Wormholes have been relegated to the realm of science fiction. But new research suggests that they might actually be real.
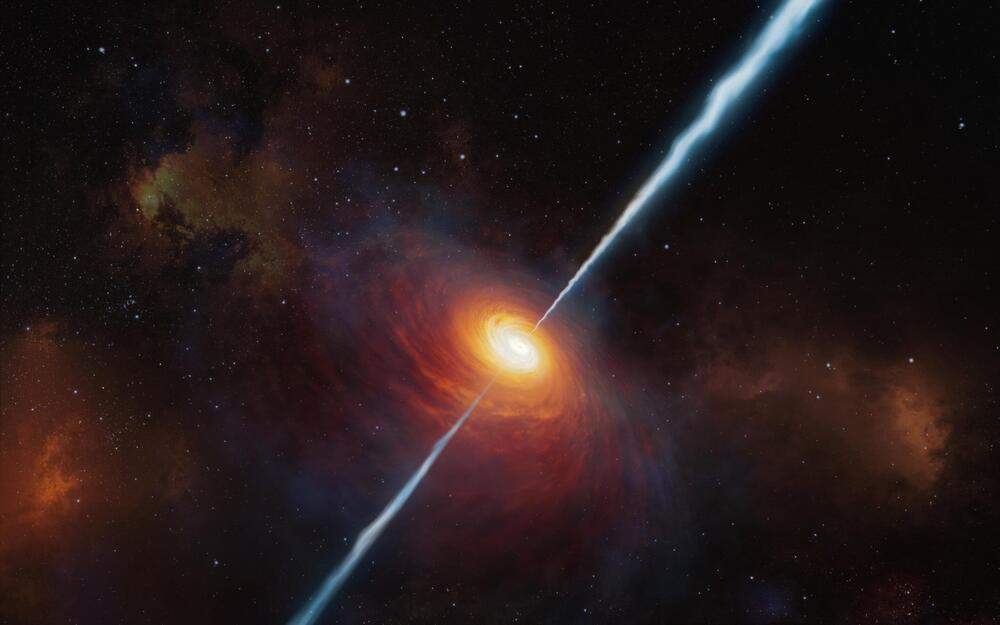



Wow. Spoiler, quasars are galaxies colliding and part of the gases reacting with black holes in the middle of the galaxies. Does that mean we’re all doomed though we could galaxy hop in the distant future I suppose. And the rest of the dispersed gases will take millions or was it billions of years to make new stars again. Kinda reminds me of human life. We are born only to return to the Earth.
Scientists have unlocked one of the biggest mysteries of quasars—the brightest, most powerful objects in the universe—by discovering that they are ignited by galaxies colliding.
First discovered 60 years ago, quasars can shine as brightly as a trillion stars packed into a volume the size of our solar system. In the decades since they were first observed, what could trigger such powerful activity has remained a mystery. New work led by scientists at the Universities of Sheffield and Hertfordshire has now revealed that it is a consequence of galaxies crashing together.
The work is published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
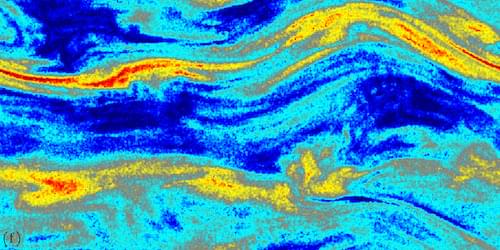
New computer simulations show that wave-particle interactions endow thin plasmas with an effective viscosity that regulates their turbulent motions and heating.
Most of the regular matter in the Universe is plasma, an ebullient state characterized by charged particles interacting collectively with electromagnetic fields. When individual particles collide on scales much shorter than those of bulk plasma motions, the latter are described well by a 3D fluid theory: magnetohydrodynamics. That condition prevails in the interiors of stars and planets and in protoplanetary accretion disks. But many hot, low-density astrophysical plasma flows are only weakly collisional. Accounting for stellar winds, accretion around black holes, and the motions of the plasma that pervades intergalactic space requires a statistical kinetic description of the particle positions and velocities in a 6D space. Numerical simulations by Lev Arzamasskiy of the Institute of Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, and his colleagues [1] shed new light on magnetized kinetic turbulence in such plasmas.
Note that this is very far away from a return to an anthropocentric worldview, to pre-Copernican times when the Earth was the center of Creation. (I call it biocentric to make the distinction clear.) Biocentrism is necessarily post-Copernican. I am saying that we are unique and important — but not for having been created by a god, or for being the result of a purposeful cosmic directive.
We are unique and important for being self-aware living entities capable of asking questions about their origin and future. We may not be the measure of all things as Protagoras of Abdera proclaimed long ago, but we are the things that can measure. We experience the world, we measure it, and we tell stories about what we see and what we feel. And what we are finding out is that we may very well be the only ones asking such questions — or, at the very least, the only ones we know of, which effectively amounts to the same thing. Even if “they” exist and tell stories, their stories will not be ours. There is only one human voice in the cosmos. And if we ruin our project of civilization, the Universe will once again become silent.
