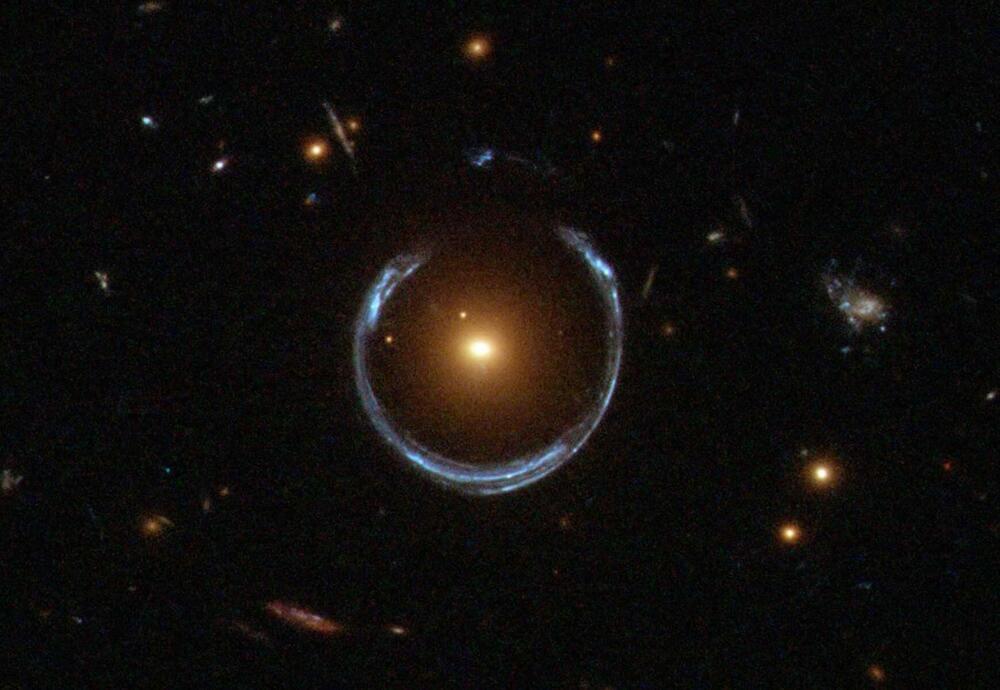
Black holes are some of the most mysterious phenomena in space that have puzzled scientists ever since their discovery. Extreme levels of gravitational pull suck in everything around the black hole, even light. Black holes are the complete absence of any source of light, resulting in total darkness.
According to a video posted by the popular YouTube channel Riddle, a black hole’s origins can be traced back to a star that has burnt up and turned into a supernova. One of the largest known black holes has a mass that is forty billion times larger than our sun in our solar system. This black hole is situated in a galaxy called “Holmberg 15A,” which is approximately 700 million lightyears away.
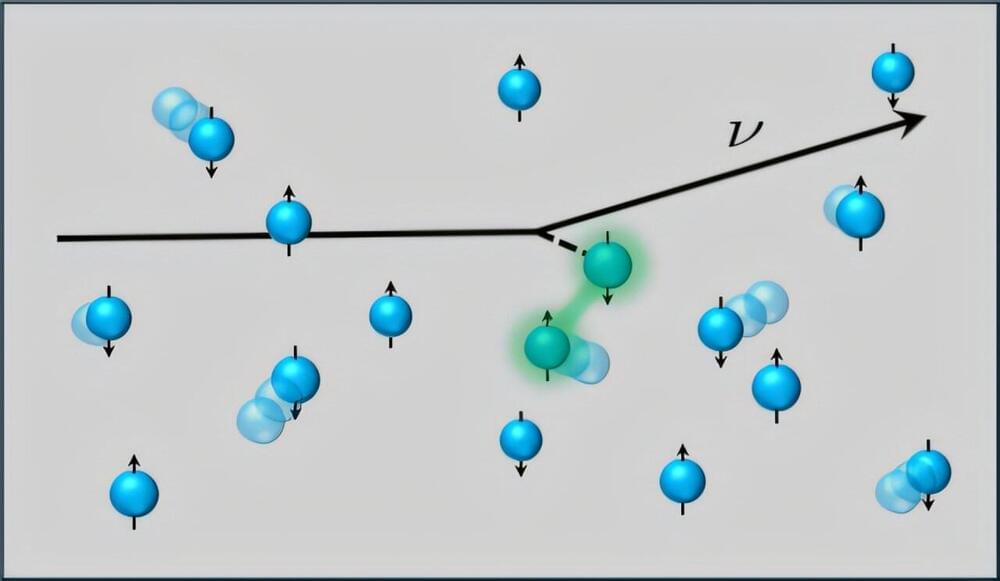
When any matter approaches a black hole, several different events occur. One of these outcomes is known as the “accretion disk,” which changes the properties of the item approaching the black hole. Although black holes are typically associated as ever present and enduring vacuums that continuously “take,” they eventually dissipate over time.