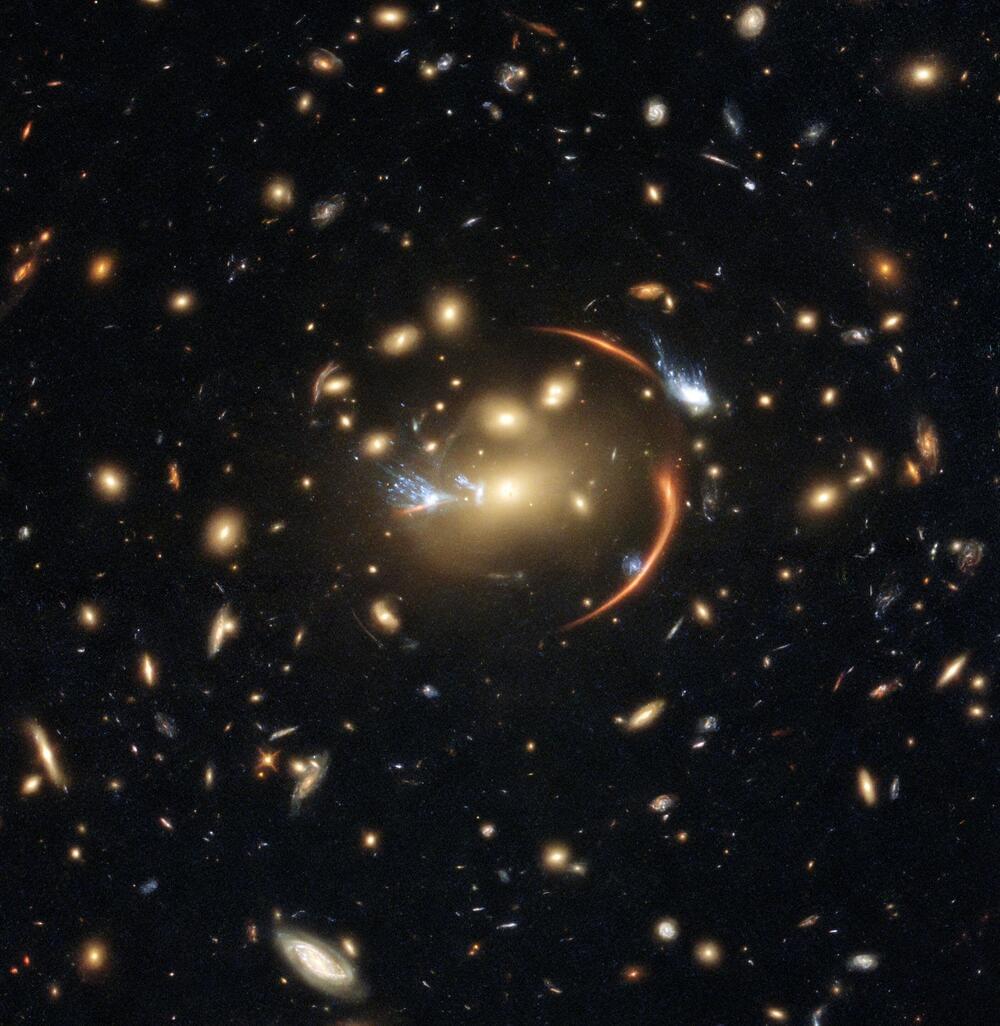



Unprecedent measurements confirm galaxies idle when they run out of cold gas.
New research, published in Nature and led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has just answered one of the fundamental questions about our universe: Why did some of the oldest, most massive galaxies go quiescent early in their formation? The answer, we now know, is because they ran out of cold gas.
The most massive galaxies in our universe formed incredibly early, just after the Big Bang.