The acceptance of our cosmic loneliness and the rarity of our planet is a wakeup call, ringing to awaken a new collective consciousness. I believe it to be the new unifying myth of our generation, with the power to go beyond tribal divides and bigotry, to lead us into a new era of human flourishing. But for this to happen, we need to change how we relate to life and to the planet that allows us to exist. We are not above nature, and we don’t own it. We are a part of it and depend on it for our existence.
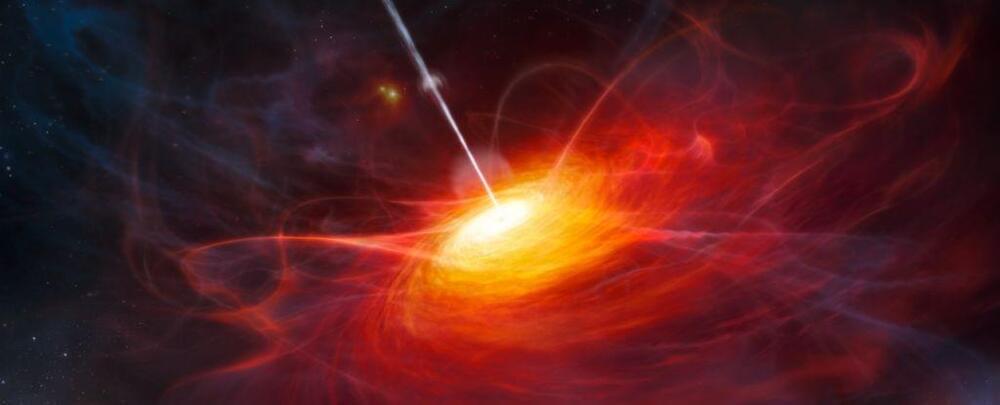

The Universe is swarming with galaxies, billions upon billions as far as the eye can see. And among this multitude, some galaxies really stand out in a spectacular way.
These are the quasar galaxies. Powered by an active supermassive black hole guzzling material at such a tremendous rate, they blaze with some of the brightest light in the Universe, lighting up the galactic center right across the electromagnetic spectrum. For decades, astronomers have wondered why some galaxies have such extreme activity and others do not.
Now they think they’ve cracked it. By making a careful study of nearby quasar and non-quasar galaxies, a team led by astrophysicist Jonny Pierce of the University of Hertfordshire in the UK concludes that, in a majority of cases, quasar activity is triggered when two galaxies start the process of colliding and merging.
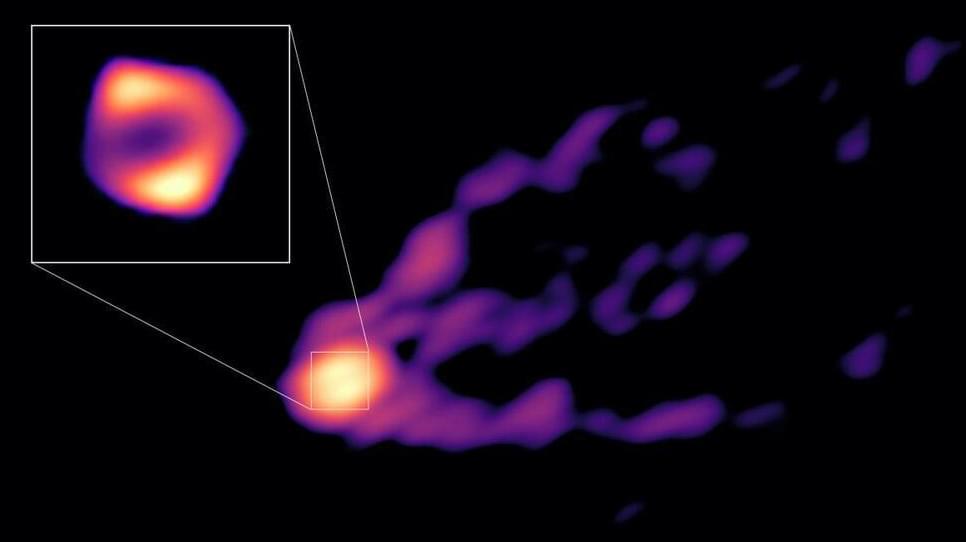
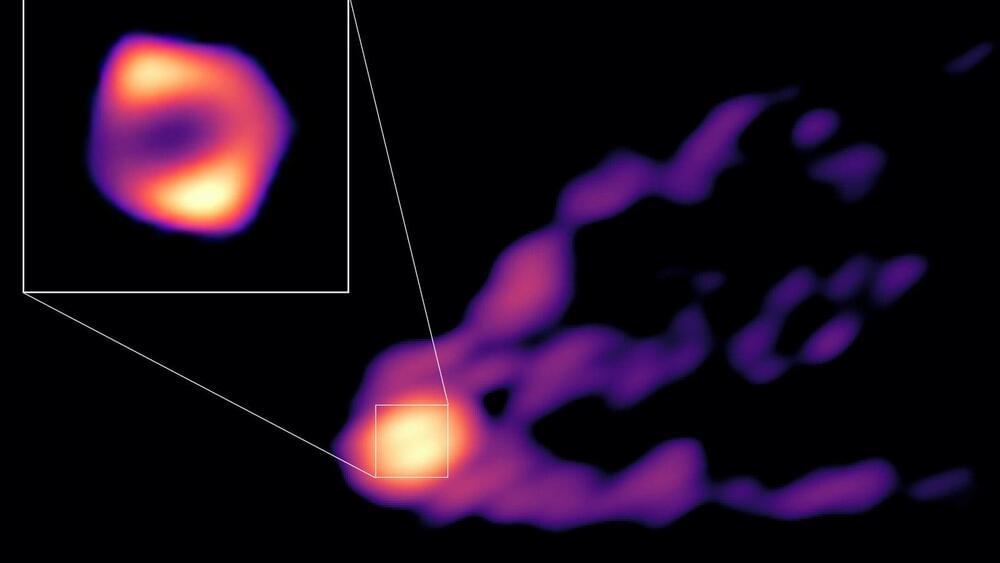
A video about the Webb telescope making it seem like there was no big bang. This is by Mikio Kaku.
We’ve always wondered about life out there. But what if we told you that the possibility of more lifeforms has become surer than ever? Six shocking galaxies have been discovered that defy all explanations. Join us as we discuss Michio Kaku breaking his silence on the James Webb telescope’s clearest image in history.