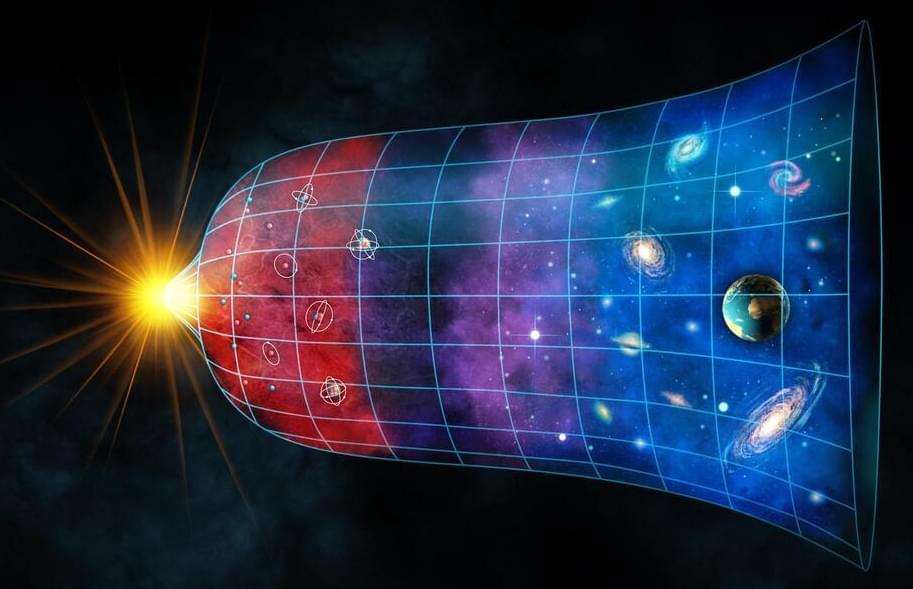
Last year, physicists reported that an experimental dark matter detector picked up a strange signal that could hint at new physics, with several suspects highlighted. Now, Cambridge scientists have proposed an answer that wasn’t considered at the time – the experiment may have picked up the first direct detection of dark energy, the mysterious force that’s accelerating the expansion of the universe.
Although it’s thought to outnumber regular matter five to one, dark matter remains elusive. It doesn’t interact with light and seems to mostly make itself known through gravitational influence on cosmic scales, like stars, galaxies and galaxy clusters. But once in a while, a dark matter particle might bump into a regular matter particle in a way that we could detect, with the right equipment.
XENON1T was one version of that equipment. Running in Italy between 2016 and 2,018 the experiment was essentially a big tank full of liquid xenon, kept deep underground. The idea was that if a dark matter particle zipped through the tank, it would excite the xenon atoms to produce a flash of light and free electrons, which a suite of sensors can detect.

Thu, Sep 30 at 4 PM PDT.
Black holes are cosmic objects so small and dense that nothing, not even light, can escape their gravitational pull. Until recently, no one had ever seen what a black hole actually looked like. Einstein’s theories predict that a distant observer should see a ring of light encircling the black hole, which forms when radiation emitted by infalling hot gas is lensed by the extreme gravity near the event horizon. The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a global array of radio dishes, linked together by a network of atomic clocks to form an Earth-sized virtual telescope that can resolve the nearest supermassive black holes where this ring feature may be measured. On April 10th, 2,019 the EHT project reported success: we imaged a black hole, and saw the predicted strong gravitational lensing that confirms the theory of General Relativity at the boundary of a black hole. This talk will cover how this was accomplished, details of the first results, as well as future directions that will enable real-time black hole movies.
About Dr. Shep Doeleman:
THEOGENESIS: Transdimensional Propagation & Universal Expansion ― a new book on quantum cosmology, computational physics and posthumanism by evolutionary cyberneticist Alex M. Vikoulov ― comes with a trailer you might find more than just interesting:
Release Date: October, 1 2021; Written by Alex M. Vikoulov; Publisher: Ecstadelic Media Group, Burlingame, California, USA; Format: Kindle eBook; Print Length: 211 pages; ISBN: 9781733426183; Discounted Pre-Order Price: $7.99.
*Pre-order eBook now with just 1 click and get your copy auto-delivered to your device on October 1 2021: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B09F858NBZ?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20
#THEOGENESIS #QuantumCosmology #ComputationalPhysics #CyberneticTheoryofMind #posthumanism #cybernetics #theosophy #futurism
“Having invented the gods, perhaps we can turn into them.”
–Alan Harrington, The Immortalist.
Whereas the level of our posthuman syntelligence may be trillions upon trillions of times more powerful than it is today, nothing will prevent it to expand both in outer space and inner space. Isn’t it the nature of intelligence to acquire the ultimate knowledge — everything that can be known? A number of prominent physicists argue that the Technological Singularity is inevitable and the destiny of our Syntellect is to live forever, expand universally and finally reach the networked mind of universal proportions, living conscious universal superbeing.
If we extrapolate the past and current trends in increasing complexity and integration of self-aware neural networks leading to the Syntellect, we can ultimately envision a superintelligent entity encompassing our entire Universe, creating an infinite number of simulated universes, as well as many other spectacular emergent features. This picture bears a striking resemblance to the familiar concept of an immortal, omnipresent, omniscient, omnipotent, and omnibenevolent entity. Spiritually inclined rationalists may view this ongoing evolutionary process as one of ‘Theogenesis’. An interesting question is whether it has already happened elsewhere. We are now laying the foundation for the cognitive architecture of the Universal Mind. Many of our achievements in information engineering may persist forever and eventually become parts of the internal architecture of “God.”
- Excerpt from THEOGENESIS: Transdimensional Propagation & Universal Expansion, The Cybernetic Theory of Mind series by Alex M. Vikoulov, available for pre-order on Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B09F858NBZ?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20
Multiverse Cosmology, Nobel Laureates, Theories Of Everything, And Much More! — Dr. Brian Keating Ph.D., Chancellor’s Distinguished Professor of Physics, UC San Diego.
Dr. Brian Keating, Ph.D. (https://briankeating.com/) is Chancellor’s Distinguished Professor of Physics, at the Center for Astrophysics & Space Sciences (CASS), in the Department of Physics, at the University of California, San Diego (https://bkeating.physics.ucsd.edu/).
Dr. Keating is a public speaker, inventor, and an expert in the study of the universe’s oldest light, the cosmic microwave background (CMB), using it to learn not just about the origins and evolution of the universe, but to gain potential insights into an even bigger picture, that of the “multiverse”, a hypothetical group of multiple universes that comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them.
Dr. Keating is also a writer, the best-selling author of one of Amazon Editors’ Best Non-fiction Books of All Time, “Losing the Nobel Prize” (https://www.amazon.com/Losing-Nobel-Prize-Cosmology-Ambition…atfound-20 and his new book is entitled “Into The Impossible: Think Like A Nobel Prize Winner”.
Dr. Keating is also a prolific podcaster on the Into The Impossible podcast (https://briankeating.com/podcast.php).

THEOGENESIS: Transdimensional Propagation & Universal Expansion ― my new book on quantum cosmology, computational physics and posthumanism ― is about to be released by Ecstadelic Media Group on October 1 2021!
Here’s the Table of Contents:
Introduction.
1. Our Post-Singularity Future: Are We Destined to Become Cybergods?
2. Transcension: Exponential Miniaturization.
3. Computational Physics: Reinterpreting Relativity.
4. Transcendental Cybernetics: The Ultimate Code of Reality.
5. Universality of Computation.
6. Quantum Gravity: Quest for the Final Theory of Everything.
7. The Shadow Multiverse: Parallel Space-Times, Dark Matter and Dark Energy.
8. Ontological Holism: All is One, One is All.
9. Why Materialism is a Flatlander Philosophy.
10. Seeking the Ultimate Truth: The Battle of Ideologies.
11. Quantum Cosmology: From the Holographic Principle to the Fractal Multiverse.
12. The Omega Singularity: Your Cosmic Self.
13. The Axioms of Divinity: Cybertheistic Foundation.
14. Experiential Matrix: A Playground of Subjectivity.
15. Transcendent Realm: Redefining God.
16. God of Spinoza: The Conscious Universe.
17. A New Kind of Pantheism: The Cybertheism Argument.
18. Are We Alone in the Universe?
19. The Chrysalis Conjecture: Our Second Womb.
Conclusion.