The possible levels of information mastery in the future of technology.
This series focus will be on the Information Mastery version of the Kardashev scale. In his book, The Cosmic Connection, Carl Segan proposed an alternative approach to the Kardashev Scale. He added another dimension to the original scale in addition to the pure energy usage that was first used to characterize different civilizations. Sagan believed that the amount of information available to a civilization should be an important criterion when trying to come up with a useful metric to measure different types of civilizations. So he assigned a lettered scale from A-Z where each letter meant an order of magnitude increase in the volume of information a civilization can hold. This information, he proposed, could be described in terms of bits, the number of yes or no statements concerning different civilizations, and the universe that such civilizations occupy.
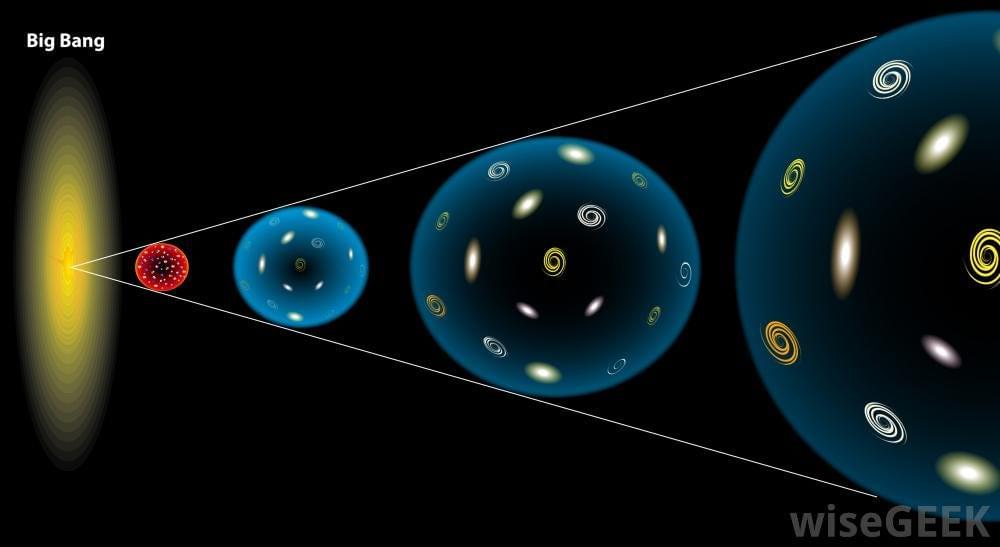
The Big Bang Theory is widely accepted as the explanation for the origin of the universe, but it doesn’t tell us what came before it. The idea of a universe before the Big Bang may seem impossible, but recent scientific discoveries suggest otherwise. In this article, we’ll explore the strongest evidence for a universe before the Big Bang.
The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted explanation for the origin of the universe. According to this theory, the universe began as a singularity, a point of infinite density and temperature. But what caused the Big Bang? And what came before it? These questions have puzzled scientists and philosophers for centuries.