Appendix A. Tenets of The Cybernetic Theory of Mind: The Five Foundational Axioms.
Glossary of Terms.
Acknowledgements.
About the Author.
Bibliography.
The launch date of NASA’s Webb Space Telescope is December 18. It will study exoplanets, the Big Bang, and more.
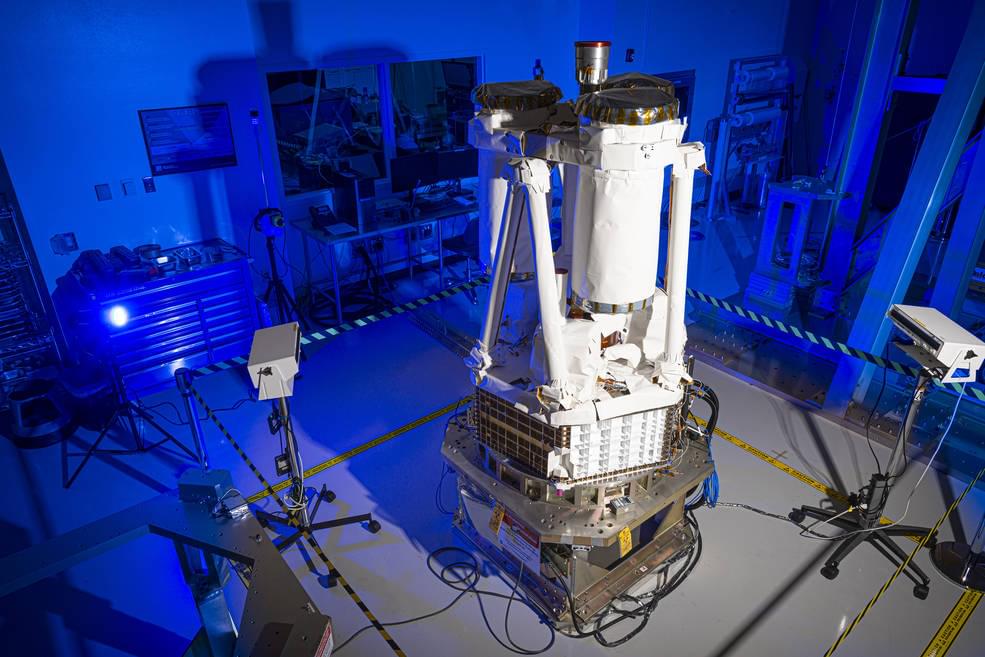

The launch of the Imaging X-Ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) observatory is now targeting December 13 2021, onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The IXPE X-Ray observatory is the latest spacecraft in NASA’s historic Small Explorers (SMEX) program.
The IXPE mission was first selected as a part of the Explorers program in January 2017. NASA awarded the IXPE team $188 million for the spacecraft and mission, including the cost of the launch vehicle, post-launch operations, and data analysis. The spacecraft will be used to study Black Holes and other cosmic X-ray mysteries.
Built by Ball Aerospace at facilities in Boulder, Colorado, the IXPE spacecraft is based on the Ball Configurable Platform (BCP)-100 satellite bus. The BCP-100 is one of Ball Aerospace’s offerings for a modular satellite bus for low-Earth orbit (LEO) operations. It was most recently used by NASA’s Green Propellant Infusion Mission (GPIM) to test a new type of Green propellant for space operations.
– SciTechDaily o.o!!!!
Dark energy, the mysterious force that causes the universe to accelerate, may have been responsible for unexpected results from the XENON1T experiment, deep below Italy’s Apennine Mountains.
A new study, led by researchers at the University of Cambridge and reported in the journal Physical Review D, suggests that some unexplained results from the XENON1T experiment in Italy may have been caused by dark energy, and not the dark matter the experiment was designed to detect.
“It was surprising that this excess could in principle have been caused by dark energy rather than dark matter. When things click together like that, it’s really special.” —